Copyright
©The Author(s) 2015.
World J Immunol. Nov 27, 2015; 5(3): 99-112
Published online Nov 27, 2015. doi: 10.5411/wji.v5.i3.99
Published online Nov 27, 2015. doi: 10.5411/wji.v5.i3.99
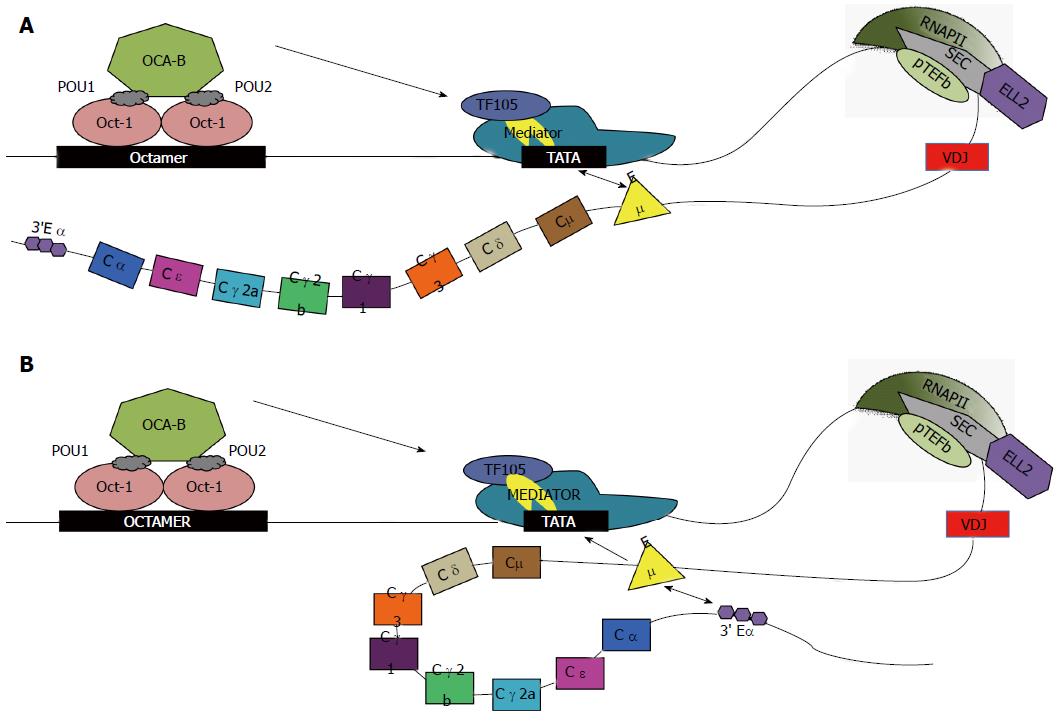
Figure 1 Transcription of Igh with alternative enhancer interactions.
Oct-1 and -2 bind to the octamer sequence; OCA-B binds to Oct-2 and with TF105 (purple oval), a TFIID variant that is part of the basal transcription complex including TBP (yellow). Mediator (large teal complex) is a large complex of proteins that facilitates binding of RNAP-II to INR. Factors in Mediator like cdk8/cyclin C phosphorylate RNAP-II at ser-5 in the CTD consensus 7-mer for initiation. Then P-TEFb (cyclinT and cdk9, green oval) phosphorylates the ser-2 position of the CTD repeats of RNAP-II. Many genes have stalled polymerases awaiting the SEC, which contains ELL2 (purple hexagon) and P-TEFb[60]. Phosphorylation of the CTD by ser-5 and ser-2 is high near the Igh promoter[61]. The other members of the SEC are shown in gray. Differential transcription elongation occurs due to the potential interaction of the Igh enhancers. Cμ enhancer (annotated Eμ) interacts with promoter of Igh. A: In the first case, classical transcription of Igh can occur due to interaction between the promoter and enhancer, depicted by double arrow, without large-scale chromosomal looping; B: In the second case, along with promoter-enhancer interactions, Cμ enhancer has been hypothesized to interact with the 3’ Cα enhancer (3’ Eα), causing chromosomal looping. CTD: Carboxyl-terminal domain; SEC: Super elongation complex; TBP: TATA-binding protein; P-TEFb: Positive elongation factor b.
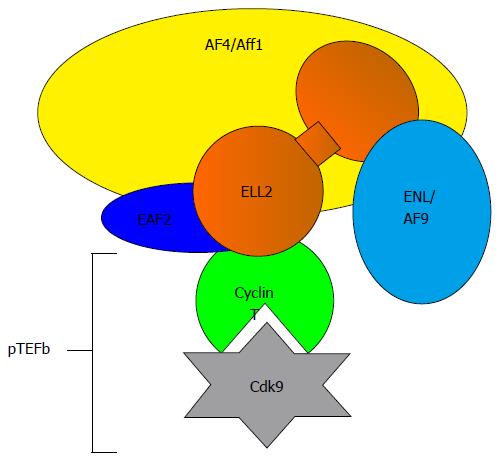
Figure 2 Components of the super elongation complex.
ELL2 is part of the super elongation complex important for releasing RNA polymerase II from pausing. Cdk9 phosphorylates the ser-2 of the heptad repeats in the carboxyl-terminal domain of RNAP-II, negative elongation factor negative elongation factor, and DRB sensitive factor the DRB-sensitive factor, which becomes activated. ELL2: Eleven lysine rich leukemia protein 2; Cdk9: Cyclin dependent kinase 9.
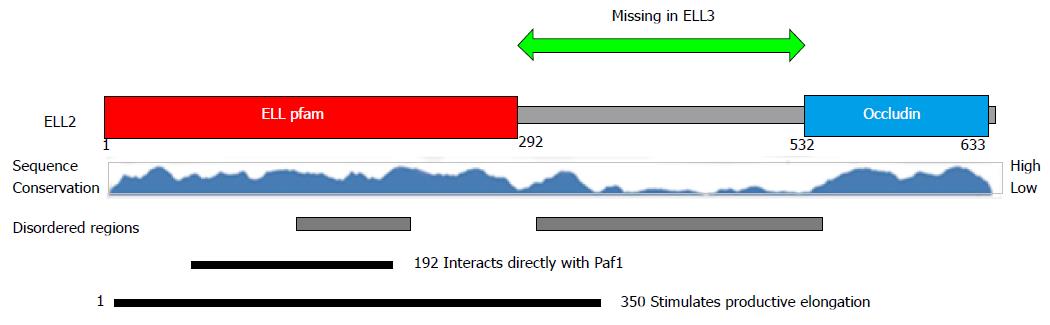
Figure 3 Protein structure of ELL2 vs ELL3.
ELL2 contains three domains the common ELL protein family domain the disordered region and the occludin homology domain. The central disordered region is missing in ELL3 and the amino acid sequences vary in other regions as well. ELL: Eleven-nineteen lysine rich leukemia protein; pfam: Protein family; Paf1: Polymerase associated factor 1.
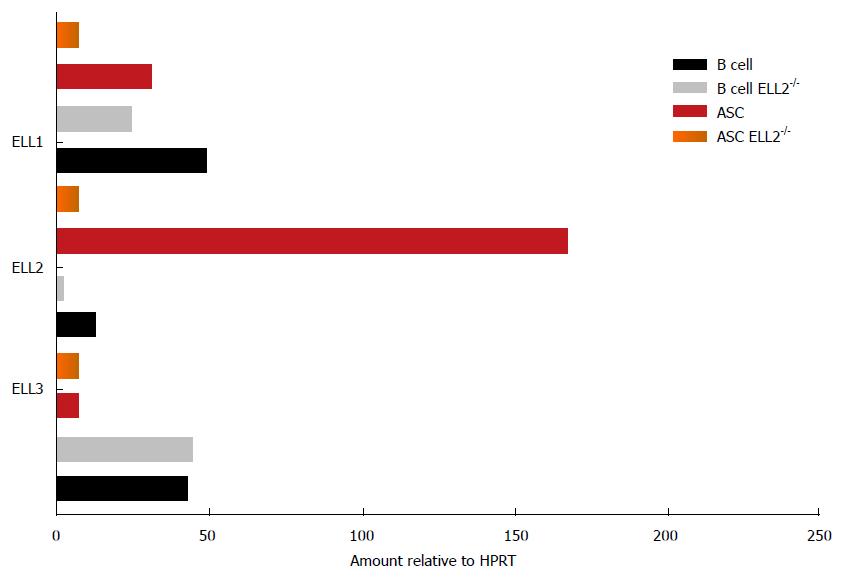
Figure 4 Expression of ELL1, 2 and 3 varies between B cells and antibody secreting cells.
The expression of the mRNA for the three factors was measured by RT-QPCR relative to HPRT in both wild type mice and mice lacking ELL2 in their B cell compartment. HPRT: Hypoxanthine phosphoribosyltransferase; ASC: Antibody secreting cell; RT-QPCR: Reverse transcriptase quantitative polymerase chain reaction; ELL: Eleven-nineteen lysine rich leukemia protein.
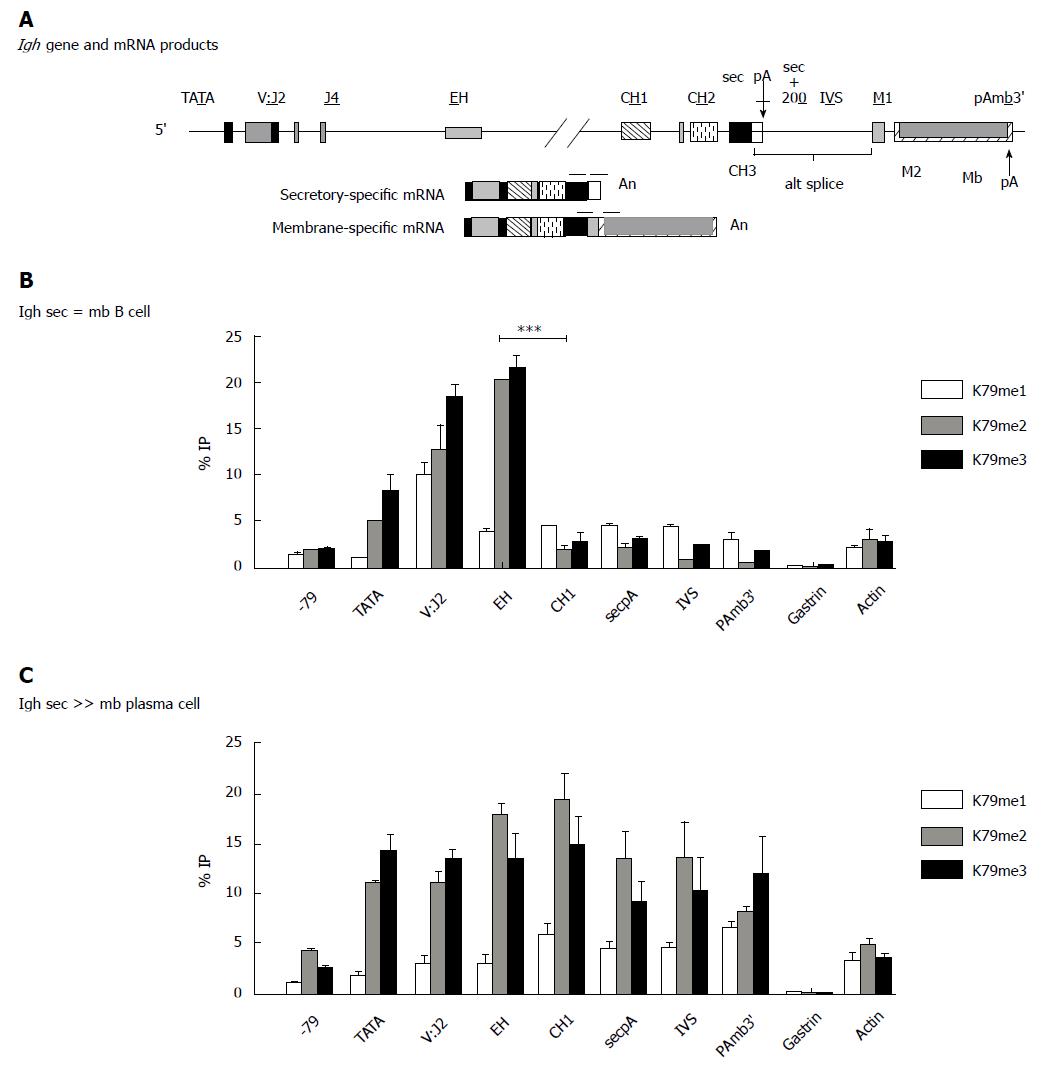
Figure 5 Igh gene has a different pattern of H3K7methylation in B cells vs antibody secreting cells.
Distribution of histone H3K7me is enhanced in the region downstream of the internal Igh enhancer in plasma cells (ASCs). The 11 kb Igh gamma 2a gene is identical in the B and PC (hybridoma) lines and located in the intact Igh locus. A: Location of probes used in QPCRs. Cells were fixed and chromatin IP performed with the indicated antibodies specific to the individual K79 methylations; B: The B cell line A20; C: The plasma/hybridoma line AxJ which is an ASC. ASCs: Antibody secreting cells; QPCR: Quantitiative polymerase chain reaction; IP: Immunoprecipitation.
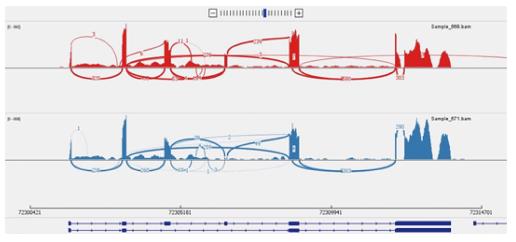
Figure 6 Sashimi plot depicting exon skipping.
Xaf1 Sashimi plot obtained from RNA-Seq of ELL2 WT (red track) and cKO (blue track) antibody secreting cell samples. This plot demonstrates the exon skipping of exon 4 occurring in the cKO. The arcs indicate splice junction reads, with the thickness of the arc correlating with the number of junction reads spanning the two exons being connected by the arc. cKO: Conditional knockout; RNA-seq: RNA sequencing; WT: Wild type.
- Citation: Smith SM, Carew NT, Milcarek C. RNA polymerases in plasma cells trav-ELL2 the beat of a different drum. World J Immunol 2015; 5(3): 99-112
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2219-2824/full/v5/i3/99.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5411/wji.v5.i3.99