Copyright
©2013 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Surg Proced. Nov 28, 2013; 3(3): 54-59
Published online Nov 28, 2013. doi: 10.5412/wjsp.v3.i3.54
Published online Nov 28, 2013. doi: 10.5412/wjsp.v3.i3.54
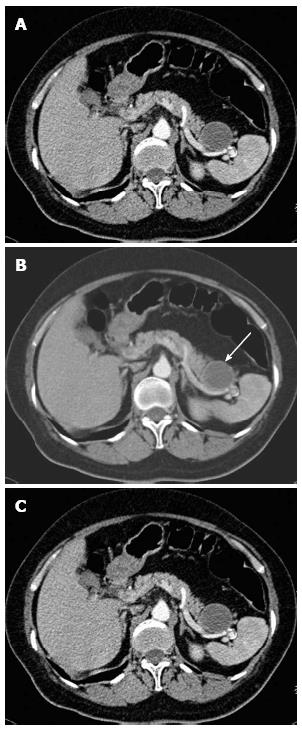
Figure 1 Computed tomography scan of the abdomen revealed a 4 cm round cystic lesion (arrow) anterior to the spleen near the tail of the pancreas with enhancement of the cystic wall.
A: Plain computed tomography (CT) scan; B, C: Enhanced CT scan.
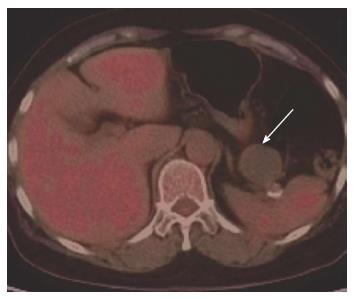
Figure 2 Fluorine-18 fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography image showed no increased uptake of fluorodeoxyglucose (arrow) detected in the cyst of pancreatic tail.
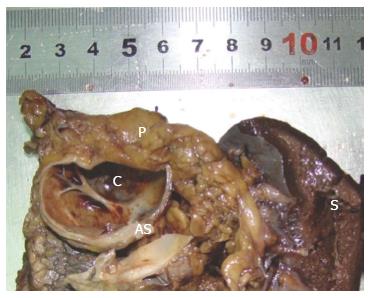
Figure 3 The cut section of surgical specimen contained a 4.
2 cm cyst in its greatest diameter located near the pancreatic tail. C: Cyst; AS: Accessory spleen; P: Pancreas; S: Spleen.
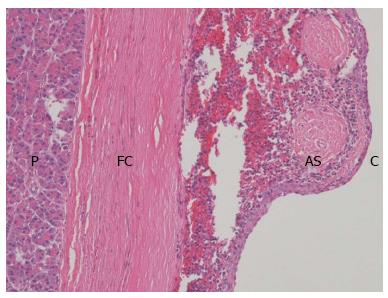
Figure 4 Microscopically, the cyst (C) was covered with stratified squamous epithelium and was surrounded by normal splenic tissue.
A fibrous capsule (FC) separates the intrapancreatic accessory spleen (AS) from pancreas (P) (HE, × 100).
- Citation: Lee CL, Di Y, Jiang YJ, Jin C, Fu DL. Epidermoid cyst of intrapancreatic accessory spleen: A case report and literature review. World J Surg Proced 2013; 3(3): 54-59
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2219-2832/full/v3/i3/54.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5412/wjsp.v3.i3.54