Copyright
©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Exp Med. Mar 20, 2025; 15(1): 99516
Published online Mar 20, 2025. doi: 10.5493/wjem.v15.i1.99516
Published online Mar 20, 2025. doi: 10.5493/wjem.v15.i1.99516
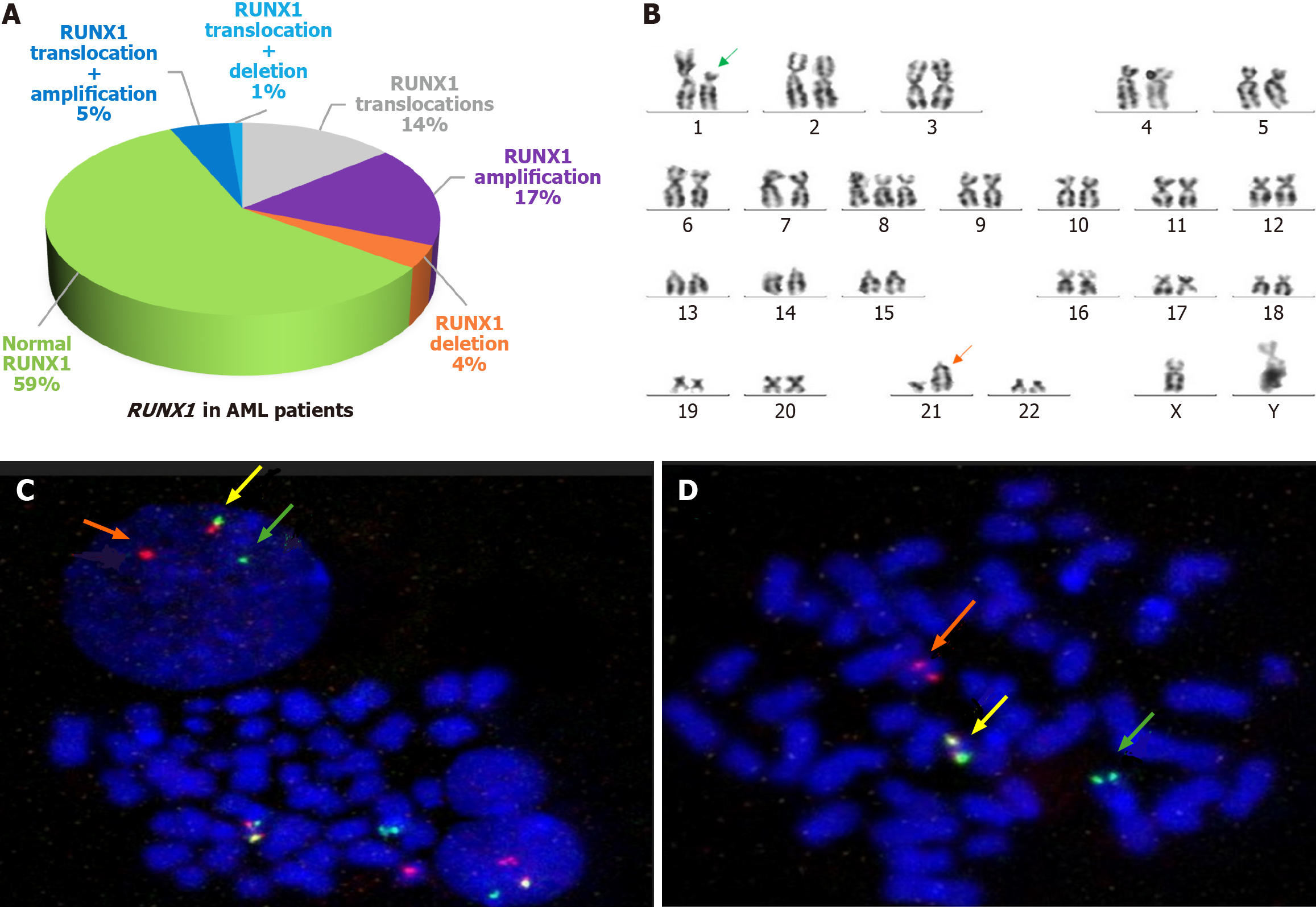
Figure 1 Runt-related transcription factor-1 in patients with acute myeloid leukemia.
A: Runt-related transcription factor-1 (RUNX1) gene alterations in acute myeloid leukemia (AML) cases; B: G-banded karyotype of a case of t (1; 21). 48, XY, +X, t (1; 21) (p36; q22), +8; C: Interphase fluorescence in situ hybridization using RUNX1 break apart probe showing a split of RUNX1 signal; D: Metaphase fluorescence in situ hybridization using a RUNX1 break apart probe showing a split of the RUNX1 signal. The magnification factor is × 63.
Figure 2 Kaplan-Meier survival curves.
A: Runt-related transcription factor-1 (RUNX1) abnormality; B: RUNX1 amplification; C: RUNX1 translocation; D: RUNX1 deletion on overall survival rates in acute myeloid leukemia patients.
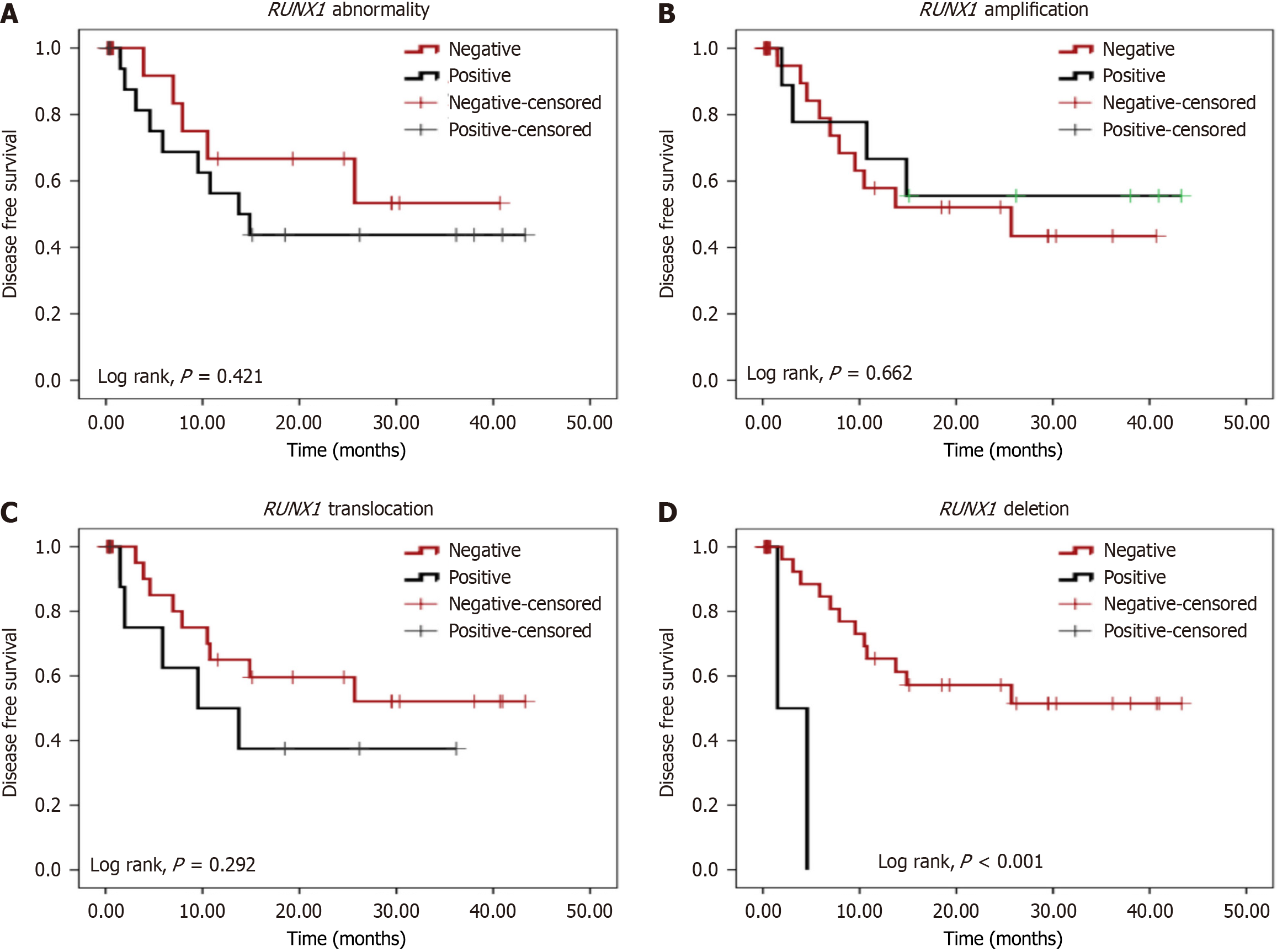
Figure 3 Kaplan-Meier survival curves.
A: Runt-related transcription factor-1 (RUNX1) abnormality; B: RUNX1 amplification; C: RUNX1 translocation; D: RUNX1 deletion on disease-free survival of patients with adult acute myeloid leukemia.
- Citation: Abd El-Ghany HM, El Ashry MS, Abdellateif MS, Rabea A, Sultan N, Abd El Dayem OY. Prevalence of RUNX1 gene alterations in de novo adult acute myeloid leukemia. World J Exp Med 2025; 15(1): 99516
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2220-315x/full/v15/i1/99516.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5493/wjem.v15.i1.99516