Copyright
©The Author(s) 2015.
World J Exp Med. Nov 20, 2015; 5(4): 225-231
Published online Nov 20, 2015. doi: 10.5493/wjem.v5.i4.225
Published online Nov 20, 2015. doi: 10.5493/wjem.v5.i4.225
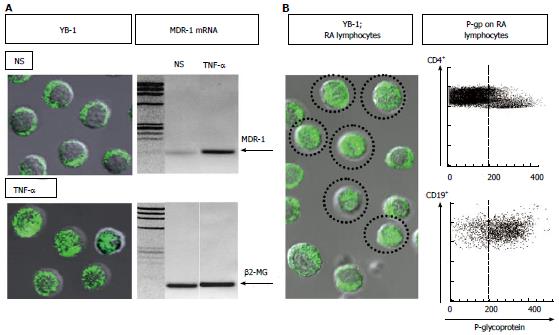
Figure 1 Up-regulation of nuclear translocation of Y-box-binding protein-1, transcription of multidrug resistance 1 in lymphocytes, and P-glycoprotein expression on lymphocytes.
A: Left: Immunostaining and confocal microscopy analysis of Y-box-binding protein-1 (YB-1) in 1 × 105 of peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs). YB-1 was expressed in the cytoplasm of all non-stimulated PBMCs (NS). In contrast, nuclear translocation of YB-1 was induced in 30% or more of PBMCs incubated with 10 ng/mL of tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α). Immunostaining for YB-1 using a specific antibody (Ab) against YB-1[19] with FITC-conjugated anti-rabbit IgG Ab (BD Biosciences Pharmingen). Confocal analysis of YB-1 using a LSM 5 Pascal invert Laser Scan Microscope (Carl Zeiss Microscope Systems, Germany). Magnification, × 600; Right: Multidrug resistance-1 (MDR-1) mRNA expression was examined by RT-PCR using total RNA extracted from PBMCs incubated with 10 ng/mL of TNF-α or no stimulation (NS). The primer sequences were as follows: human β2-microglobulin forward 5’-ACCCCCACTGAAAAAGATGA-3’, reverse 5’-ATCTTCAAACCTCCATGATG-3’; human MDR-1 forward 5’-CCCATCATTGCAATAGCAGG-3’, reverse 5’-GTTCAAACTTCTGCTCCTGA-3’. Amplified products were electrophoresed with Marker 4 (Nippon Gene, Tokyo) on 3% agarose gels; B: Spontaneous nuclear translocation of YB-1 and P-glycoprotein (P-gp) expression on lymphocytes from a typical patient with active rheumatoid arthritis (RA). Left: Immunostaining and confocal microscopy analysis of YB-1 in 1 × 105 of PBMCs. YB-1 was expressed in the nuclei of a proportion of unstimulated PBMCs (encircled cells). Magnification, × 600; Right: P-gp expression on CD4+ and CD19+ peripheral blood lymphocytes. The dotted line represents the gate set to discriminate negative from positive stained cells as determined by control FITC-conjugated anti-mouse IgG Ab. The specific antibodies for staining and flow cytometric analysis were as follows: staining for P-gp using MRK16 (a specific monoclonal Ab against P-gp; Kyowa Medex, Tokyo) with FITC-conjugated goat anti-mouse IgG Ab (BD Biosciences Pharmingen), cy-chrome-conjugated CD4 monoclonal Ab, cy-chrome-conjugated CD19 monoclonal Ab (BD Biosciences Pharmingen).
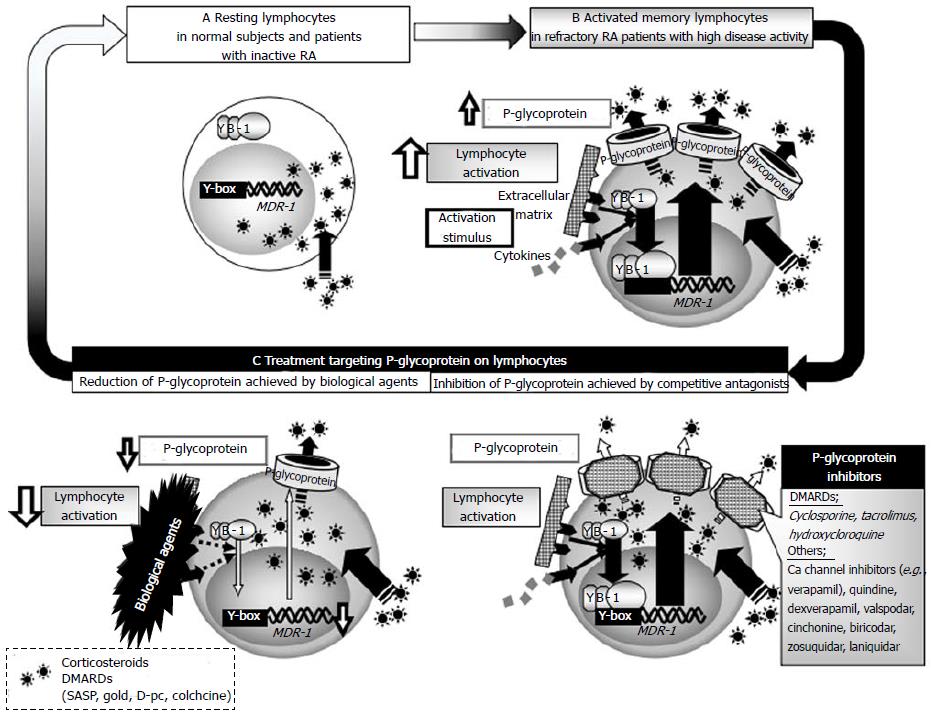
Figure 2 Schematic diagram of the relevance of P-glycoprotein to drug resistance in rheumatoid arthritis.
A: Y-box-binding protein-1 is located in the cytoplasm of lymphocytes and P-glycoprotein (P-gp) is only marginally expressed on normal lymphocytes of normal subjects and patients with inactive RA; B: In patients with highly active rheumatoid arthritis (RA), various stimuli induce P-gp expression on lymphocytes, which leads to active efflux of drugs from lymphocytes, resulting in drug-unresponsiveness and failure to control disease activity; C: Reduction of P-gp achieved by intensive immunosuppressive therapy and inhibition of P-gp by competitive antagonists, such as cyclosporine, could overcome P-gp-related drug-resistance in patients with highly active RA. DMARDs: Disease modifying antirheumatic drugs; MDR-1: Multidrug resistance 1.
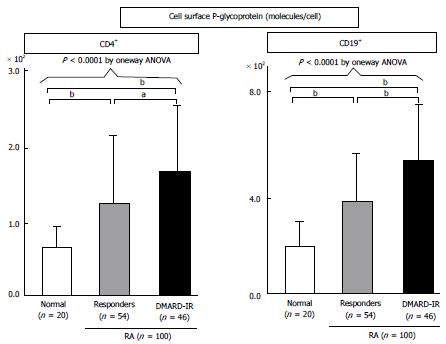
Figure 3 Expression of P-glycoprotein on lymphocytes from patients with refractory rheumatoid arthritis, as determined by flow cytometry.
P-glycoprotein (P-gp) expression on CD4+ or CD19+ peripheral blood lymphocytes from 20 normal volunteers (open bar) and 100 RA patients [responders, hatched bars; with inadequate response to DMARDs (DMARD-IR), closed bars]. The specific antibodies for staining and flow cytometric analysis were as follows: staining for P-gp using MRK16 [a specific monocloncal antibody (Ab) against P-gp; Kyowa Medex, Tokyo] with FITC-conjugated goat anti-mouse IgG Ab (BD Biosciences Pharmingen), cy-chrome-conjugated CD4 monoclonal Ab, cy-chrome-conjugated CD19 monoclonal Ab (BD Biosciences Pharmingen). Data represent the number of molecules expressed per cell, calculated using standard QIFIKIT beads. Values are mean ± SD of independent experiments. One-way ANOVA were used to compare data between groups. aP < 0.05, bP < 0.01, by multiple comparison. DMARD: Disease modifying antirheumatic drug; RA: Rheumatoid arthritis.
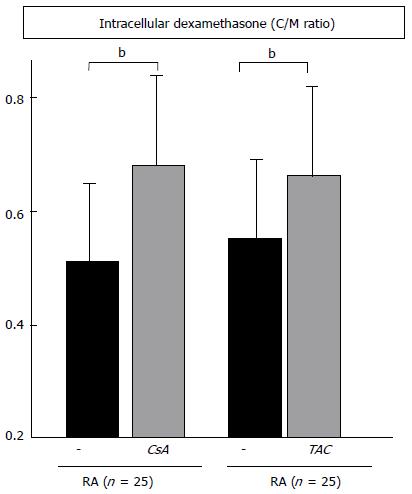
Figure 4 Inhibition of P-glycoprotein-related dexamethasone efflux by cyclosporine and tacrolimus.
The C/M ratio in peripheral blood mononuclear cells of 25 rheumatoid arthritis (RA) patients was measured in the absence or presence of 100 ng/mL of cyclosporine (CsA), or 10 ng/mL of tacrolimus (TAC). Data are mean ± SD. bP < 0.01, by the paired t test.
- Citation: Tsujimura S, Tanaka Y. Disease control by regulation of P-glycoprotein on lymphocytes in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. World J Exp Med 2015; 5(4): 225-231
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2220-315X/full/v5/i4/225.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5493/wjem.v5.i4.225