Copyright
©The Author(s) 2017.
World J Exp Med. Aug 20, 2017; 7(3): 84-96
Published online Aug 20, 2017. doi: 10.5493/wjem.v7.i3.84
Published online Aug 20, 2017. doi: 10.5493/wjem.v7.i3.84
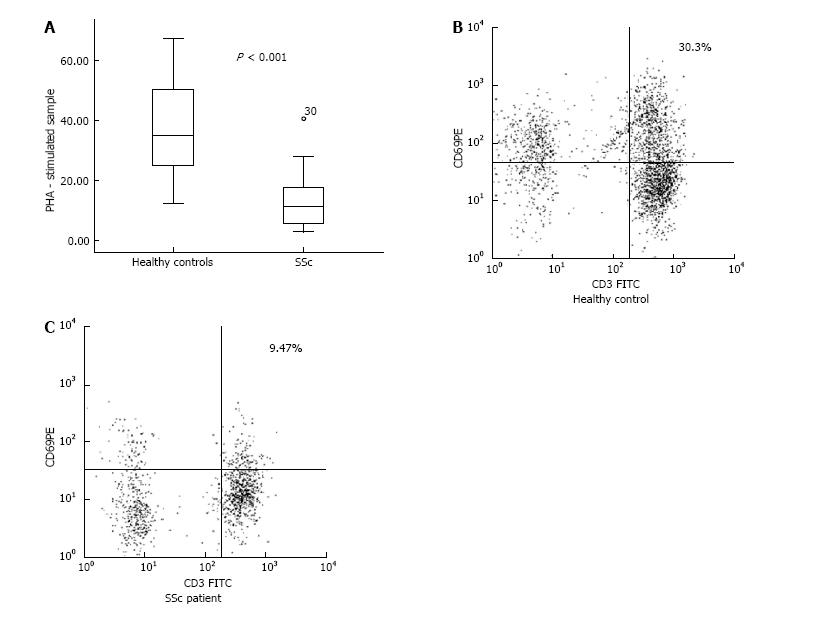
Figure 1 Decreased percentage of CD3+CD69+ cells upon PHA stimulation in the circulation of patients with systemic sclerosis as opposed to healthy controls.
A: Percentage of CD3+CD69+ cells in PHA-stimulated samples from SSc patients (n = 24) and healthy controls (n = 16), as it follows: 13.35% ± 2.90% vs 37.03% ± 2.33%, P < 0.001. The boxplots represent mean ± SD; B and C: PHA stimulated sample of one representative subject from each group is shown. The percentage of CD69+ cells in the whole T cell pool (CD3+ cells) is depicted. SSc: Systemic sclerosis.
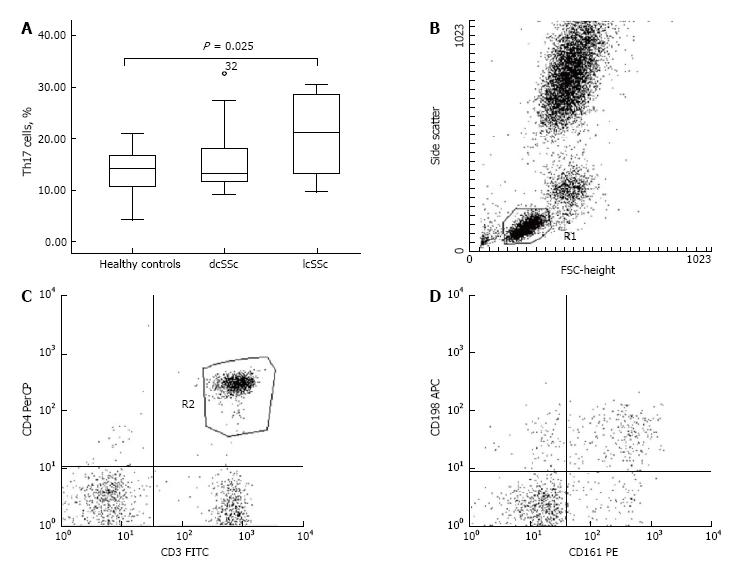
Figure 2 Increased percentage of Th17 cells within limited cutaneous systemic sclerosis subset vs healthy controls.
A: Percentage of Th17 cells for lcSSc (n = 11), dcSSc (n = 13), and healthy controls (n = 16) is presented. Increased percentage of Th17 cells within lcSSc patients as opposed to controls, respectively, 20.46% ± 2.41% vs 13.73% ± 1.21%, P = 0.025. Boxplots are expressed as means ± SD; B-D: Panel B depicts the flow cytometric analysis of Th17 cells. A representative patient with lcSSc phenotype is shown. The lymphocytes were gated according to their physical characteristics (FSC and SSC) in R1; afterwards T helper cells (CD3+CD4+) were gated in R2. T helpers, which were detected double positive for CD161 and CD196 surface expression (R3, upper right quadrant) were defined as Th17 cells. lcSSc: Limited cutaneous systemic sclerosis.
Figure 3 Increased percentage of CD4+CD25-Foxp3+ T cells within diffuse cutaneous systemic sclerosis phenotype vs healthy controls.
A: Increased percentage of CD4+CD25-Foxp3+ T cells within dcSSc patients (n = 13) as opposed to controls (n = 16), respectively, 10.94% ± 1.65% vs 6.88% ± 0.91%, P = 0.032. Boxplots are expressed as means ± SD; B-D: Panel B depicts the flow cytometric analysis of CD4+CD25-Foxp3+ T cells. A representative patient with dcSSc phenotype is shown the lymphocytes were gated according to their physical characteristics (FSC and SSC) in R1; afterwards T helper cells were gated in R2. T helpers, which were found negative for CD25 surface expression and positive for Foxp3 intracellular expression (R3, upper left quadrant) were defined as CD4+CD25-Foxp3+ T cells. dcSSc: Diffuse cutaneous systemic sclerosis.
Figure 4 Elevated serum levels within the limited cutaneous systemic sclerosis (n = 11) and diffuse cutaneous systemic sclerosis (n = 13) phenotypes vs healthy controls (n = 16).
Boxplots are expressed as means ± SD. A: Increased serum levels of IL-6 in lcSSc phenotype vs controls, P < 0.001. Raised serum levels of IL-6 in dcSSc patients vs controls, P < 0.001; B: Raised serum levels of TGF-β1 in lcSSc patients vs controls, P = 0.031; C: Elevated serum levels of IL-17 A in lcSSc phenotype vs dcSSc patients, P = 0.008, and vs controls, P < 0.001. The IL-17A were also increased in dcSSc patients vs controls, P < 0.001; D: Raised serum levels of IL-10 in lcSSc patients vs controls, P = 0.003. lcSSc: Limited cutaneous systemic sclerosis; dcSSc: Diffuse cutaneous systemic sclerosis; TGF-β1: Tissue growth factor-β1; IL: Interleukin.
- Citation: Krasimirova E, Velikova T, Ivanova-Todorova E, Tumangelova-Yuzeir K, Kalinova D, Boyadzhieva V, Stoilov N, Yoneva T, Rashkov R, Kyurkchiev D. Treg/Th17 cell balance and phytohaemagglutinin activation of T lymphocytes in peripheral blood of systemic sclerosis patients. World J Exp Med 2017; 7(3): 84-96
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2220-315X/full/v7/i3/84.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5493/wjem.v7.i3.84