Copyright
©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Crit Care Med. Sep 9, 2025; 14(3): 101327
Published online Sep 9, 2025. doi: 10.5492/wjccm.v14.i3.101327
Published online Sep 9, 2025. doi: 10.5492/wjccm.v14.i3.101327
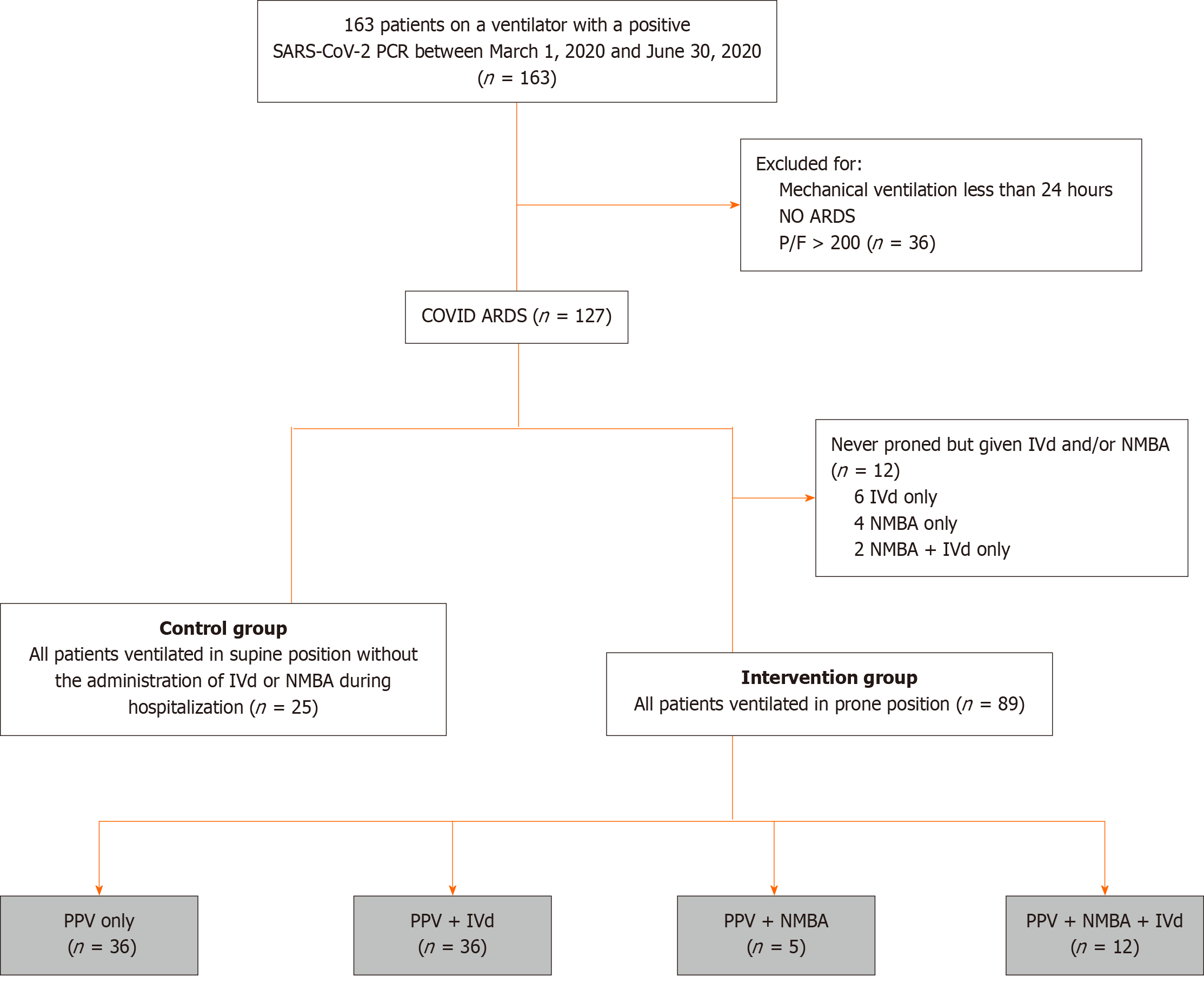
Figure 1 Flowchart of patients analyzed for the study.
Intervention group was further subdivided (gray) by therapy combination for secondary analysis. ARDS: Acute respiratory distress syndrome; COVID: Coronavirus disease; IVd: Inhaled vasodilators; NMBA: Neuromuscular blocking agents; PCR: Polymerase chain reaction; P/F: Arterial oxygen partial pressure/fractional inspired oxygen; PPV: Prone position ventilation; SARS-CoV-2: Severe acute respiratory coronavirus 2.
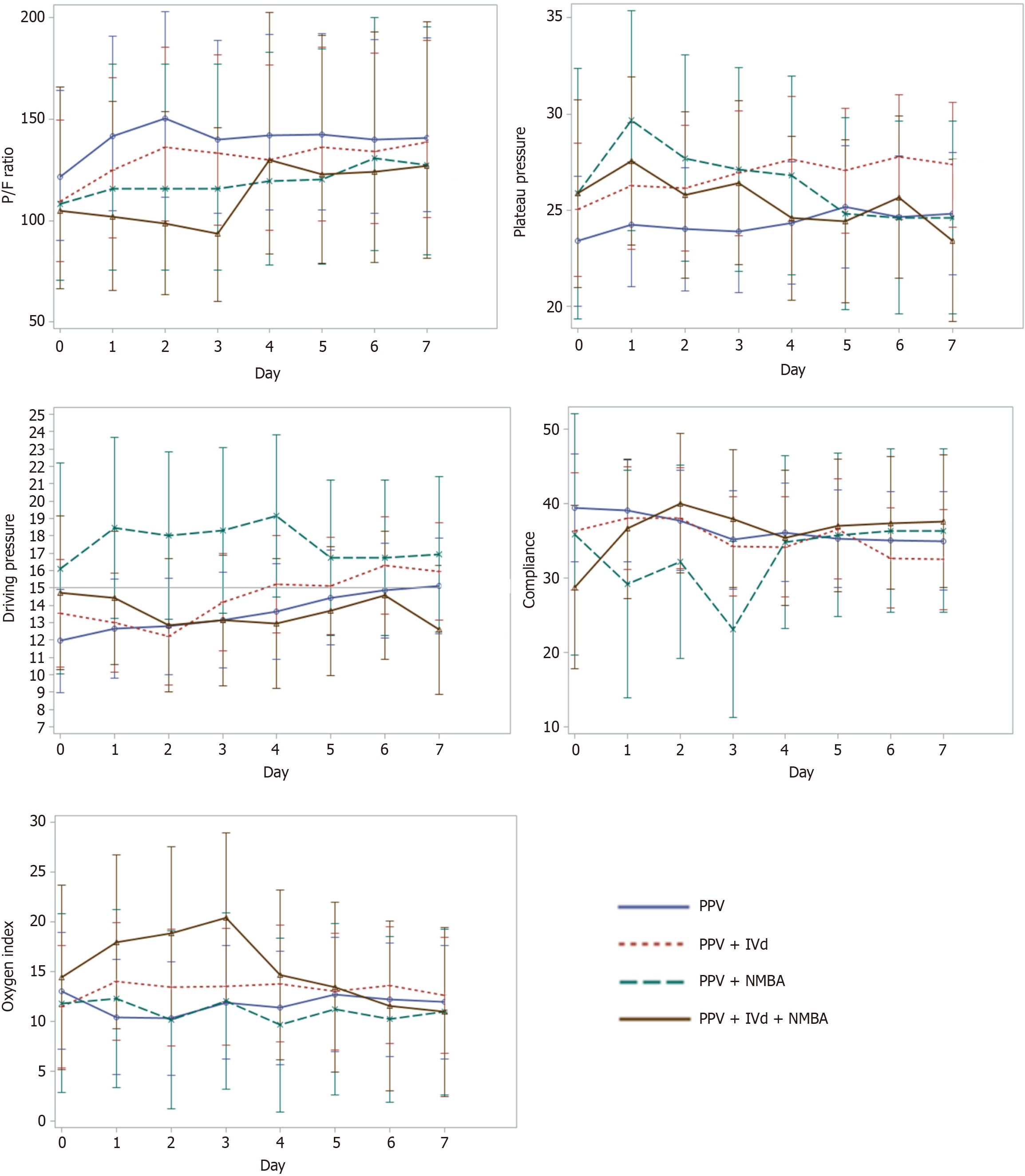
Figure 2 Trends in secondary outcomes including ventilator parameters 7 days following initiation of prone ventilation.
IVd: Inhaled vasodilators; NMBA: Neuromuscular blocking agents; P/F: Arterial oxygen partial pressure/fractional inspired oxygen; PPV: Prone position ventilation.
- Citation: Cabrera M, Bharil S, Chin M, Yohannes S, Clark P. Impact of proning with and without inhaled pulmonary vasodilators and neuromuscular blocking agents in COVID acute respiratory distress syndrome. World J Crit Care Med 2025; 14(3): 101327
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2220-3141/full/v14/i3/101327.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5492/wjccm.v14.i3.101327