Copyright
©The Author(s) 2023.
World J Exp Med. Sep 20, 2023; 13(4): 75-94
Published online Sep 20, 2023. doi: 10.5493/wjem.v13.i4.75
Published online Sep 20, 2023. doi: 10.5493/wjem.v13.i4.75
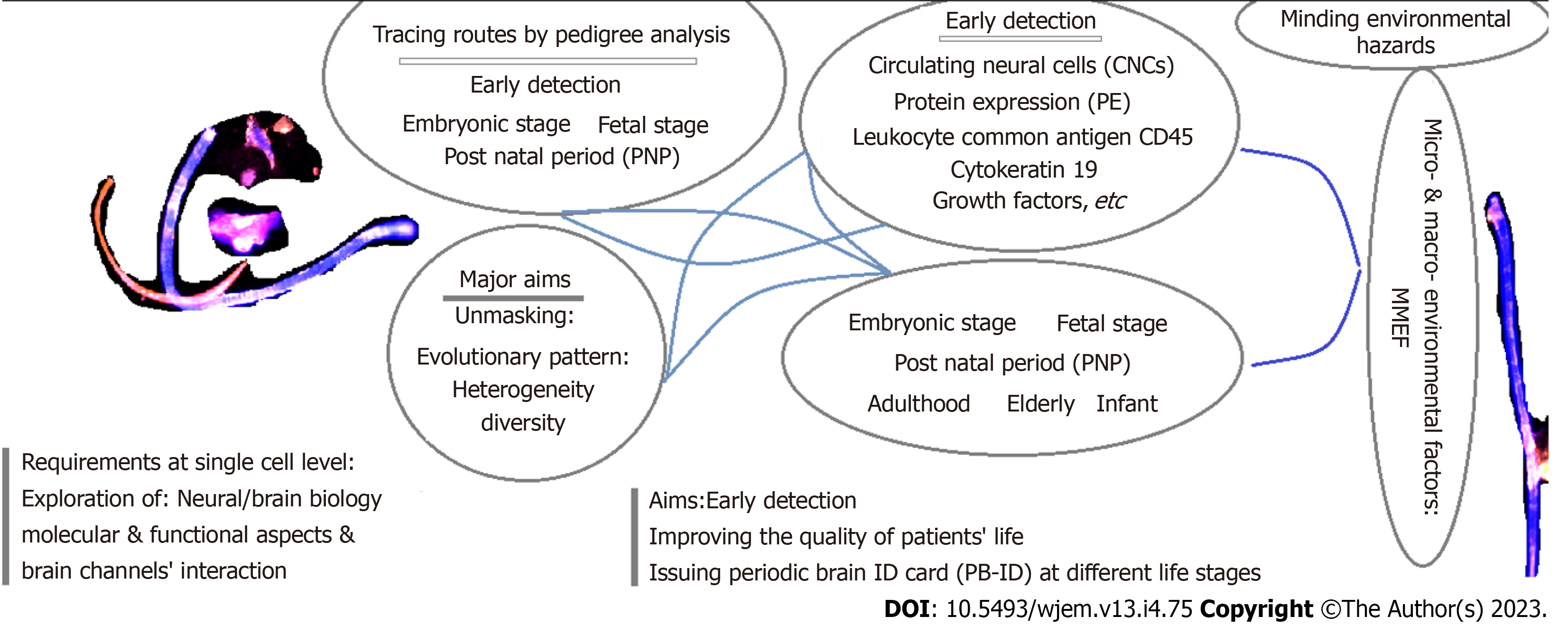
Figure 1
The required managements for early detection and therapy: A Journey from embryonic and fetal periods to elderly.
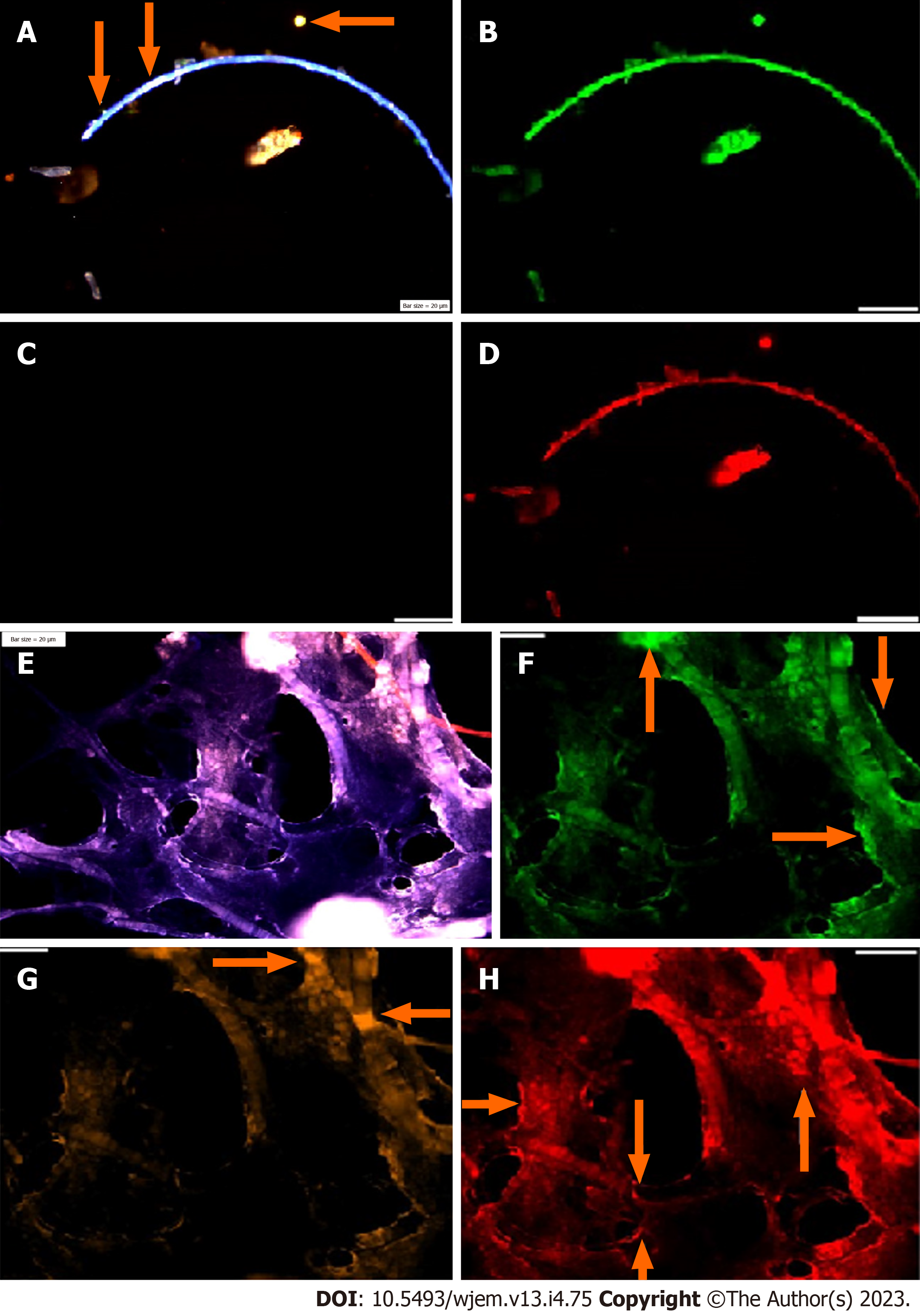
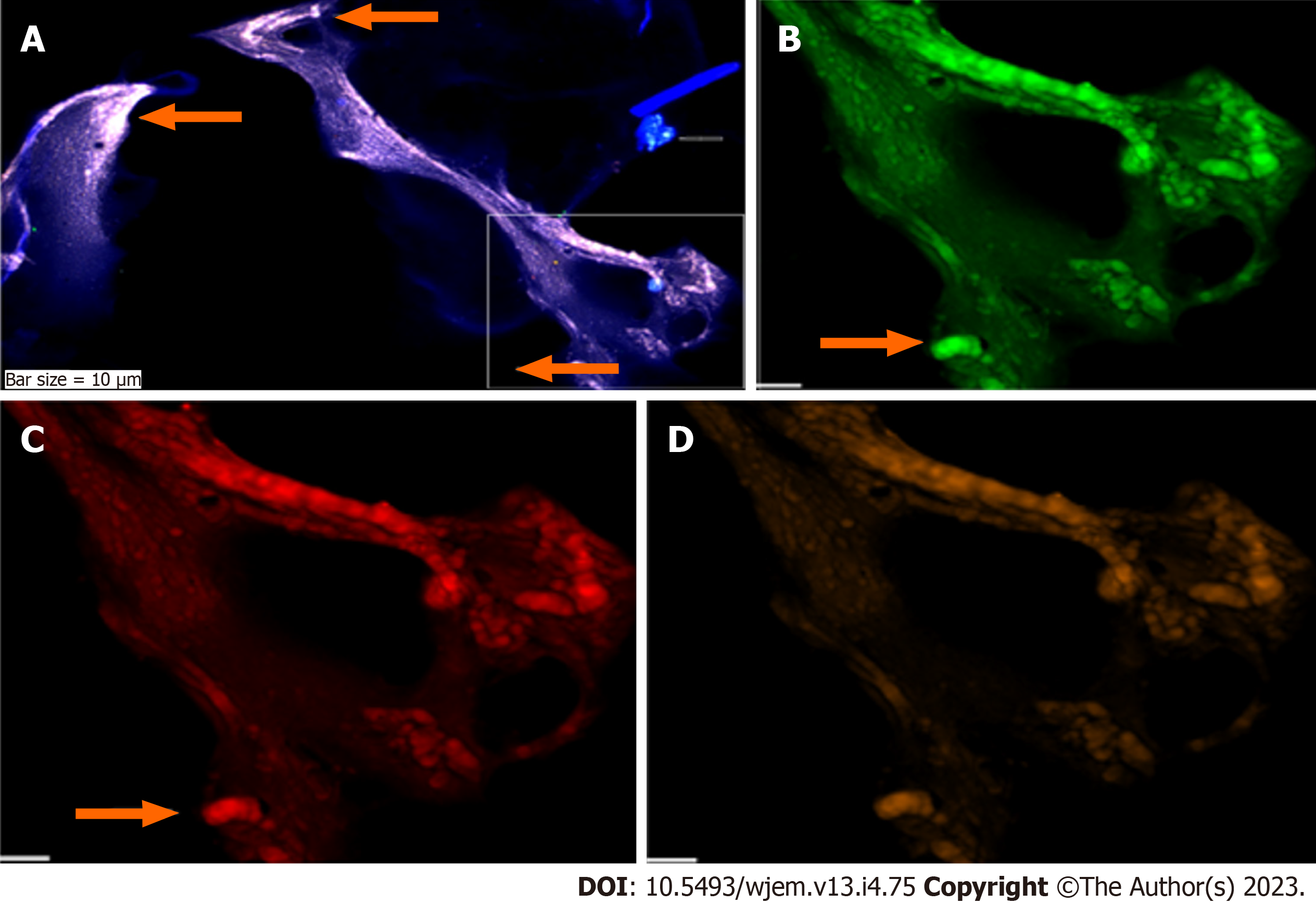
Figure 2 Circulating neural cells in embryonic and chorionic villus samples.
A: Circulated neural cells (CNCs) conjugated with Dapi/Ne/CD133/vascular endothelial growth (VEG); B: Same cells conjugated with fluorescein isothiocyanate (FITC) (Ne) reflecting high protein expression in the limited cells; C: Same cells conjugated with Rpe (CD133), totally lacks expression in stem cells; D: Same cells conjugated with Pe-Cy5, reflecting high protein expression, accompanied by few cells with low expression; E-H: Reflect protein expression in chorionic villus sample including; E: CNCs conjugated with Dapi/Ne/CD133/VEG; F: Same cells conjugated with FITC (Ne) reflecting high protein expression; G: Same cells conjugated with Rpe (CD133), lack of expression is observable, accompanied by few cells with positive CD133; H: Same cells conjugated with Cy5 (VEGF), reflecting high protein expression and remarkable angiogenesis. Bars = 20 μm.
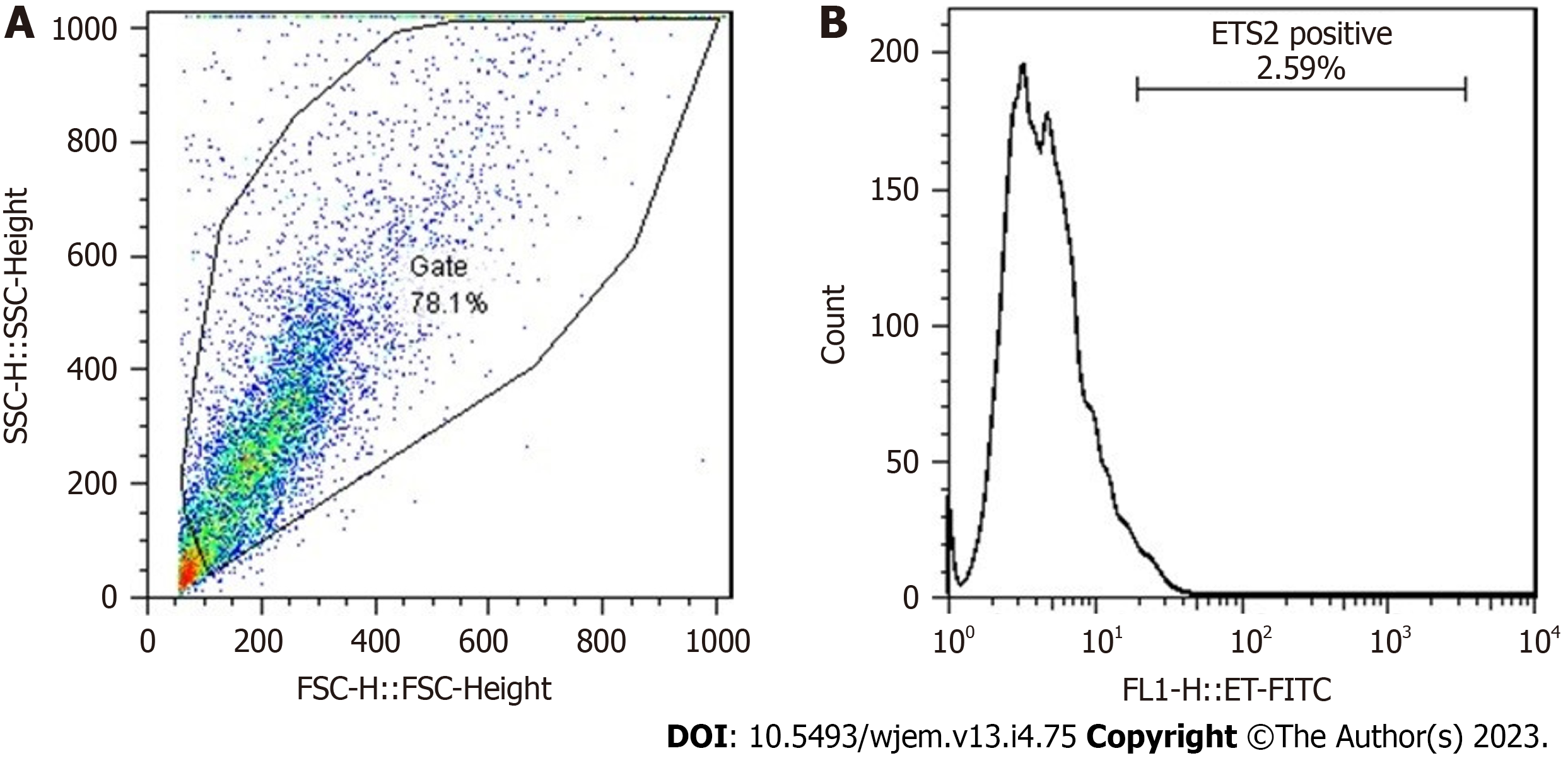
Figure 3 Flow-cytometry results of erythroblastosis virus E26 oncogene homolog 2 protein expression in a patient affected with Alzheimer disease.
A: R1: 78.1 % (7812/10000 cells); B: Erythroblastosis virus E26 oncogene homolog 2: 2.59 % (202/7812 cells). Ets2: Erythroblastosis virus E26 oncogene homolog 2; SSC: Side scatter reflects the internal complexity. Adapted from Reference[11].
Figure 4 Protein expression of Ataxia Telangiectasia mutated gene, erythroblastosis virus E26 oncogene homolog 2, and vascular endothelial growth factor in the circulated neural cells from the neural system to the blood stream in a patient with Alzheimer disease.
A: Circulated neural cells (CNCs) with dapi; B: CNCs conjugated with Ataxia Telangiectasia mutated (Rpe), reflecting lack or very low expression; C: The same cells conjugated with Ets2 (Fluorescein isothiocyanate) with a mosaic pattern of expression; D: Same cells conjugated with vascular endothelial growth factor (Rpe), reflecting mosaic angiogenesis.
Figure 5 Protein expression of neural marker, CD133, and vascular endothelial growth factor in the circulated neural cells from the neural system to the blood stream in a patient with Alzheimer disease.
A: Merged of dapi/fluorescein isothiocyanate/CD133/vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF); B: Neural cells, conjugated with FITC with low expression, accompanied by the cells with high expression; C: Neural cells conjugated with Pe-cy5 also with low expression, accompanied by the cells with high expression; D: Cells conjugated with R-phycoerythrin and VEGF, majority of cells reflecting low expression, accompanied with a minor cells with lack of expression.
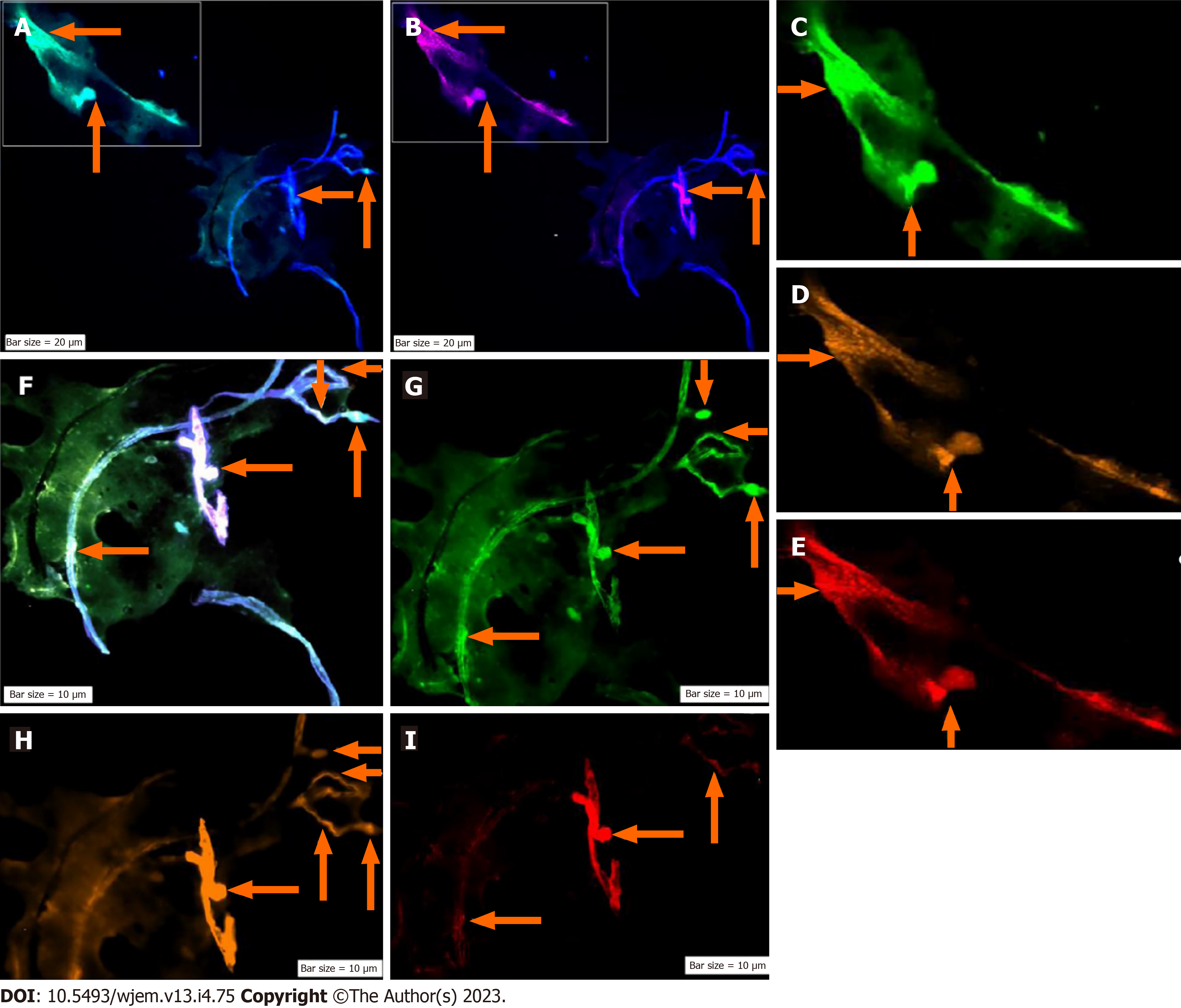
Figure 6 Protein expression of neural marker/CD133/vascular endothelial growth factor in the circulated neural cells from the neural system to the blood stream in a patient with Alzheimer disease.
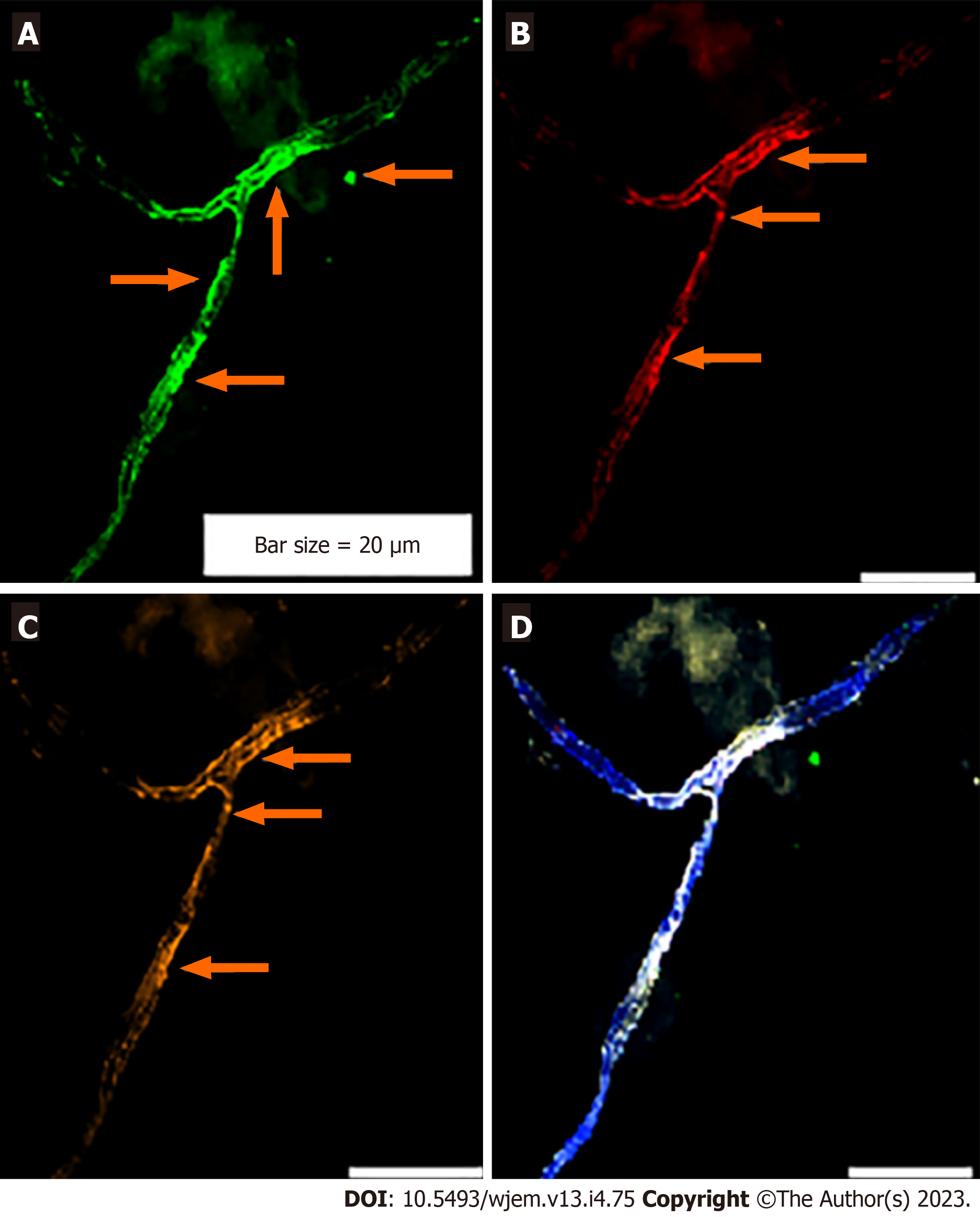
A: Merged of dapi/Ne (Ne: Neural cells conjugated with dapi/Ne); B: Merged of dapi/Pe-cy5, CD133, Same cells conjugated with fluorescein isothiocyanate reflecting high expression; C: Neural cells, conjugated with fluorescein isothiocyanate (FITC)/Ne; D: Neural stem cells, conjugated with Pe-cy5 with mosaic pattern including the cells with high, very low-, and lacking-expression; E: Conjugated with Pe-cy5/neural cells; F: Co-expression of Dapi/Ne/CD133/VEGF; G: Neural cells conjugated with FITC; H: Vascular endothelial growth factor conjugated with Rpe; I: CD133 conjugated with Pe-cy5. The migrated neural cells with high or low expression are shown with arrows. The micro-vesicle and the vascular section harboring the migrated neural cells are detectable. The micro-vesicle and the vascular section harboring the migrated neural cells are detectable. Ne: Neural cells conjugated with FITC; CD133: Neural stem cells, conjugated with Pe-cy5; VEGF: Vascular endothelial growth factor, conjugated with RPe; The CNCs were explored by IF method for combination of neural marker, neural stem cell for Ne/CD133 (Figure 7).
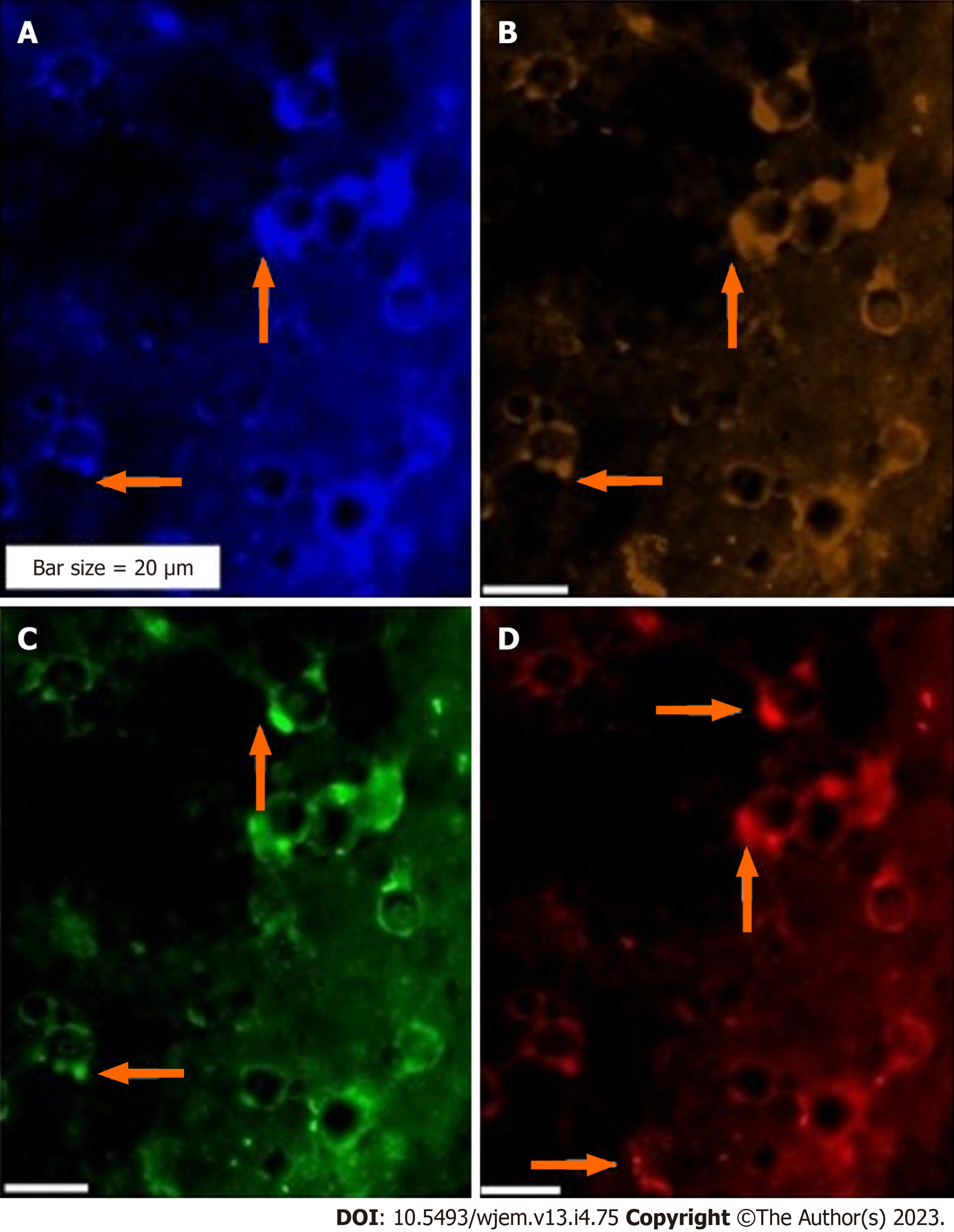
Figure 7 Protein expression of neural marker, and CD133 in the circulated neural cells from the neural system to the blood stream in a patient with Alzheimer disease.
A: Merged of phase contrast/dapi/neural marker (NE)/CD133, in which the presence of beta-Amyloid is remarkable in the background of this image; B: Merged dapi/NE/CD133, reflects the co-expression between NE and CD133; C: Diverse expression of NE, reflects the dissected of only upper section of image with low expression of NE; accompanied by an isolated section with low expression of NE; including group of cells with positive expression; D: Diverse protein function including high and low expression of CD133. The protein expression of NE/vascular endothelial growth factor/erythroblastosis virus E26 oncogene homolog 2 is also provided (Figure 8).
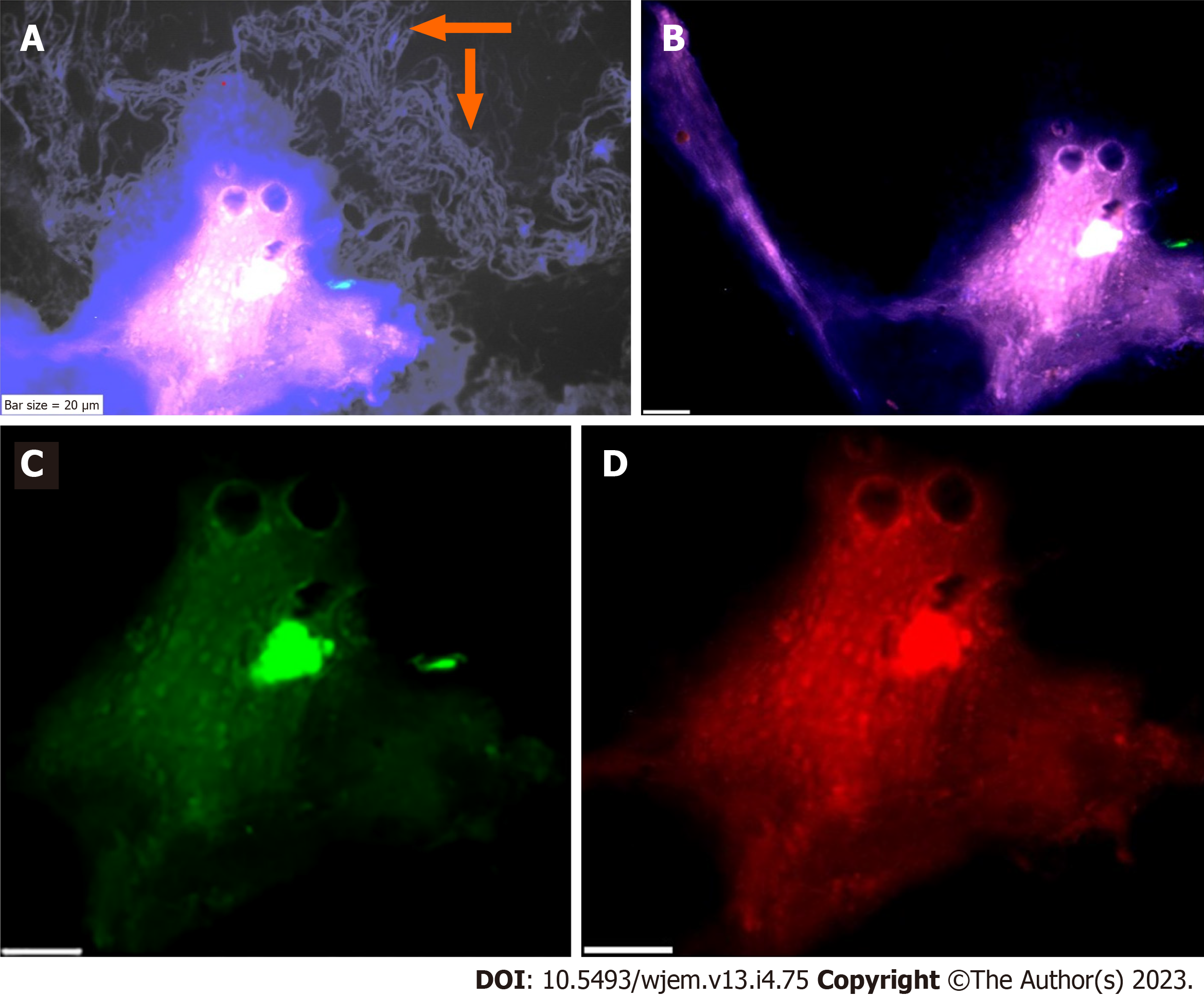
Figure 8 Protein expression of neural marker/vascular endothelial growth factor/erythroblastosis virus E26 oncogene homolog 2 in the circulated neural cells from the neural system to the blood stream in a patient with Alzheimer disease.
A: Circulated neural cells (CNCs) with dapi/neural marker/vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF)/erythroblastosis virus E26 oncogene homolog 2 (Ets2) reflecting remarkable co-epression between 3 proteins; B: Few CNCs with Ne (conjugated with fluorescein isothiocyanate), reflecting high expression; C: The cells are conjugated with RPe and reflects VEGF with diverse high-, low- expression; D: Cells are conjugated with Pe-cy5 reflects Ets2 with diverse, mostly low-, accompanied by cells with high- and lack of expression.
Figure 9 Protein expression of cytokeratin-19/CD45/endothelial growth factor in circulating neural cells in the blood stream of an apparently healthy individual under mediation with light music.
A: The circulating neural cells (CNCs), conjugated with fluorescein isothiocyanate for cytokeratin 19 (CK19); B: Same image with Cy5 for endothelial growth factor (EGF); presenting less cells expressing than CK19; C: Same image with R-phycoerythrin for CD45, and expressing less than CK19; D: Co-expression of dapi/CK19/EGF/CD45. The arrow refers to the CNCs cells with remarkable expression. Presence of CNCs was confirmed by the mode of cytokeratin 19+/CD45.
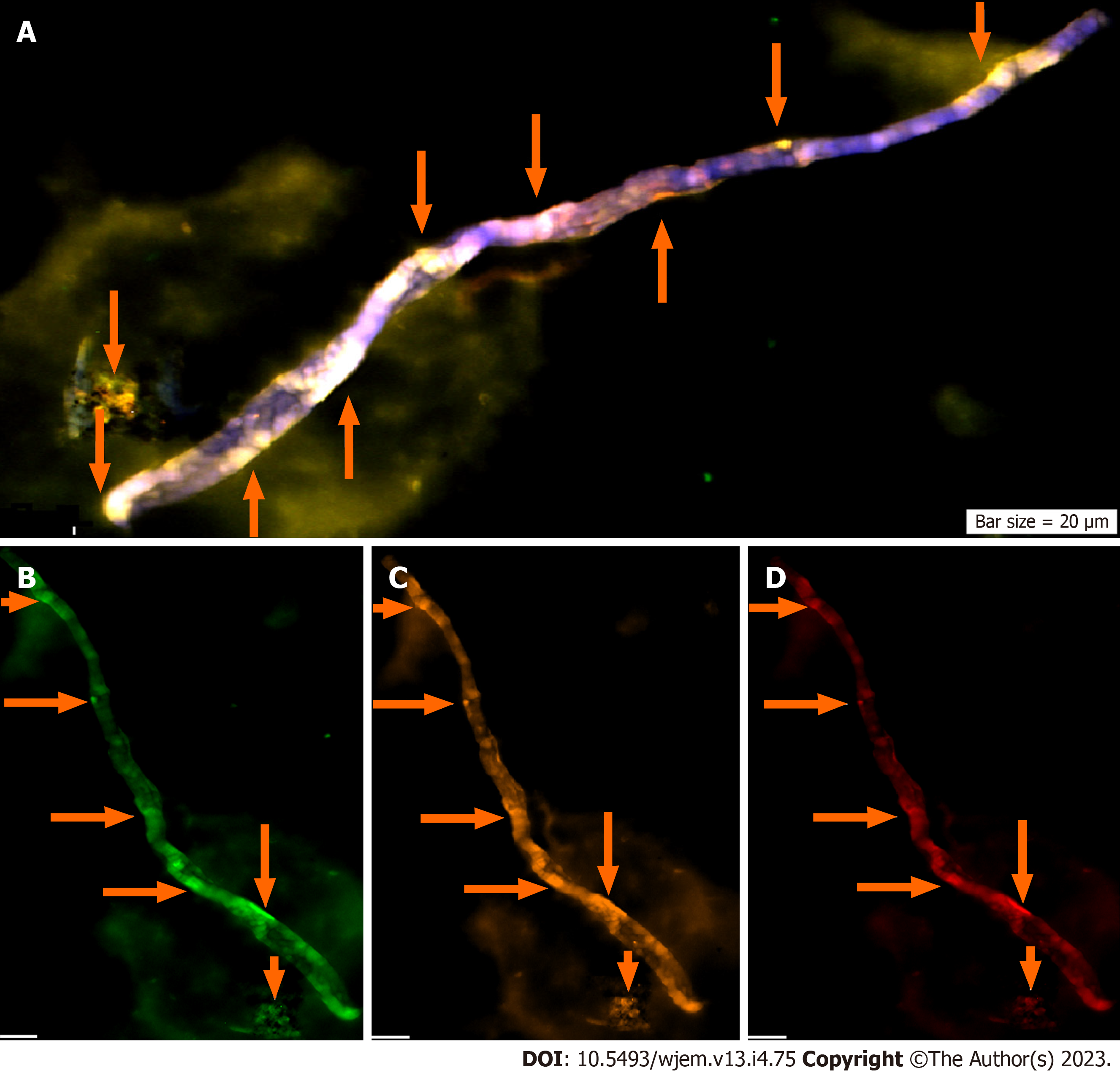
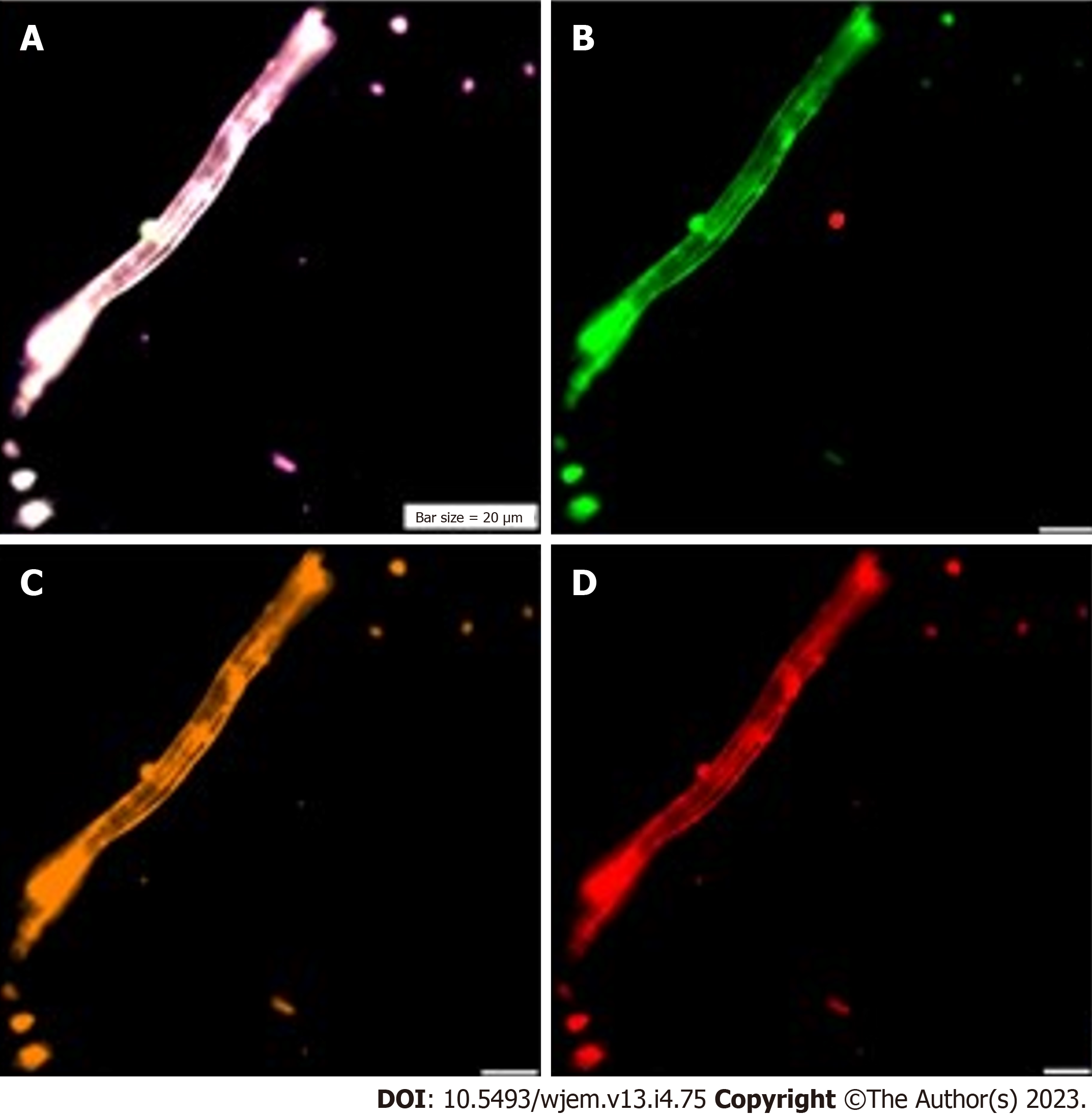
Figure 10 Circulating neural cells.
A: Co-expression of Dapi/NE/CD133/vascular endothelial growth (VEG); B: Neural marker, conjugated with fluorescein isothiocyanate; C: CD133: Neural stem cell, conjugated with R-phycoerythrin; D: Vascular endothelial growth factor, conjugated with Pe-cy5. A-D images present circulating neural cells within the blood stream. Neural marker (B) reflects high expression; neural stem cell (C) and VEGF (D) are characterized with the harmonic and higher protein expression.
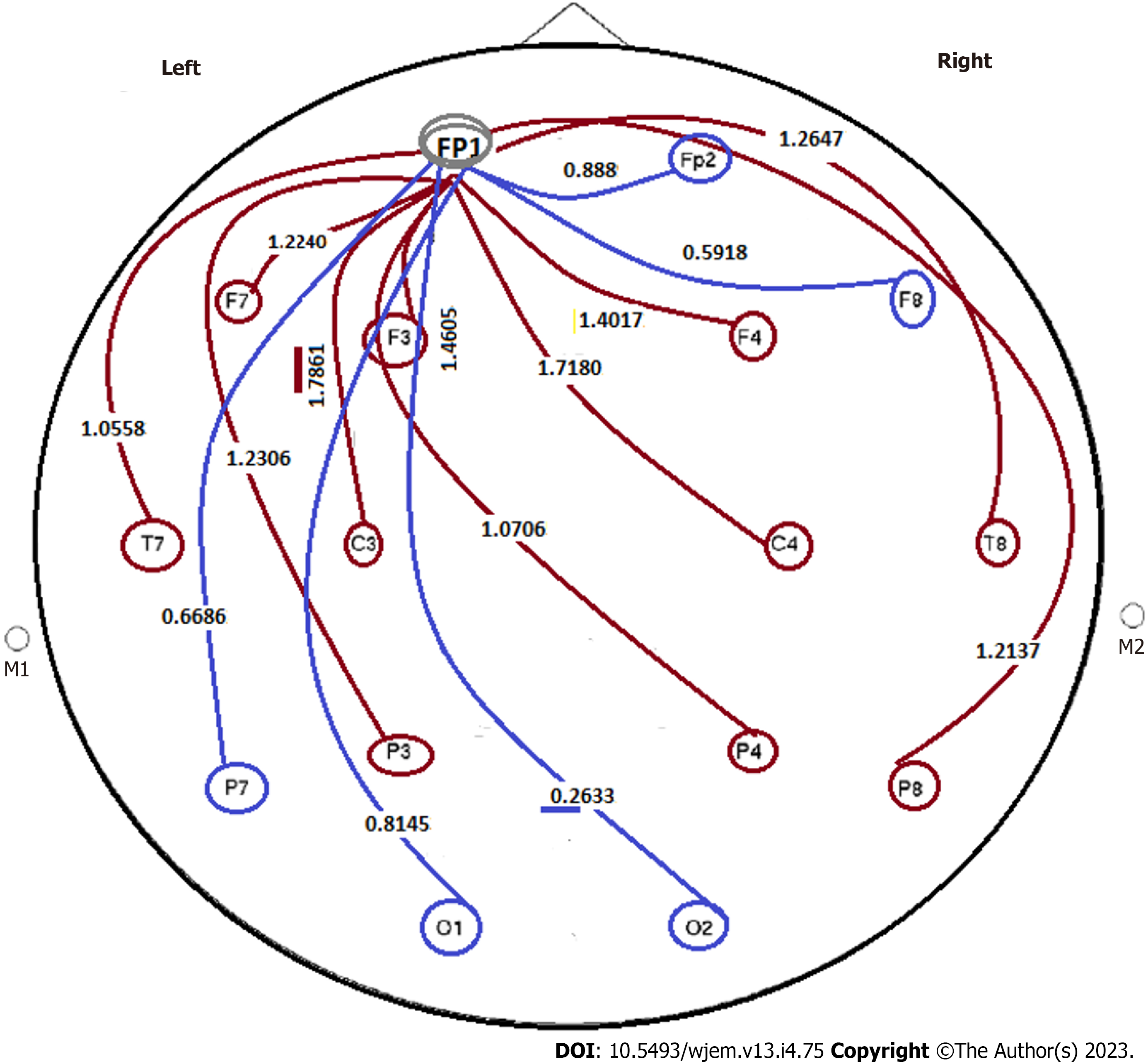
Figure 11 Power ratio at pre- to post applied condition of closed/open eyes in an apparently healthy individual.
By considering the applied condition- model as closed/opened eyes, evaluation was performed by considering the ratio of FP1 to other channels: (1) Minor group: Cooperation from polar section of brain, i.e., between FP1/Fp2 = 0.888; FP1/F8 = 0.5918; FP1/O2 = 0.2633; FP1/O1 = 0.8145; FP1/P7 = 0.6686. All ratio < 1. Range of ratio: 0.2633-0.8145; (2) major group: have diverse destinations including FP1/T8 = 1.2647; FP1/P8 = 1.2137; FP1/F4=1.4017; FP1/C4 = 1.7180; FP1/P4 = 1.0706; FP1/F3 = 1.4605; FP1/C3 = 1.7861; FP1/F7 = 1.2240; FP1/P3 = 1.2306; and FP1/T7 = 1.0558. All ratio > 1. Range of ratio: 1.0558-1.7861. In this image, FP1 is the unique station as the primary initiating action within the brian channels, as octopods. There is a uique pattern as one direction from the upper to lower-section of the brain, including 10 indices less than 1 ratio (the blue lines) and 10 indices higher than 1 (brown lines). Such remarkable diversity is indicative of the well defined as two opposite directions from a unique central station towards 20 destinations. By defining the status of closed- to open eyes including > 1 as relaxation and < 1 as stressful conditions, then the challenging points are related to two distinct-outcomes. But as the matter of fact, the imposed rule is the unique major initiator, as the main station towards two categorized destinations. This regulation is considered as: (1) The correlative/single station, as major initiator/hypothesis; and (2) two distinct Ratio based categories, including > 1 and < 1 (Figure 11). The question is related to the diverse impact on the behavioral, emotional and other related physical and/or mental behaviors. Keeping the stable behavioral balances is the major aim with the reliable, harmless, and available tools such as light music and/or any relaxation method. This data reflects: (1) An EEG, personalized based and reliable categorized hypothesis; (2) with aim of detecting the behavioral characteristics of both group of individuals including an apparently healthy and individuals with either affected with Alzheimer disease, or at primary stages of AD; (3) considering an early detective strategy; and (4) organizing the prognostic, predictive, and preventive management as early as possible. F: Frontal; O: Occipital; C: Central; FC: Between F and C; AF: Between Fp and F; C3,4: Central Lobe; F3,4,7,8,z: Frontal lobe; FP1,2: Pre frontal cortex; PF3,4,7,8: Partial Lobe; O1,2: Occipital lobe; T7,8: Temporal 7,8.
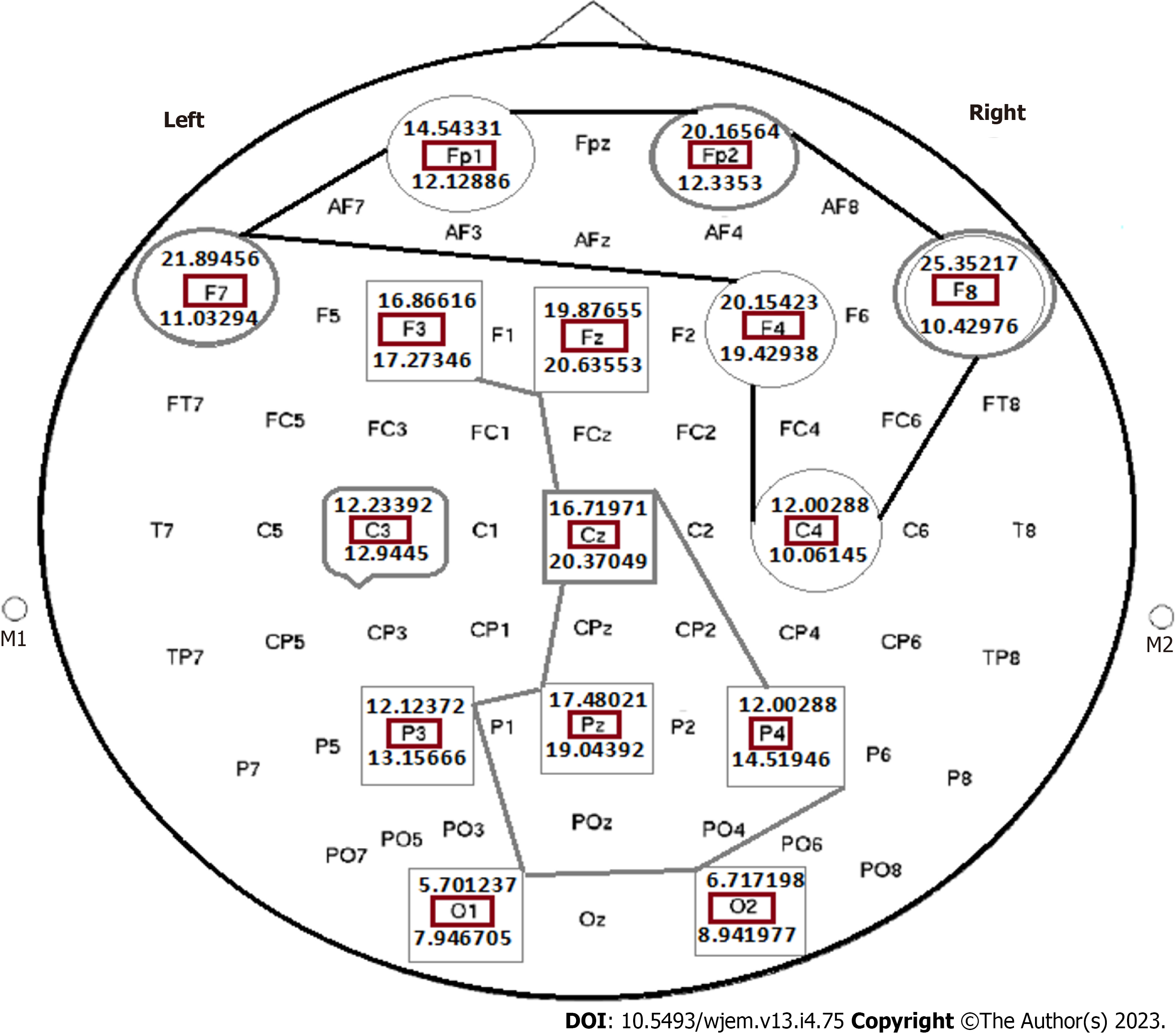
Figure 12 Status of the absolute power Ratio by considering closed eye to open eye, based on the mediation of light music on the selected brain channels of a healthy individual.
This figure includes 19 brain channels. (1) Mean power of delta (HZ) 20 min post mediation with light music; (2) channel’s names represent locations of brain including Frontal (F), Occipital, central (C), between F and C, between Fp and F; and (3) the significant value: P < 0.05. Figure 12 is indicative of the cooperative/multi-centers/and two distinct categorized correlations including 6 and 8 destinations include: (1) Indices > 1, characterized with diverse degrees of ratio as > 1; and (2) the cooperative cluster involed 8 channels, including F3, Fz, F4, Cz, P3, Pz, P4, O1, nd O2 all with ratio < 1. These channels have impact through the middle section of brain brain from up-to down-destination. Channel C3 is characterized with almost ratio = 1, and it seems that the cooperative manner with other channels, is considered as an independent chanel. Catagories: Closed eyes (CE), opened eyes (OE); CE < OE; CE > OE; CE remarkably > OE; Almost equal CE and OE. This figure includes 19 brain channels. F: Frontal; O: Occipital; C: Central; FC: Between F and C; AF: Between Fp and F; CE: Closed eyes; OE: Opened eyes. By considering 19 channels, the absolute power ratio in all brain channels by considering close eye to open eye, based on the mediation of light music in the brain channels of a healthy individual provided the following results (Figure 13): Diverse grouping with discordance index includes: The indices as discordance based grouping with < 1 ratio, at post mediation by light music, and includes: F3, Fz, Cz, P3, Pz, P4, P8, O1, O2 which are classified as discordance grouping. The indices as concordance based grouping and includes: (1) HZ Pre- and 20 min post mediation with light music; (2) channels’ names represent locations of 19 channels in the brain including: C3,4,z: Central Lobe; F3,4,7,8,z: Frontal lobe; FP1,2: Pre frontal cortex; PF3,4,7,8,z: Partial Lobe; (3) the results, based on the ratio of closed eyes to the open eyes is classified as concordance and discordance; and (4) closed eyes, and opened eyes (P value: P < 0.05). In upper frame, except F3 with ratio of < 1, the other 9 channels present ratio of > 1. The blue-line group, are reflective of mosaicism including P7, C3 and T8 with equal ratio; Cz with < 1, and C4 with > 1. Interestingly, the most harmonic channels are traced within the middle region (red line includes the cooperative panel) which are characterized with the < 1 ratio between 9 different channels through the horizontal and vertical distributed channels (Figure 13).
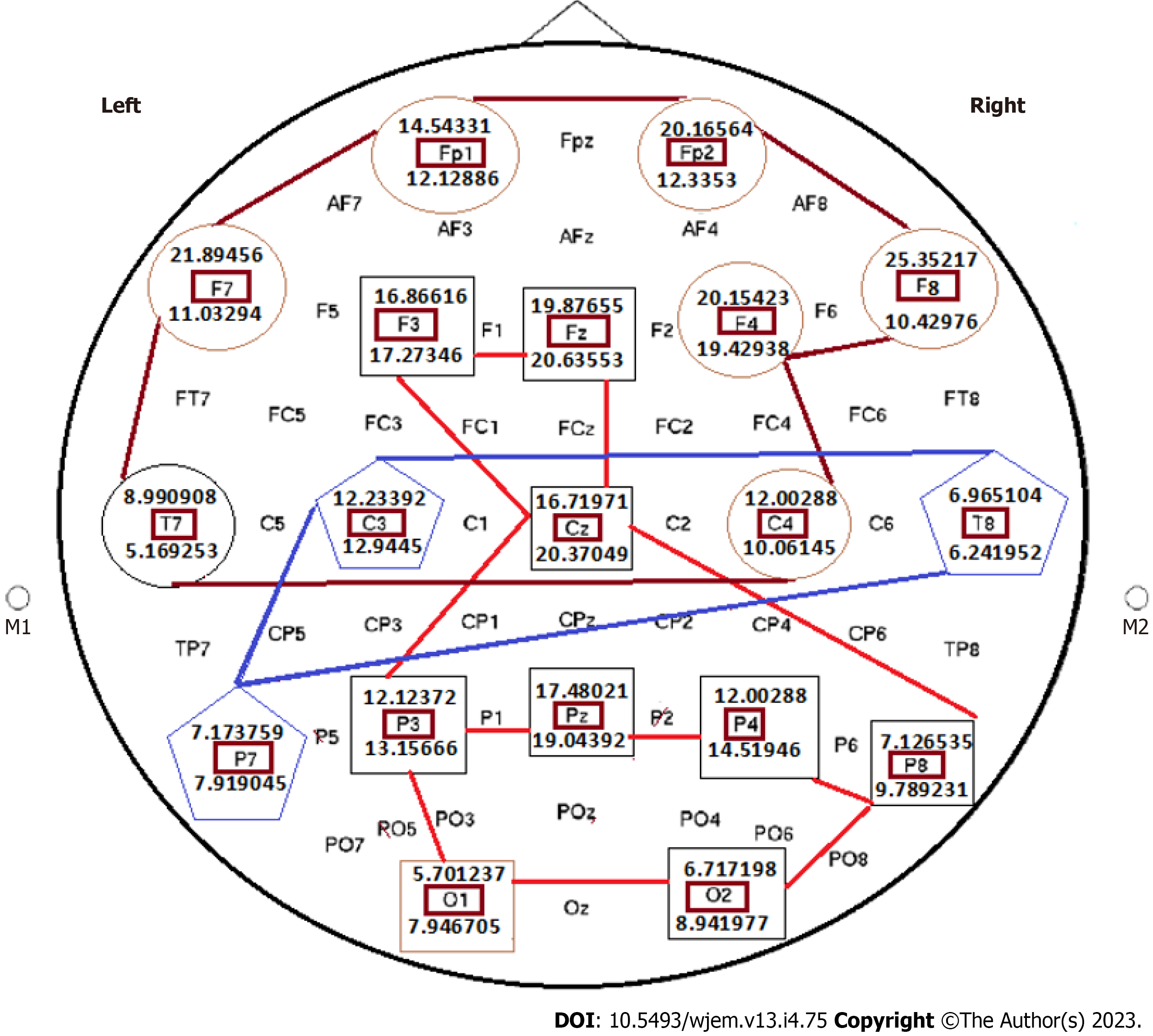
Figure 13 Status of the absolute power Ratio in all brain channels by considering close eye to open eye, based on the mediation of light music in the brain channels of a healthy individual.
This figure includes 19 brain channels. The absolute power ratio in all channels are an Informative frame in the brain research with target based translational impact on personalized classification in Medicine/Neulogy. The cooperative strategy between different channels is rather complicated in which 3 diverse, unique and cooperative platforms are established which could optimize the status of the mental behavior and health status of the target individuals. Brain is governed by multi-centered channels, being capable of influential cooperation.
- Citation: Mehdipour P, Fathi N, Nosratabadi M. Personalized clinical managements through exploring circulating neural cells and electroencephalography. World J Exp Med 2023; 13(4): 75-94
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2220-315X/full/v13/i4/75.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5493/wjem.v13.i4.75