Copyright
©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Crit Care Med. Jun 9, 2025; 14(2): 98004
Published online Jun 9, 2025. doi: 10.5492/wjccm.v14.i2.98004
Published online Jun 9, 2025. doi: 10.5492/wjccm.v14.i2.98004
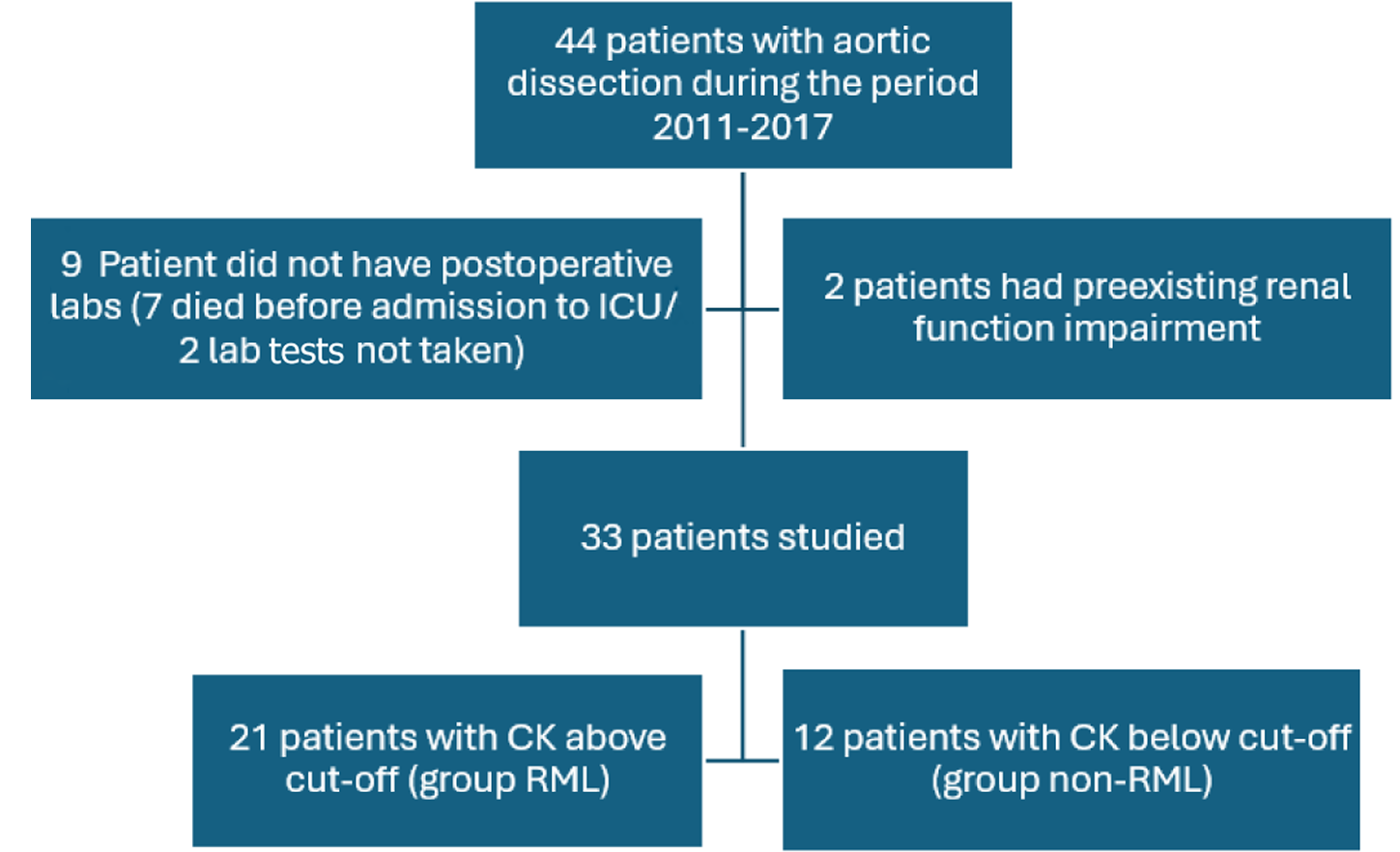
Figure 1 Study design.
CK: Creatinine kinase; ICU: Intensive care unit; RML: Rhabdomyolysis.
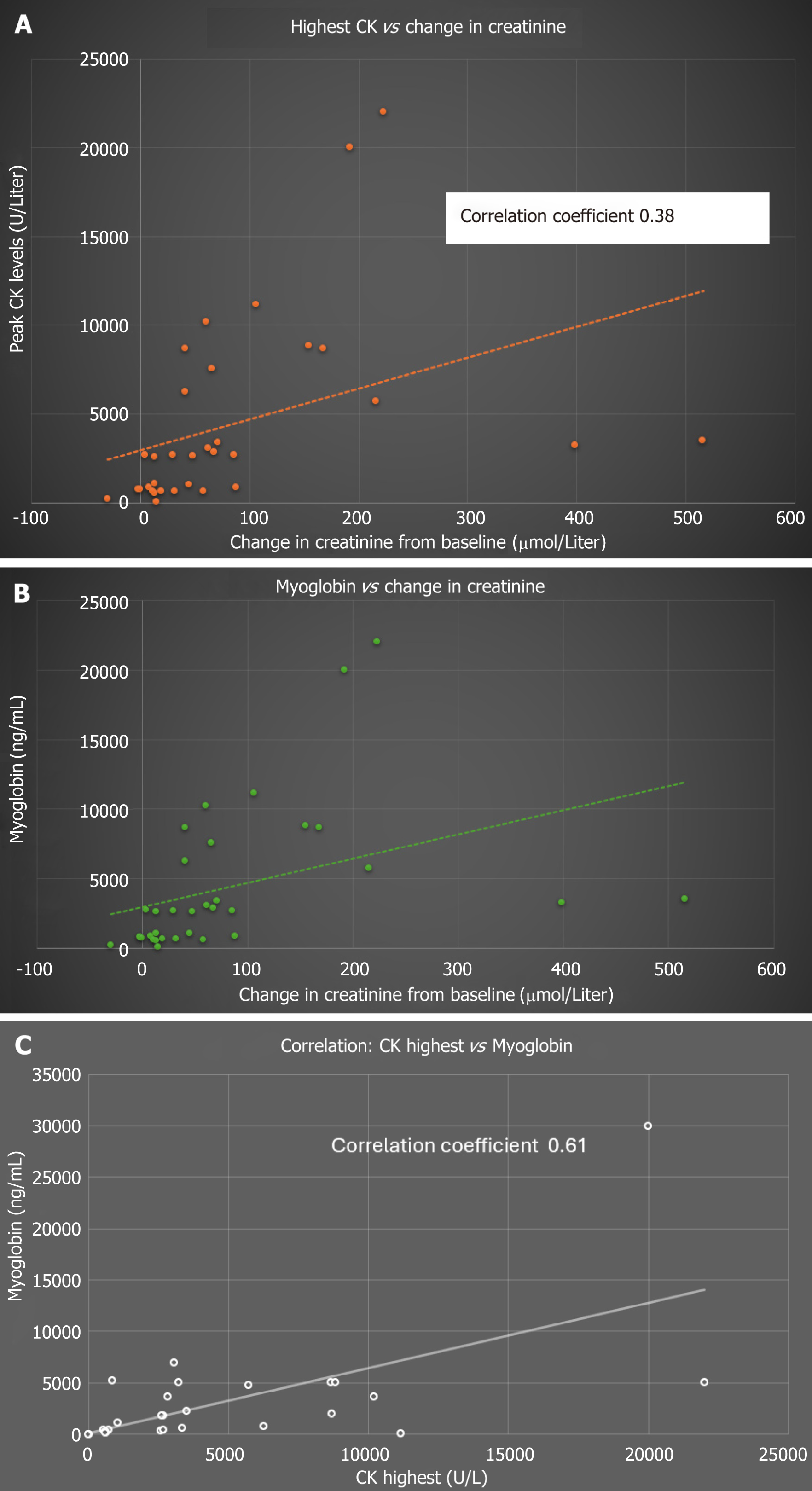
Figure 2 Correlation data-renal function and rhabdomyolysis markers.
A: Correlation between change in creatinine and creatinine kinase (CK) levels. Correlation between change in creatinine in mmol/liter (peak creatinine-baseline creatinine) on the X axis and peak CK levels U/L on the Y axis; B: Correlation between change in creatinine and myoglobin levels. Correlation between change in creatinine mmol/liter (peak creatinine-baseline creatinine) on the X axis and peak myoglobin levels ng/mL on the Y axis; C: Correlation between peak CK (U/L) and myoglobin levels (ng/mL). Correlation between peak CK values on the X axis and peak myoglobin levels on the Y axis.
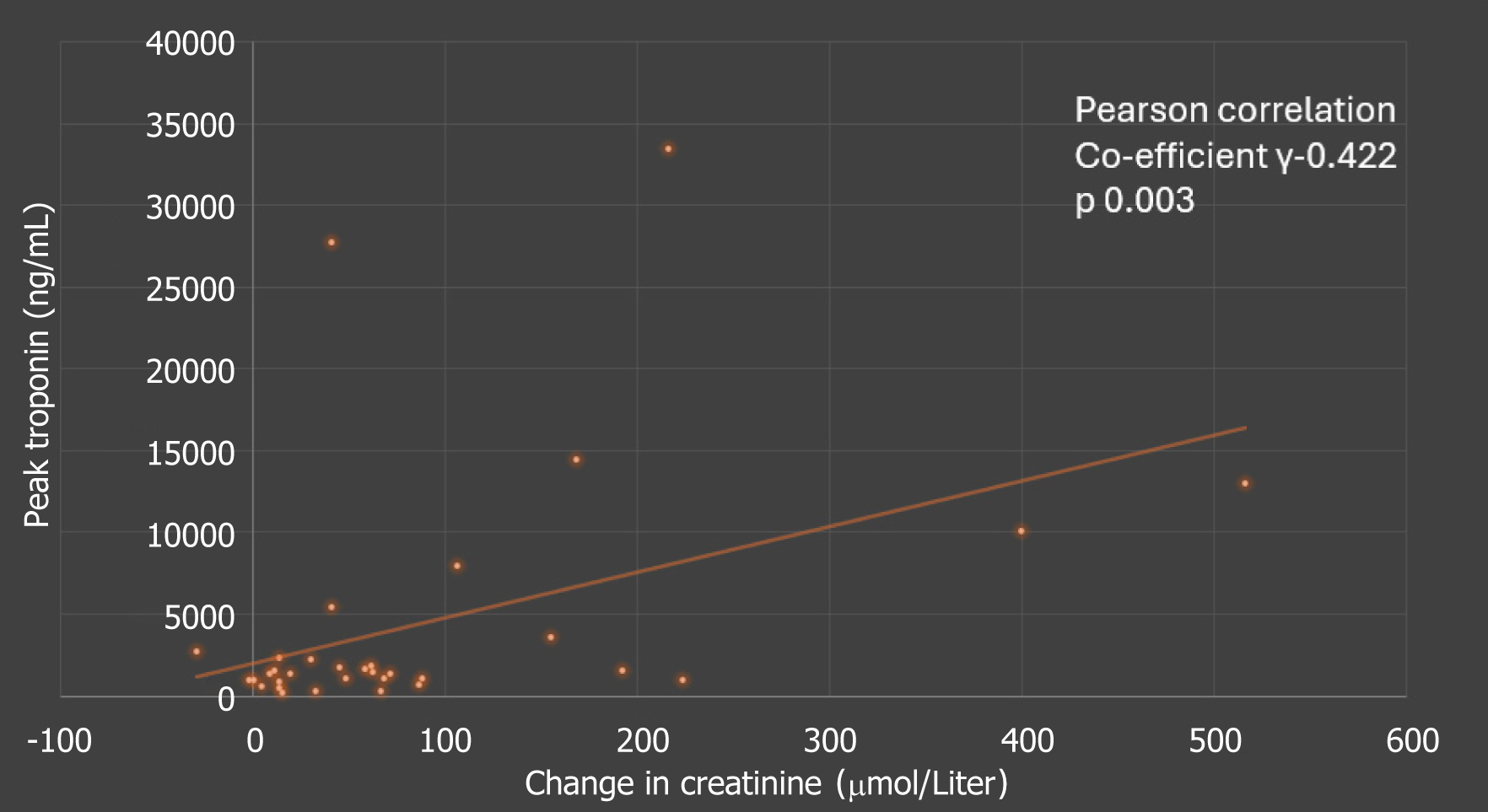
Figure 3 Peak troponin vs change in creatinine-correlation between change in creatinine (peak creatinine-baseline creatinine) on the X axis and peak troponin levels on the Y axis.
- Citation: Sivadasan PC, Carr CS, Pattath ARA, Hanoura S, Sudarsanan S, Ragab HO, Sarhan H, Karmakar A, Singh R, Omar AS. Incidence and outcome of rhabdomyolysis after type A aortic dissection surgery: A retrospective analysis. World J Crit Care Med 2025; 14(2): 98004
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2220-3141/full/v14/i2/98004.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5492/wjccm.v14.i2.98004