Copyright
©The Author(s) 2015.
World J Surg Proced. Jul 28, 2015; 5(2): 208-216
Published online Jul 28, 2015. doi: 10.5412/wjsp.v5.i2.208
Published online Jul 28, 2015. doi: 10.5412/wjsp.v5.i2.208
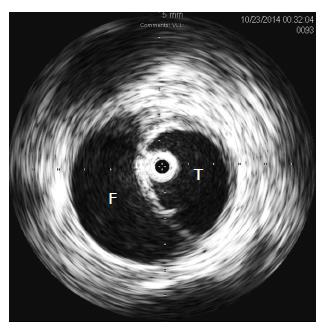
Figure 1 Intravascular ultrasound evaluation during thoracic stent grafting.
The IVUS probe (image center) is seen confirming correct orientation within the true lumen. T: True lumen; F: False lumen; IVUS: Intravascular ultrasound.
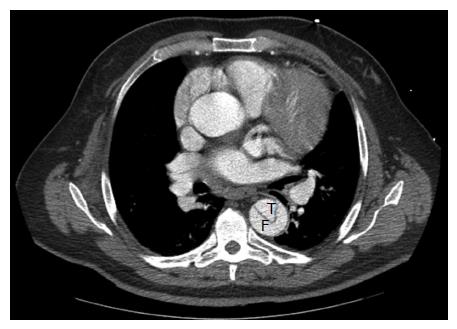
Figure 2 Computed tomography angiogram of a patient presenting with acute type B aortic dissection.
T: True lumen; F: False lumen.
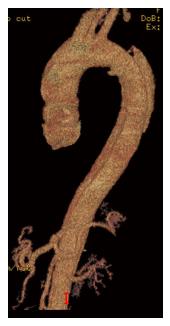
Figure 3 3D reconstruction from a computed tomography angiography of a patient presenting with acute type B aortic dissection, highlighting the entry tear originating distal to the origin of the left subclavian artery.
The dissection plan is seen to extend well into the abdominal aorta.
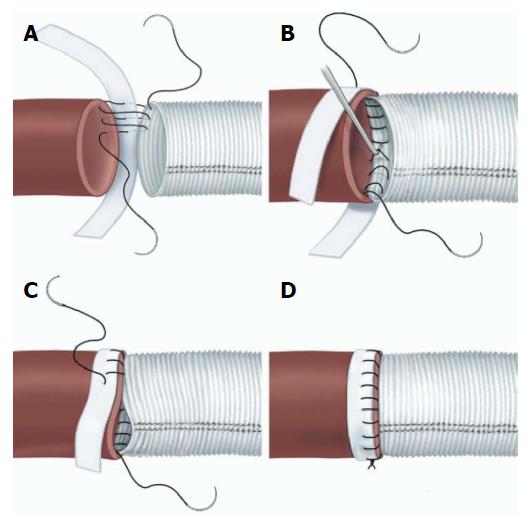
Figure 4 Suture line reinforcement with felt pledgets.
A: Performing the posterior wall of the anastomosis first, in a “parachute” fashion. The suture travels from the prosthetic graft, to native aorta, then finally through the pledget; B: The suture line is tightened with the use of a nerve hook, and care taken to place the pledge on the outer surface of the aorta; C: Once the posterior wall of the anastomosis is completed, the anterior wall of the anastomosis is completed. The graft is somewhat invaginated within the aorta; D: The completed anastomosis, whereby the native aorta is buttressed on either end with pledget and graft. Source: “Long-term integrity of teflon felt-supported suture lines in aortic surgery,” by Strauch et al[9]. Copyright 2005 by Elsevier, reprinted with permission.
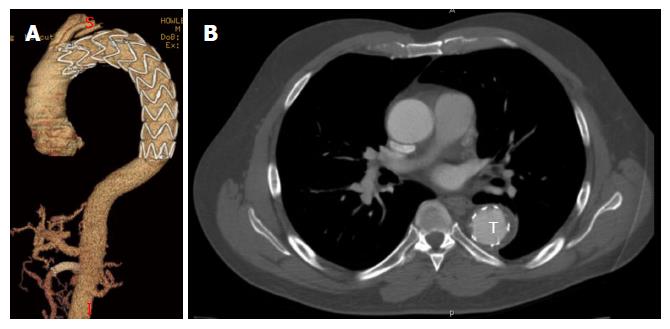
Figure 5 Remodeling after thoracic endovascular aortic repair.
A: Follow-up 3D reconstruction from a computed tomography angiography of a patient who underwent TEVAR with adjunct superior mesenteric artery stenting for acute type B aortic dissection with malperfusion. There no evidence of endoleak or aneurysmal degeneration; B: Axial sections from same patient highlighting T expansion with evidence of false lumen thrombosis. TEVAR: Thoracic endovascular aortic repair; T: True lumen.
- Citation: Iranmanesh S, Ricotta JJ. Current management of acute type B aortic dissection. World J Surg Proced 2015; 5(2): 208-216
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2219-2832/full/v5/i2/208.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5412/wjsp.v5.i2.208