Copyright
©2014 Baishideng Publishing Group Inc.
World J Crit Care Med. Nov 4, 2014; 3(4): 102-112
Published online Nov 4, 2014. doi: 10.5492/wjccm.v3.i4.102
Published online Nov 4, 2014. doi: 10.5492/wjccm.v3.i4.102
Figure 1 Risk prediction models for invasive candidiasis in critically ill patients with overlapping contributing factors.
Factors which are common in several risk-prediction models appear to bear a higher relative risk for IC. Given the heterogeneity in study designs and populations, these models can hardly be merged to represent a single paradigm, however their common contributing factors appear to be of higher predictive value for IC prediction. So far, the most widely applied predictive tool for IC is the Leon’s Candida Score followed by the Ostrosky-Zeichner’s model. ABx: Antibiotic; CCI: Candida colonization index; CVC: Central venous catheter; GI: Gastrointestinal; ICU: Intensive care unit; TPN: Total parenteral nutrition; LoS: Length of stay.
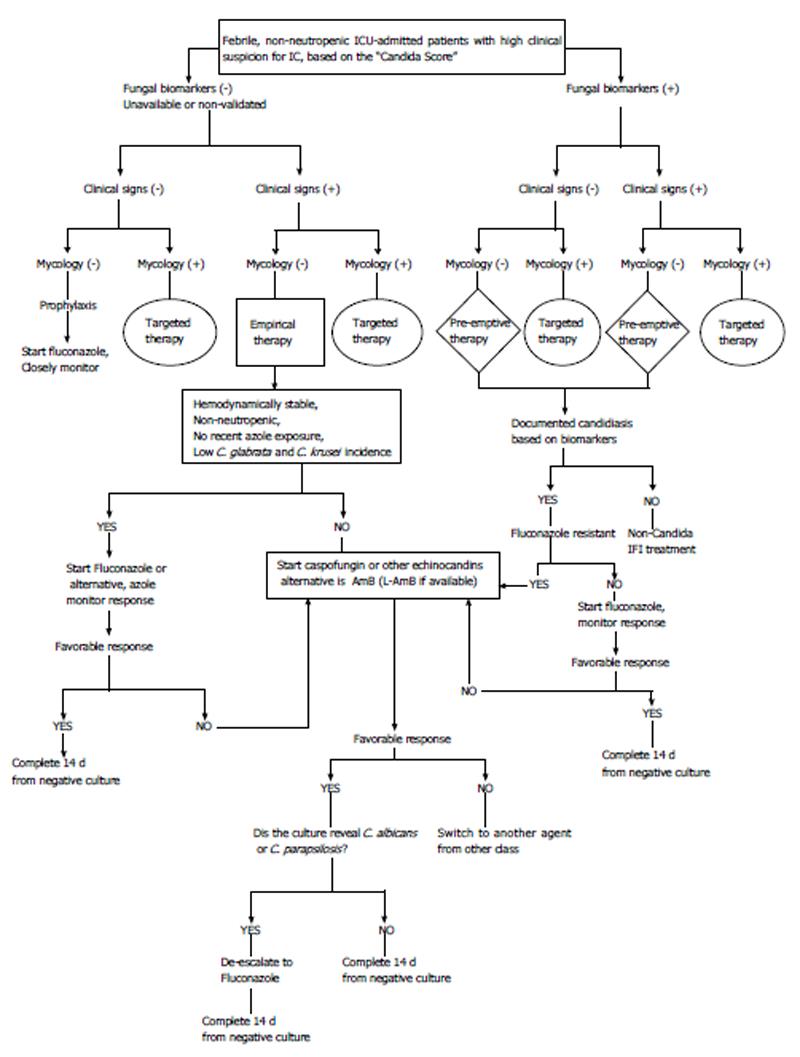
Figure 2 Management of invasive candidiasis in critical care setting.
An updated consensus from the Iranian experts at invasive fungal infection-clinical forum. For justification and referencing see “diagnostic challenges of invasive candidiasis in the intensive care unit” and “approach to invasive candidiasis in intensive care unit” in the present report. IC: Invasive candidiasis; ICU: Invasive fungal infection; AmB: Amphotericin B; L-AmB: Liposomal Amphotericin B; IFIs: Invasive fungal infections.
- Citation: Elhoufi A, Ahmadi A, Asnaashari AMH, Davarpanah MA, Bidgoli BF, Moghaddam OM, Torabi-Nami M, Abbasi S, El-Sobky M, Ghaziani A, Jarrahzadeh MH, Shahrami R, Shirazian F, Soltani F, Yazdinejad H, Zand F. Invasive candidiasis in critical care setting, updated recommendations from “Invasive Fungal Infections-Clinical Forum”, Iran. World J Crit Care Med 2014; 3(4): 102-112
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2220-3141/full/v3/i4/102.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5492/wjccm.v3.i4.102