Copyright
©The Author(s) 2023.
World J Surg Proced. Dec 28, 2023; 13(3): 22-28
Published online Dec 28, 2023. doi: 10.5412/wjsp.v13.i3.22
Published online Dec 28, 2023. doi: 10.5412/wjsp.v13.i3.22
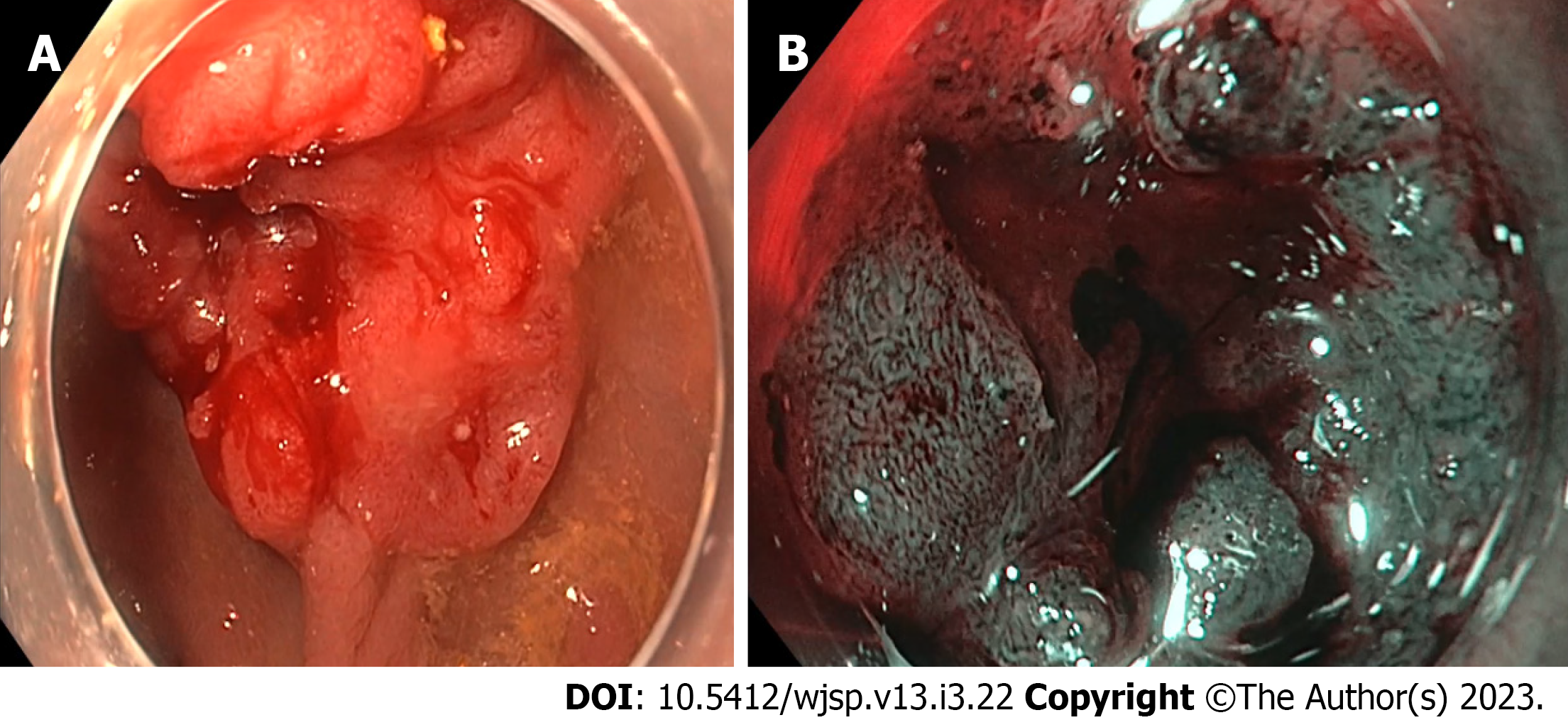
Figure 1 Endoscopic image of the lesion.
A: Lesion in white light. There is a central depression with Paris classification IIc/IIa; B: Vn type pit pattern corresponds to Narrow Band Imaging International Colorectal Endoscopic classification 3, Japan Narrow Band Imaging Expert Team classification 3 lesion.
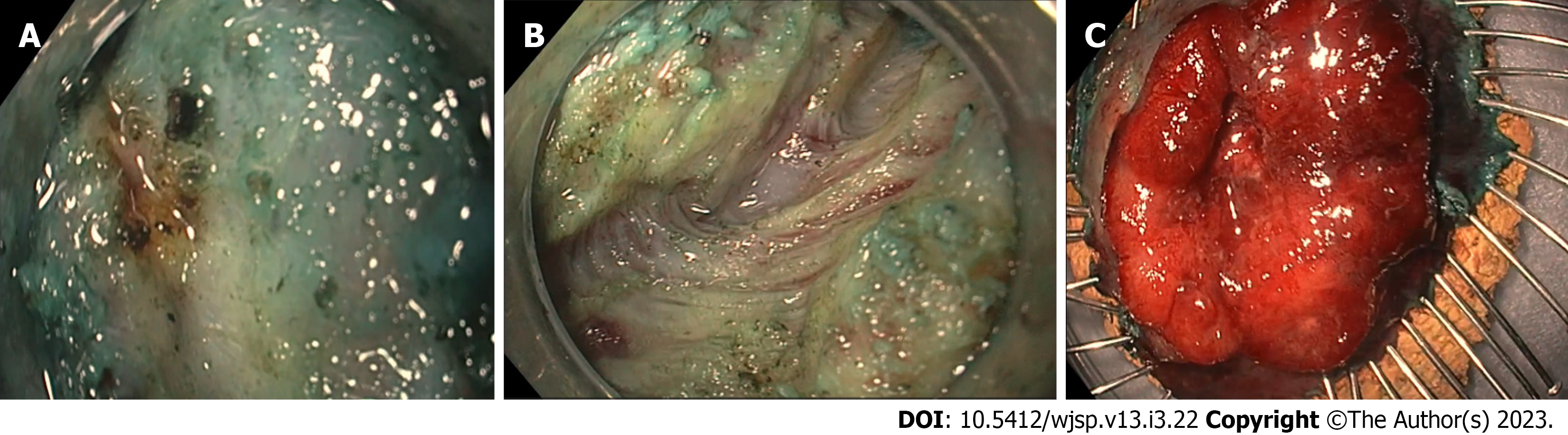
Figure 2 Lesion during dissection and after removal.
A: Significant fibrosis encountered during endoscopic intermuscular dissection; B: After dissecting the fibrotic area, the inner muscle layer was dissected, keeping the outer longitudinal layer intact; C: The tumour was released from the muscle layer and pinned on the cork board and submitted for histological analysis.
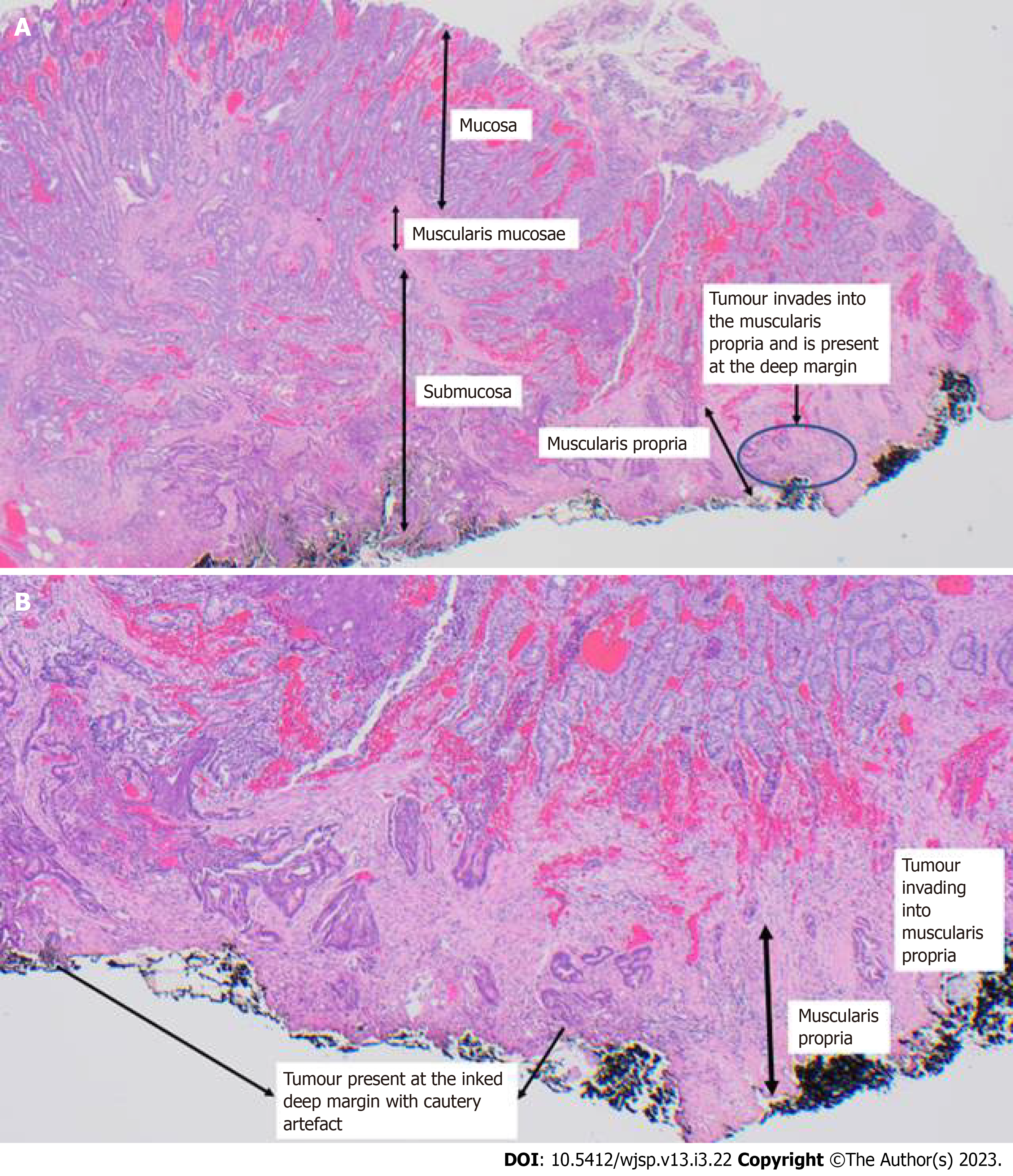
Figure 3 Pathological analysis of the lesion.
A: Endoscopic intermuscular dissection specimen, including muscularis propria. A low-grade adenocarcinoma invading into the muscularis propria as shown at the inked deep margin (at least pT2); B: Enlarged image of tumour invasion into muscularis propria.
- Citation: Sekra A, Tan T. Endoscopic intermuscular dissection for locally advanced rectal cancer: A case report. World J Surg Proced 2023; 13(3): 22-28
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2219-2832/full/v13/i3/22.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5412/wjsp.v13.i3.22