Copyright
©The Author(s) 2021.
World J Exp Med. Dec 30, 2021; 11(6): 79-92
Published online Dec 30, 2021. doi: 10.5493/wjem.v11.i6.79
Published online Dec 30, 2021. doi: 10.5493/wjem.v11.i6.79
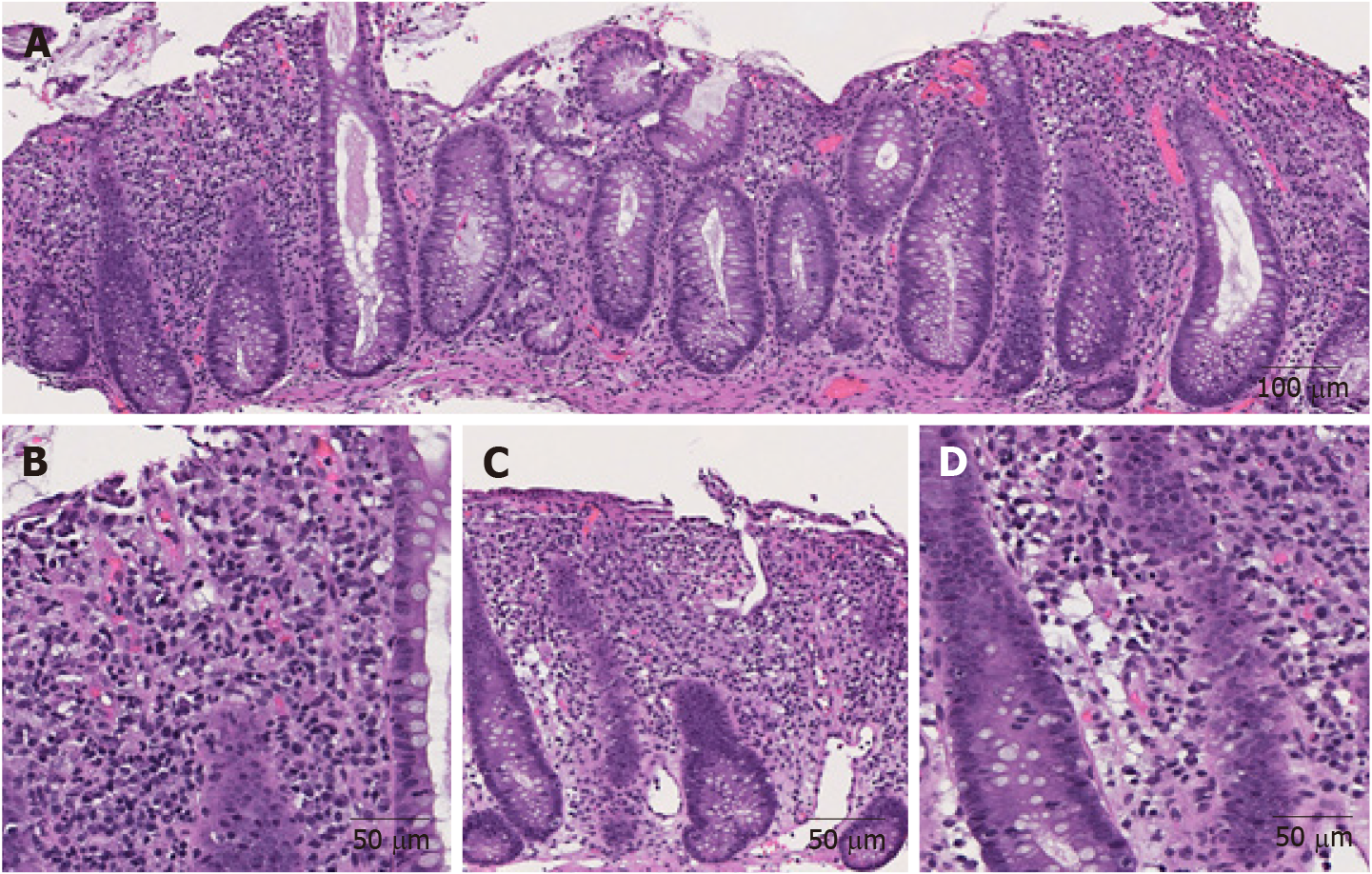
Figure 1 Representative images of immune checkpoint inhibitor-induced colitis in a patient with metastatic melanoma treated with nivolumab and ipilimumab for 2 mo (Hematoxylin and eosin).
A: Active colitis characterized by mixed inflammatory cell infiltrates in the lamina propria and surface erosion (100 ×); B: High magnification of A. Note the neutrophils, lymphocytes, and plasma cells in the lamina propria (200 ×); C: Active colitis with mild crypt architectural irregularity (100 ×); D: Active colitis with neutrophilic cryptitis (200 ×).
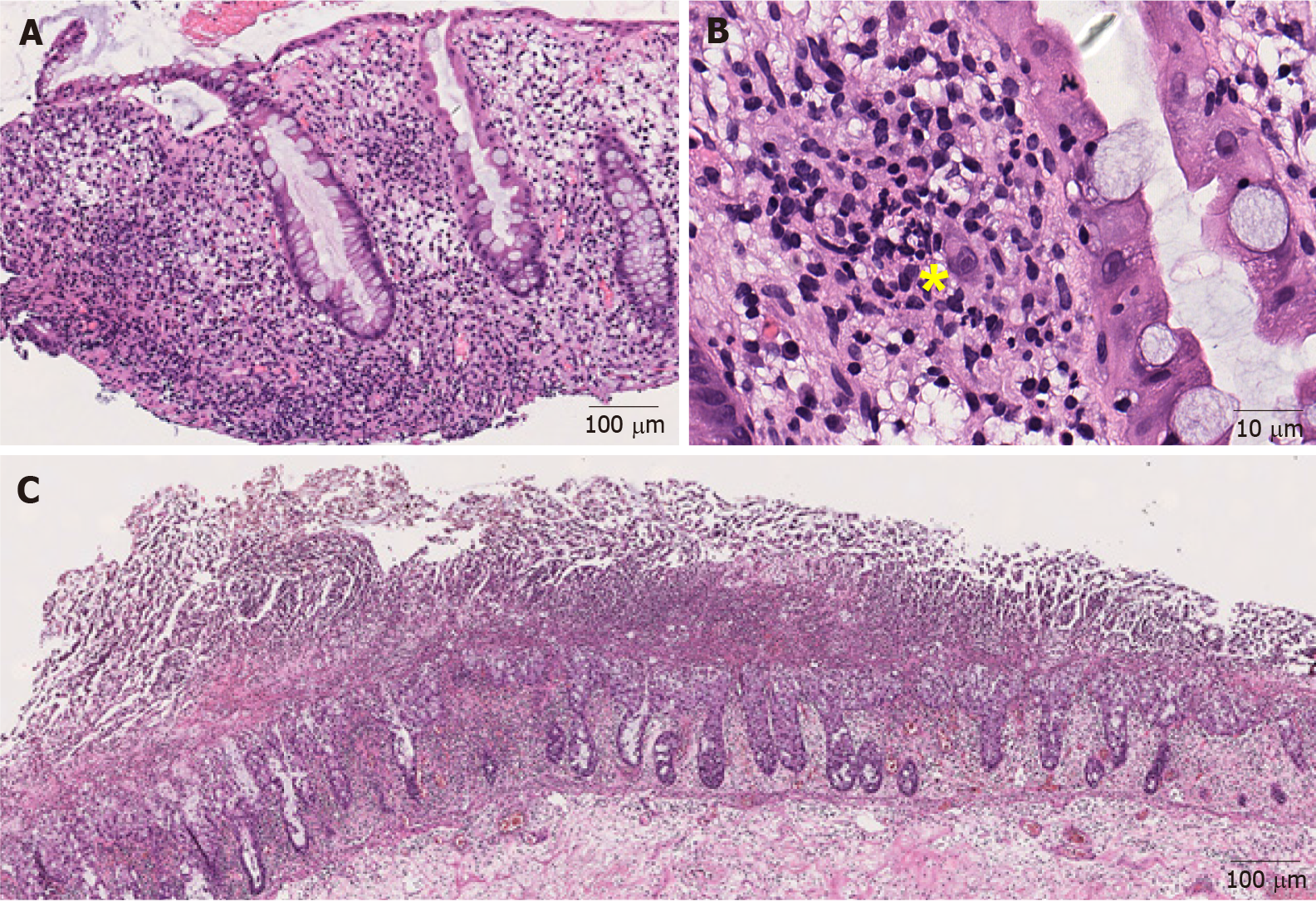
Figure 2 Representative images of infectious colitis (Hematoxylin and eosin).
A: Low magnification view of cytomegaloviral (CMV) colitis. Notice the lymphocytes and neutrophils in the lamina propria (100 ×); B: Note an owl-eye inclusion characterized by enlarged nucleus with oval, eosinophilic intranuclear inclusion surrounded by clear halo, consistent with CMV inclusion (400 ×); C: Clostridium difficile colitis. Pseudomembranes composed of fibrin, neutrophils and necrotic epithelial cells are on the surface of the mucosal glands (40 ×). Yellow sign notes a viral inclusiona.
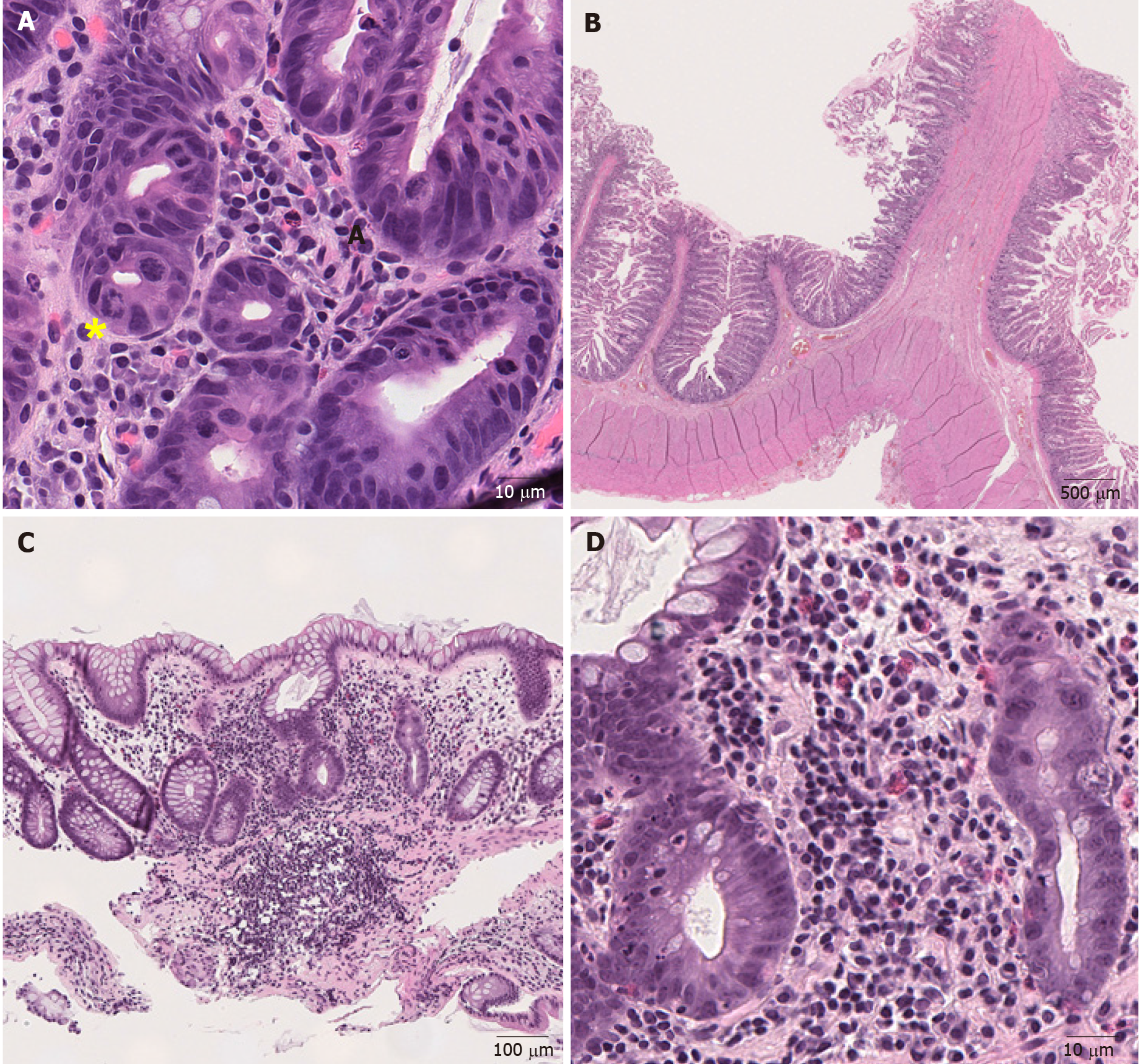
Figure 3 Representative images of medication-induced colitis (Hematoxylin and eosin).
A: Ring mitosis caused by docetaxel in duodenum (400 ×); B: Small bowel diaphragm. Fibrotic submucosa protrudes into the intestinal lumen and forms a diaphragm (8 ×); C: Low magnification view of mycophenolate mofetil-induced colitis. (100 ×); D: Higher magnification view of mycophenolate mofetil-induced colitis. There is an inflammatory cell infiltrate consisting of lymphocytes, plasma cells and eosinophils in the lamina propria with neutrophilic cryptitis (400 ×). Yellow sign notes a ring mitosis.
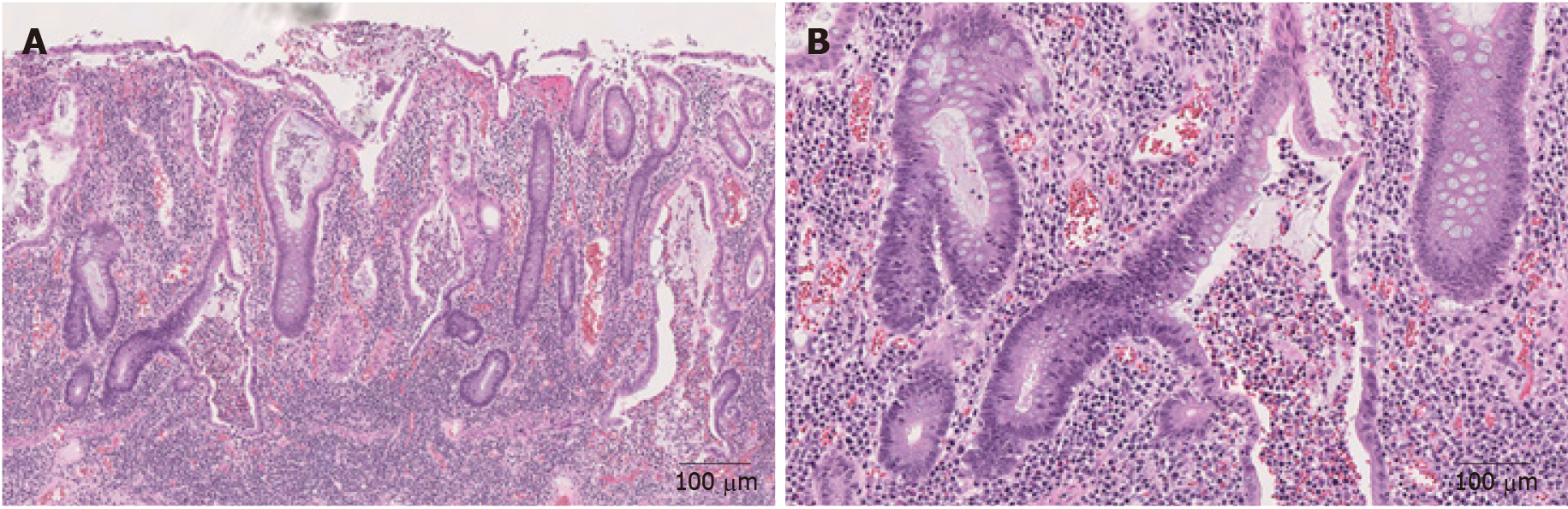
Figure 4 Representative images of inflammatory bowel disease (Hematoxylin and eosin).
A: Mucosal inflammation with marked crypt distortion and neutrophilic cryptitis and abscesses in ulcerative colitis (40 ×); B: Higher magnification view shows crypt abscess (100 ×).
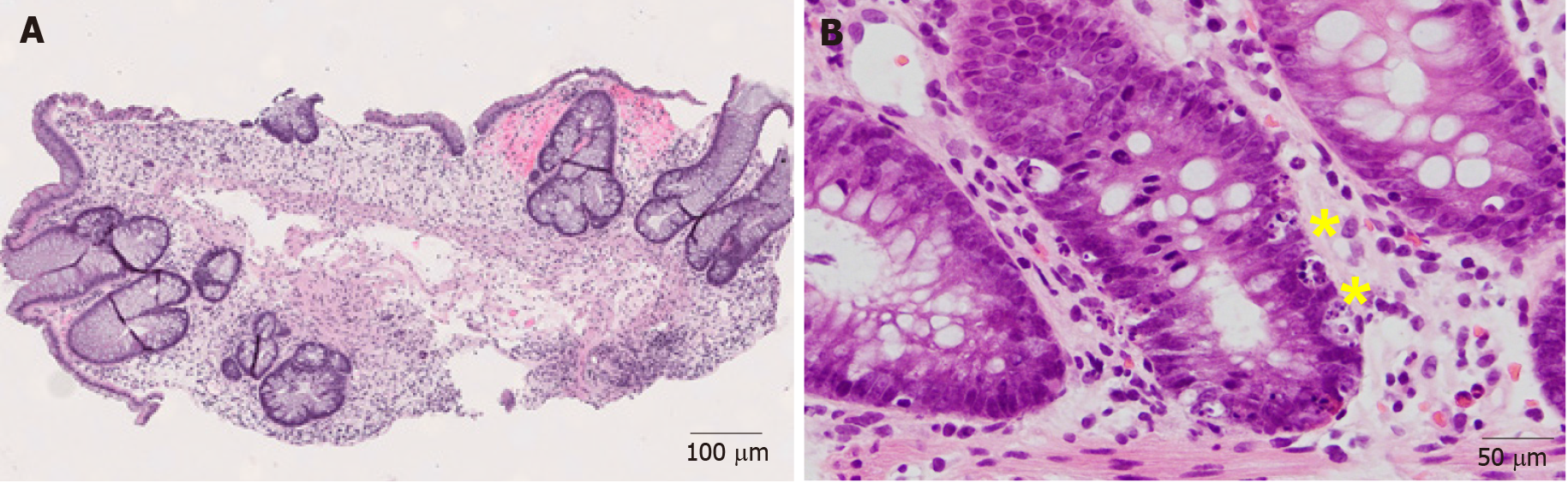
Figure 5 Representative images of graft-versus-host disease (Hematoxylin and eosin).
A: Colonic graft-versus-host disease characterized by marked crypt architectural distortion and paucity of lamina propria inflammation (40 ×); B: On higher magnification, enterocyte apoptosis (yellow sign) are readily identified (200 ×).
- Citation: Li H, Fu ZY, Arslan ME, Cho D, Lee H. Differential diagnosis and management of immune checkpoint inhibitor-induced colitis: A comprehensive review. World J Exp Med 2021; 11(6): 79-92
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2220-315x/full/v11/i6/79.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5493/wjem.v11.i6.79