Copyright
©The Author(s) 2019.
World J Crit Care Med. Sep 11, 2019; 8(5): 72-81
Published online Sep 11, 2019. doi: 10.5492/wjccm.v8.i5.72
Published online Sep 11, 2019. doi: 10.5492/wjccm.v8.i5.72
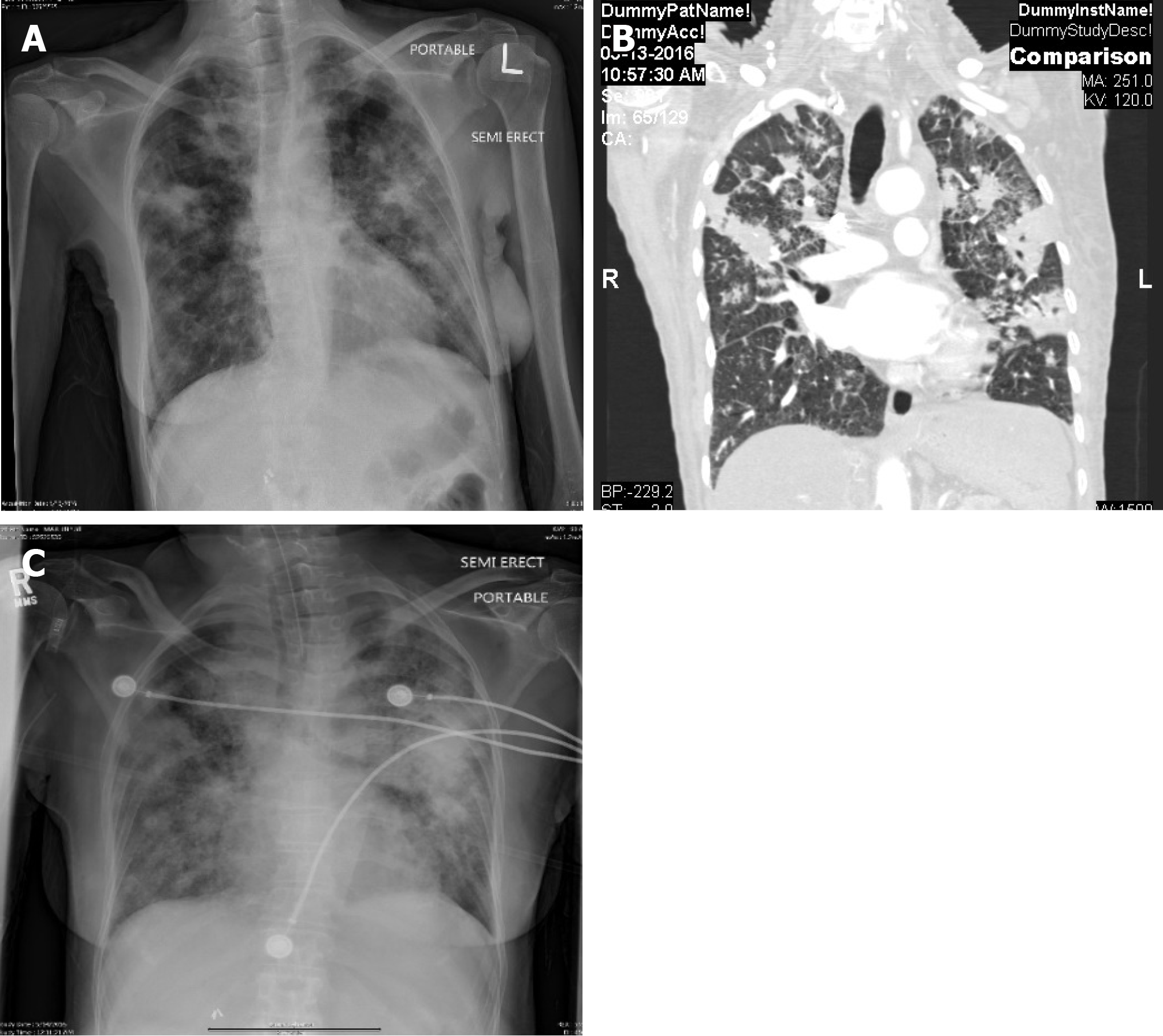
Figure 1 Chest X-ray and computed tomography (case 1).
A: Chest X-ray demonstrating the bilateral patchy infiltrates at the time of admission; B: Computed tomography scans of chest with coronal section demonstrating bilateral patchy infiltrates at the time of admission; C: X-ray chest demonstrating worsening of the bilateral infiltrates after intubation and initiation of anti tuberculosis medications.
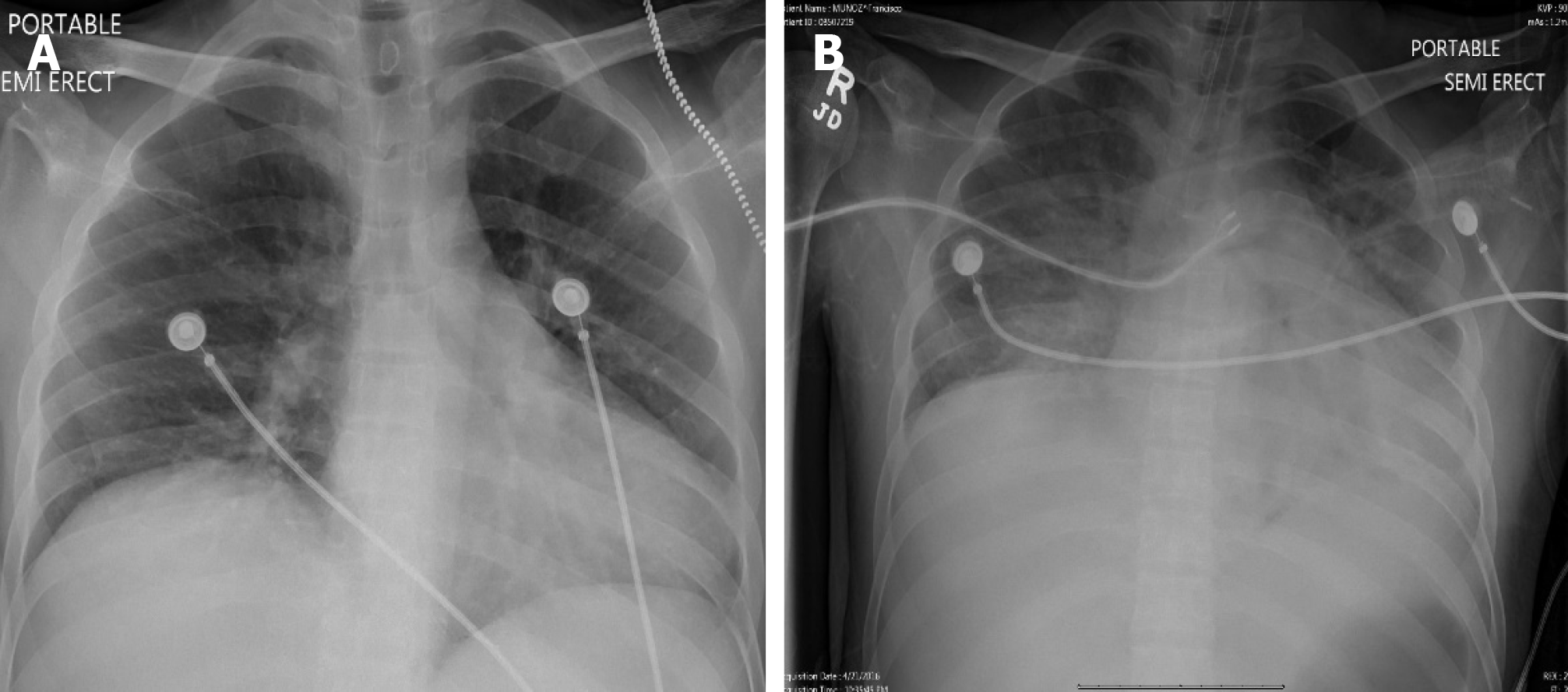
Figure 2 X-ray chest (case 2).
A: X-ray chest with no infiltrates at the time of admission; B: X-ray chest with new infiltrates and hypoxia requiring intubation and mechanical ventilation.
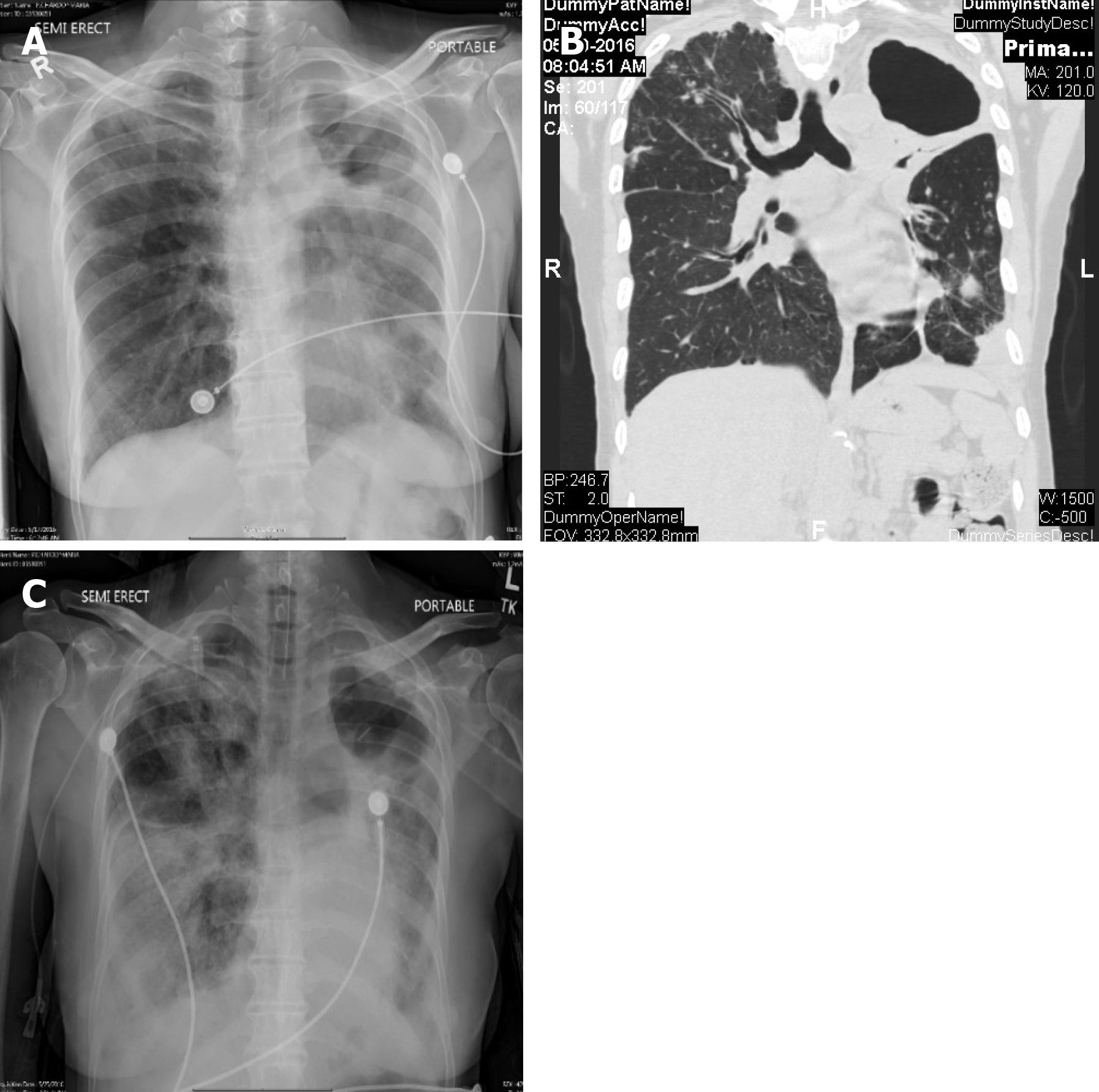
Figure 3 X-ray chest and computerized axial tomography (case 3).
A: X-ray chest revealing the left upper lobe cavity and left lower lobe infiltrates at time of admission; B: Computerized axial tomography scan of the chest at time of admission revealing left lung thick walled cavities and multiple nodules on both side; C: X-ray chest revealing worsening of the bilateral infiltrate after intubation and of the anti-tuberculosis medications.
- Citation: Mishra R, Patel HK, Singasani R, Vakde T. Tuberculosis septic shock, an elusive pathophysiology and hurdles in management: A case report and review of literature. World J Crit Care Med 2019; 8(5): 72-81
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2220-3141/full/v8/i5/72.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5492/wjccm.v8.i5.72