Copyright
©The Author(s) 2015.
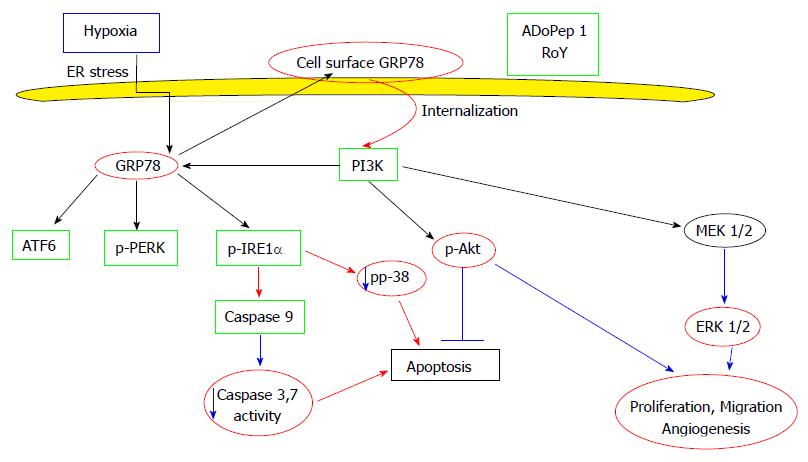
Figure 1 Cell surface GRP78 survival and apoptotic pathways in the normal cells.
Hypoxia induced apoptosis is inhibited by RoY/ADoPep1 peptide binding to cell surface GRP78. Peptide binding activates the PI3K pathway by Akt phosphorylation and the NEK pathway by ERK1/2 phosphorylation, inducing endothelial cell proliferation, migration and angiogenesis. On the other hand, peptide binding to cell surface GRP78 protects cardiomyocytes and neurons from hypoxia induced apoptosis by activation of the UPR arms. This anti-apoptotic mechanism is characterized by the inhibition of p38 phosphorylation, reduced cytochrome c release followed by a decrease in caspase 3/7 activity. ER: Endoplasmic reticulum.
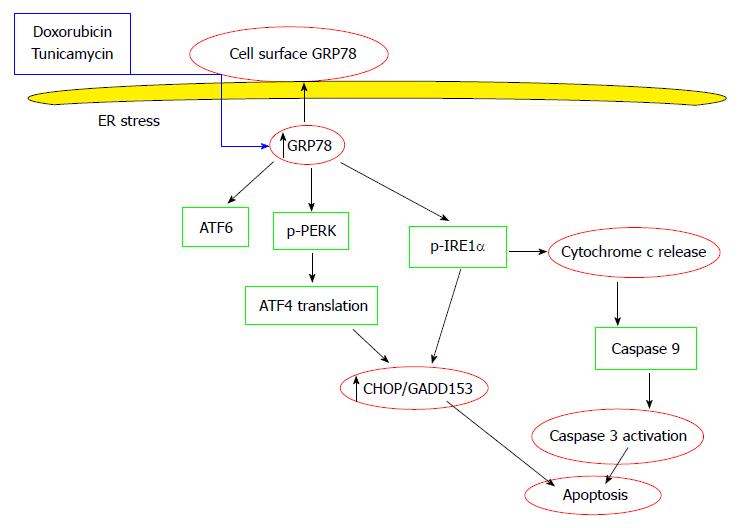
Figure 2 Cell surface GRP78 survival and apoptotic pathways in the tumor cell.
Pharmacological induction of cell surface GRP78 induces apoptosis by increase expression of CHOP/GADD153, a transcriptional target of both PERK and IRE (two of the 3 UPR sensors). In parallel, doxorubicin and tunicamycin induced cytochrome c release followed by the activation of caspase 3. ER: Endoplasmic reticulum.
- Citation: Hardy B, Raiter A. GRP78 expression beyond cellular stress: A biomarker for tumor manipulation. World J Immunol 2015; 5(2): 78-85
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2219-2824/full/v5/i2/78.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5411/wji.v5.i2.78