Copyright
©The Author(s) 2015.
World J Exp Med. May 20, 2015; 5(2): 50-63
Published online May 20, 2015. doi: 10.5493/wjem.v5.i2.50
Published online May 20, 2015. doi: 10.5493/wjem.v5.i2.50
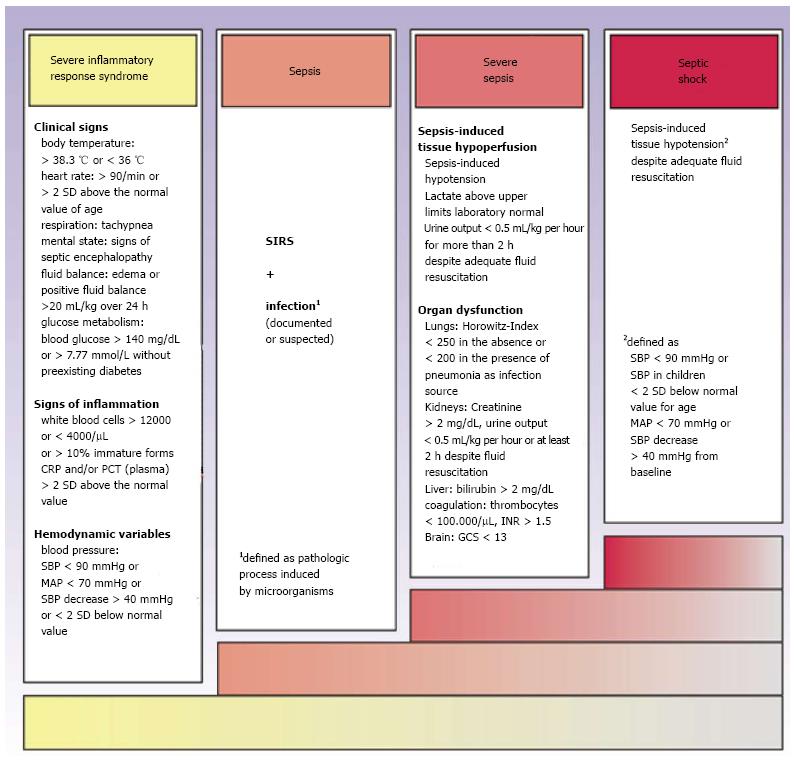
Figure 1 Diagnostic criteria of systemic inflammatory response syndrome, sepsis, severe sepsis and septic shock (modified from[5]).
CRP: C-reactive protein; PCT: Procalcitonin; SIRS: Systemic inflammatory response syndrome.
Figure 2 Simplified scheme of the impaired immunity during sepsis and the potential use of biomarkers: Initially, the body reacts to infectious stimuli with a proinflammatory immune response.
Simultaneously, compensatory mechanisms are initiated to counteract the inflammatory process. The resulting net immune suppression is characterised by an increased risk of opportunistic infections. Beside C-reactive protein and procalcitonin, further biomarkers may be used in diagnosis, therapy-guidance and outcome prediction of sepsis.
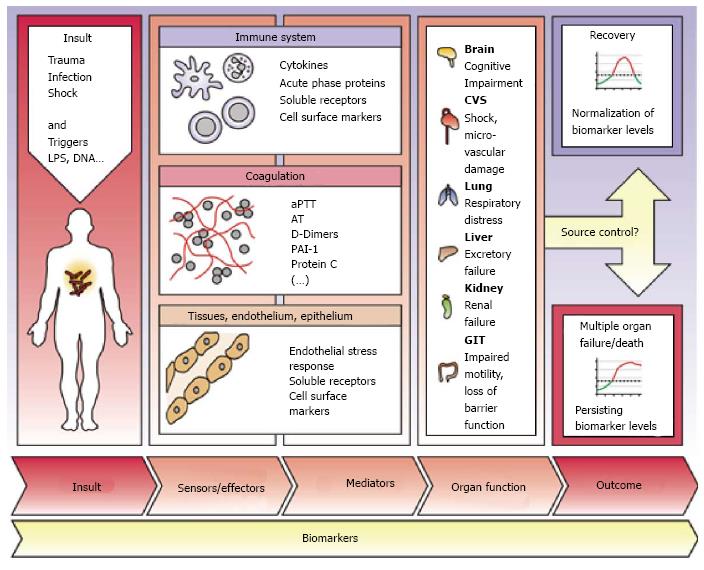
Figure 3 Use of biomarkers in sepsis: A wide range of biomarkers has been under intensive investigation to assist the clinician in diagnosis, outcome prediction and therapy guidance.
LPS: Lipopolysaccharide; aPTT: Activated partial thromboplastin time; AT: Antithrombin; PAI-1: Plasminogen activator inhibitor-1; CVS: Cardio vascular system; GIT: Gastrointenstinal.
- Citation: Kojic D, Siegler BH, Uhle F, Lichtenstern C, Nawroth PP, Weigand MA, Hofer S, Brenner T. Are there new approaches for diagnosis, therapy guidance and outcome prediction of sepsis? World J Exp Med 2015; 5(2): 50-63
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2220-315X/full/v5/i2/50.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5493/wjem.v5.i2.50