Copyright
©2012 Baishideng.
World J Exp Med. Apr 20, 2012; 2(2): 30-36
Published online Apr 20, 2012. doi: 10.5493/wjem.v2.i2.30
Published online Apr 20, 2012. doi: 10.5493/wjem.v2.i2.30
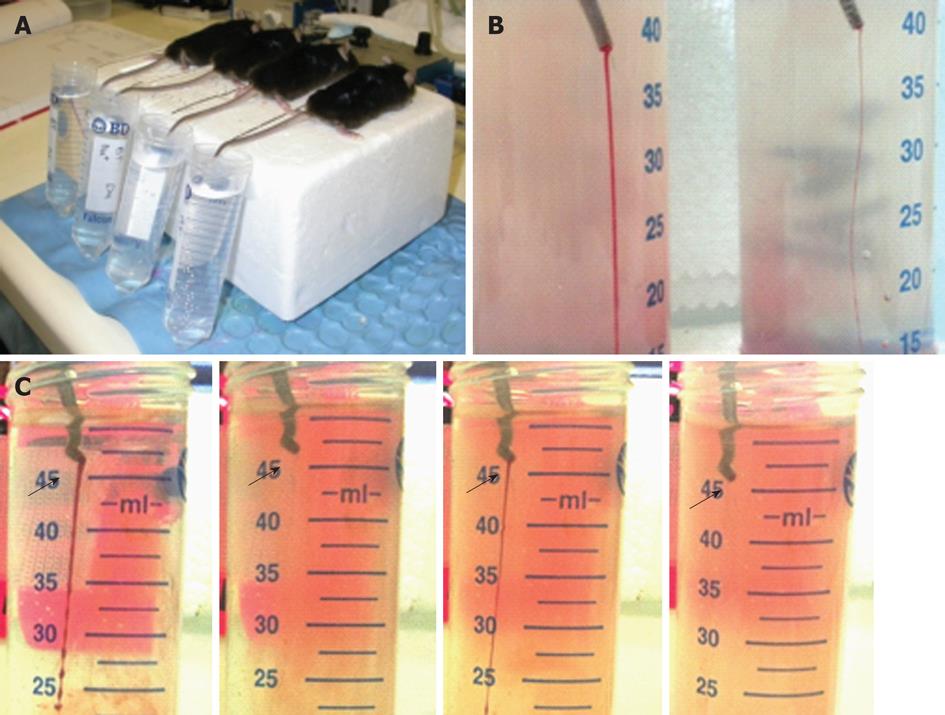
Figure 1 Setting-up of tail bleeding assay in mice.
A: Bleeding assay was performed by amputation of the tail tip which was immediately merged in saline (37°C); B: Photo showing difference in the thickness of blood streams in animals receiving prasugrel at 5 (left) or 0.5 (right) mg/kg per day; C: Starting/stopping bleeding cycles (arrows) observed in a FcRγ-/- mouse.
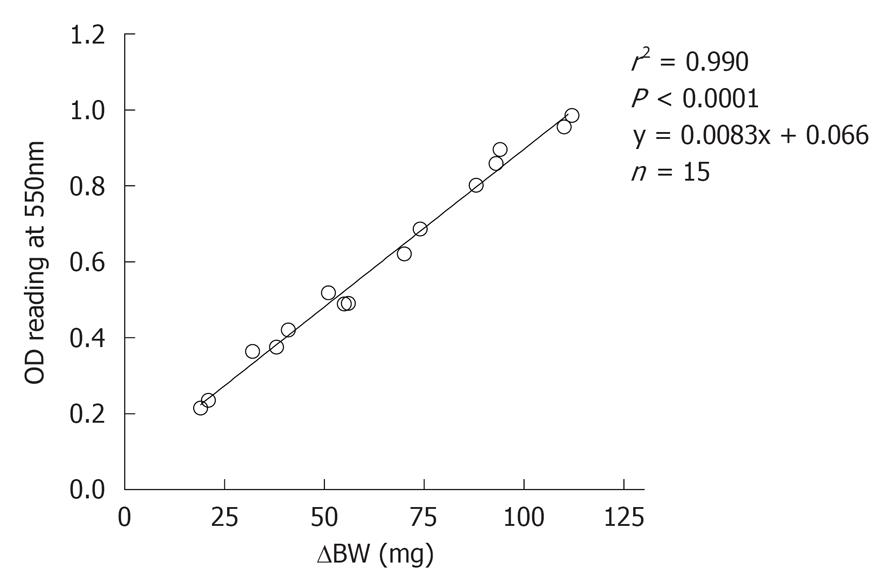
Figure 2 Correlation between changes in the body weight and OD readings for hemoglobin concentrations.
Blood was collected in saline and blood cells were separated by centrifugation and erythrocytes re-suspended in lysis buffer. Concentrations of hemoglobin were measured spectrophotometrically.
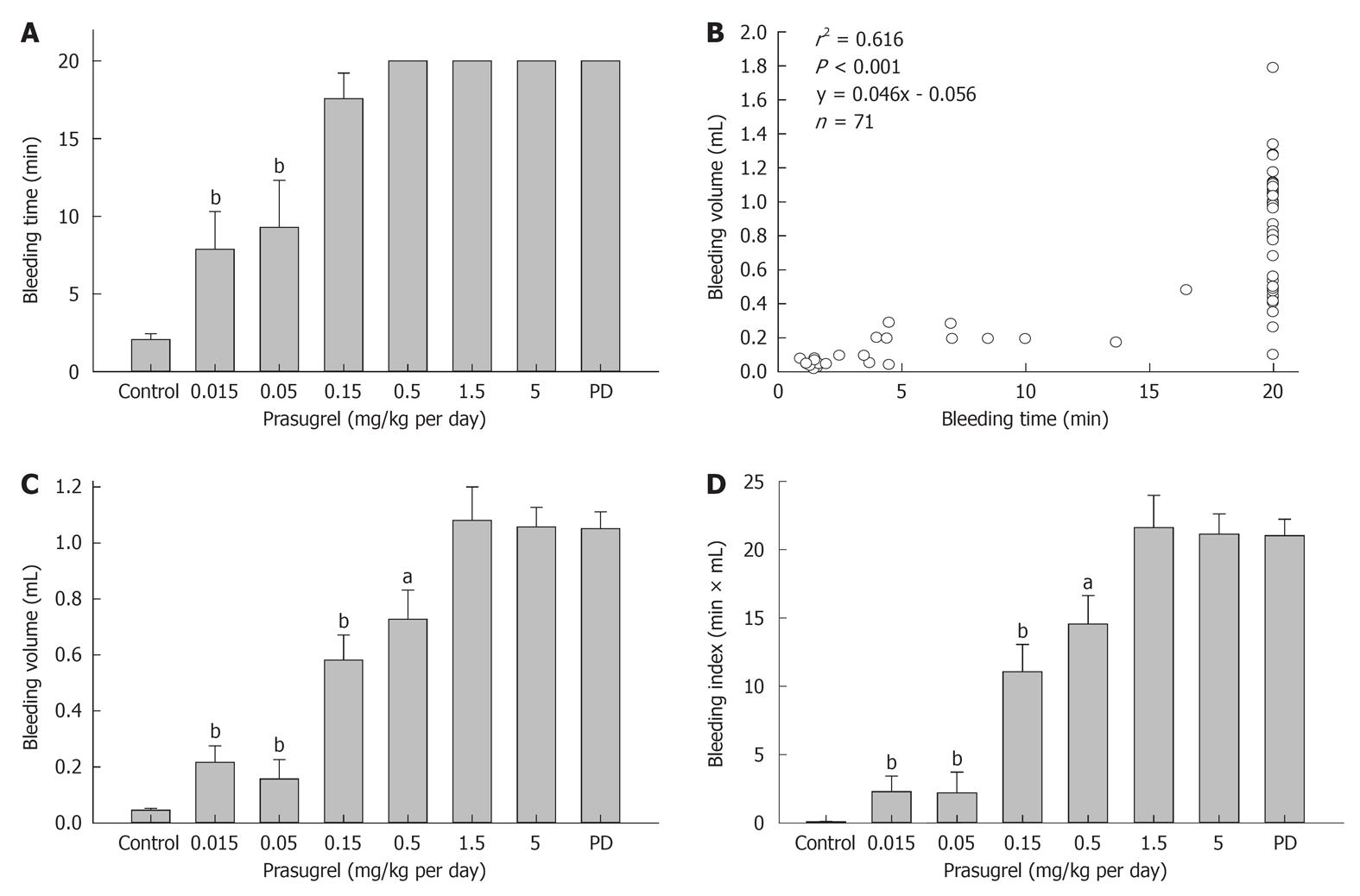
Figure 3 Dose-dependent reduction by the anti-platelet drug prasugrel on bleeding parameters.
Bleeding time failed to detect dose-effect relation only at two lowest doses (0.015 and 0.05 mg/kg per day, A), whereas bleeding volume was significantly lower vs 5 mg/kg per day starting from 0.15 mg/kg per day (B). Panel C shows the correlation between bleeding time and volume. Note the wide variation of bleeding volume in animals with bleeding time exceeding 20 min (C). The bleeding index was derived as the product of time (min) and volume (mL, D). Parameters of all treated groups were significantly higher than the untreated control. Platelet depletion (PD) group served as a positive control. aP < 0.02, bP < 0.001 vs 5 mg/kg prasugrel group. A total of 8 groups of mice (n = 6-13) were studied.
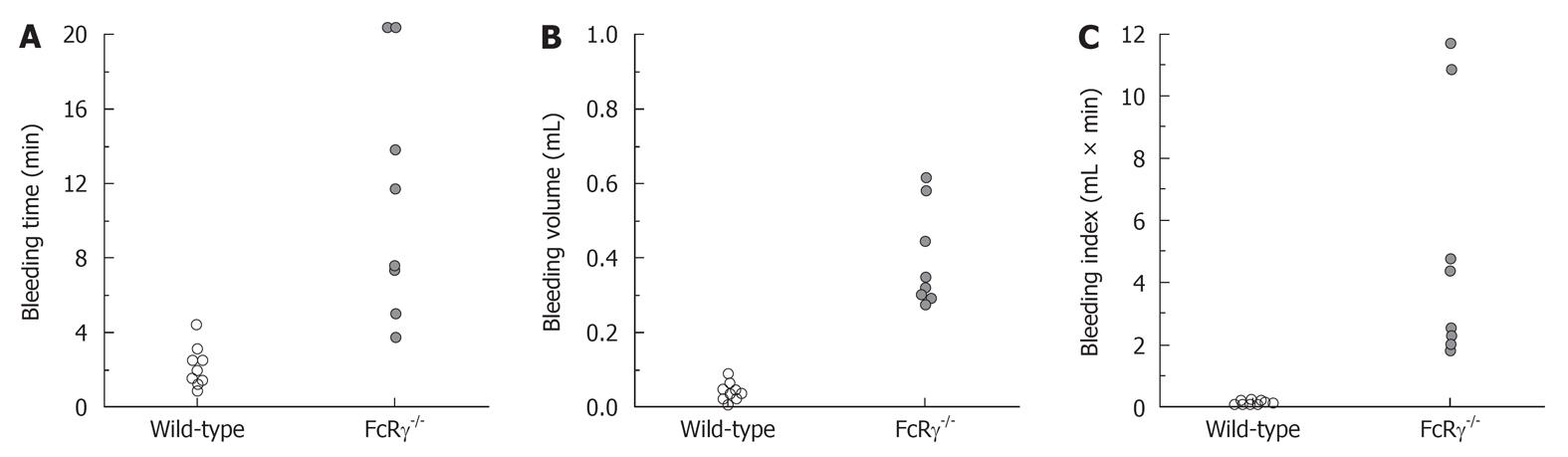
Figure 4 Tail bleeding time and volume measured in wild-type and FcRγ-/- mice.
Bleeding assay was performed by tail tip amputation and then immersing the tail in saline at 37°C. FcRγ-/- mice showed a significant increase in both bleeding time and volume (P < 0.01 vs wild-type mice) and development of recurrent bleeding in 6/8 of animals studied. Note that the better separation of FcRγ-/- and control mice by bleeding volume or index than that by bleeding time.
- Citation: Liu Y, Jennings NL, Dart AM, Du XJ. Standardizing a simpler, more sensitive and accurate tail bleeding assay in mice. World J Exp Med 2012; 2(2): 30-36
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2220-315X/full/v2/i2/30.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5493/wjem.v2.i2.30