Copyright
©2014 Baishideng Publishing Group Inc.
World J Exp Med. Aug 20, 2014; 4(3): 27-37
Published online Aug 20, 2014. doi: 10.5493/wjem.v4.i3.27
Published online Aug 20, 2014. doi: 10.5493/wjem.v4.i3.27
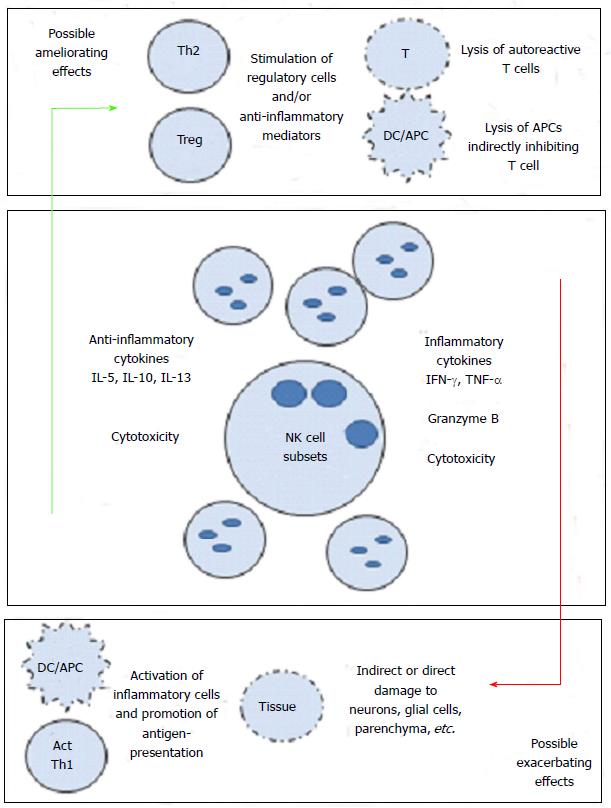
Figure 1 Natural killer cells influence multiple sclerosis pathogenesis in both protective and exacerbating ways.
Lysis of either auto-reactive cells or antigen presenting cells (APCs) may protect the central nervous system (CNS) from damage. Stimulation of protective Th2 or Treg cells may also encourage an anti-inflammatory environment. On the other hand, stimulation of APCs or auto-reactive cells may have opposite effects. IL: Interleukin; TNF: Tumor necrosis factor; IFN: Interferon; NK: Natural killer.
- Citation: Høglund RA, Maghazachi AA. Multiple sclerosis and the role of immune cells. World J Exp Med 2014; 4(3): 27-37
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2220-315X/full/v4/i3/27.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5493/wjem.v4.i3.27