Copyright
©The Author(s) 2022.
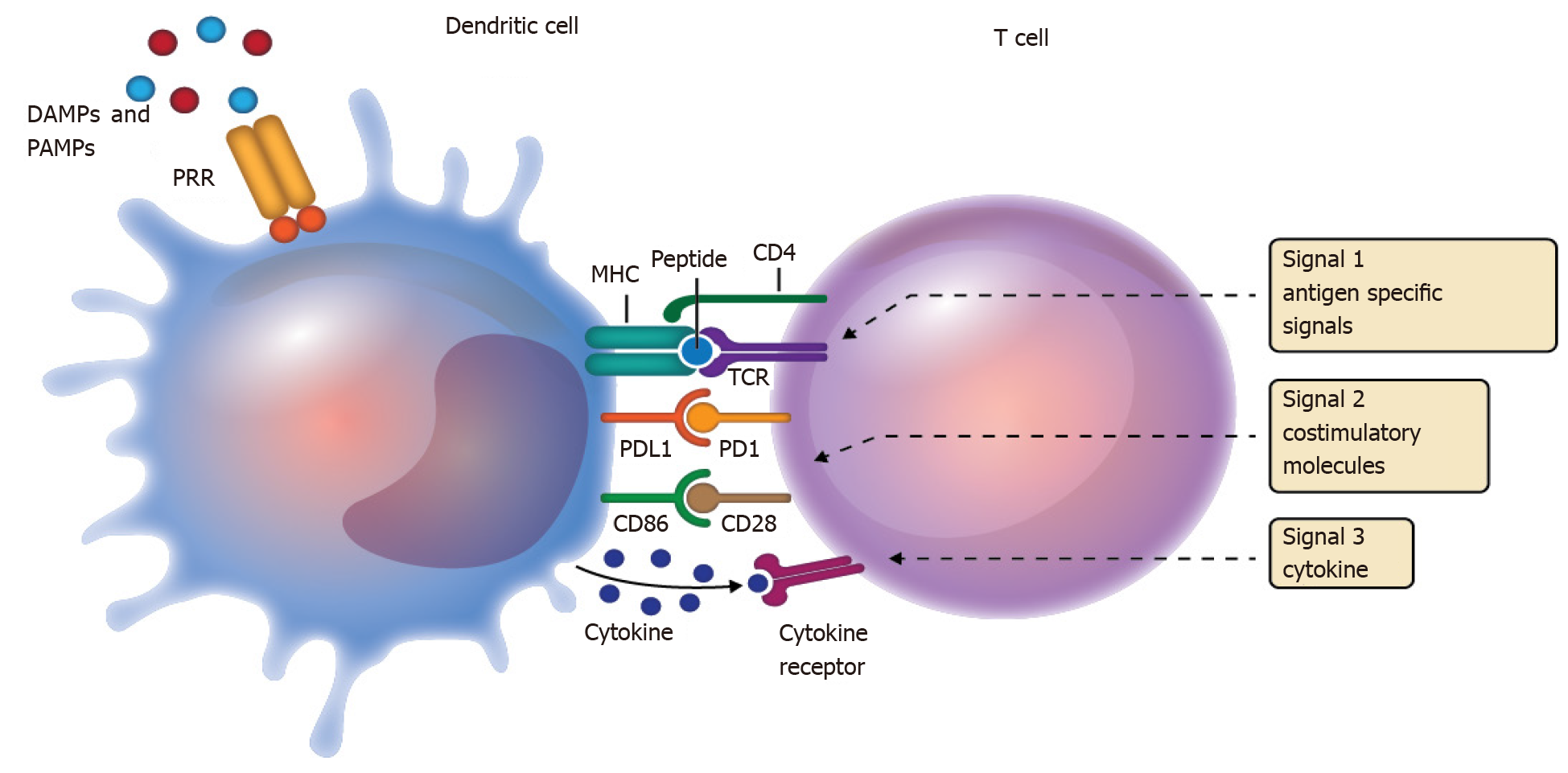
Figure 1 Overview of antigen presentation and the three-signal model.
The three-signal model proposes: (1) Antigen presentation to the T cell receptor by the major histocompatibility complex; (2) Interaction of co-stimulatory molecules with their receptors; and (3) Cytokine production and recognition by the cytokine receptors of T cells. DAMPs: Damage-associated molecular patterns; PAMPS; Pathogen-associated molecular patterns; PD1: Programmed death-1; PDL1: Programmed death ligand 1; PRR: Pattern recognition receptor.
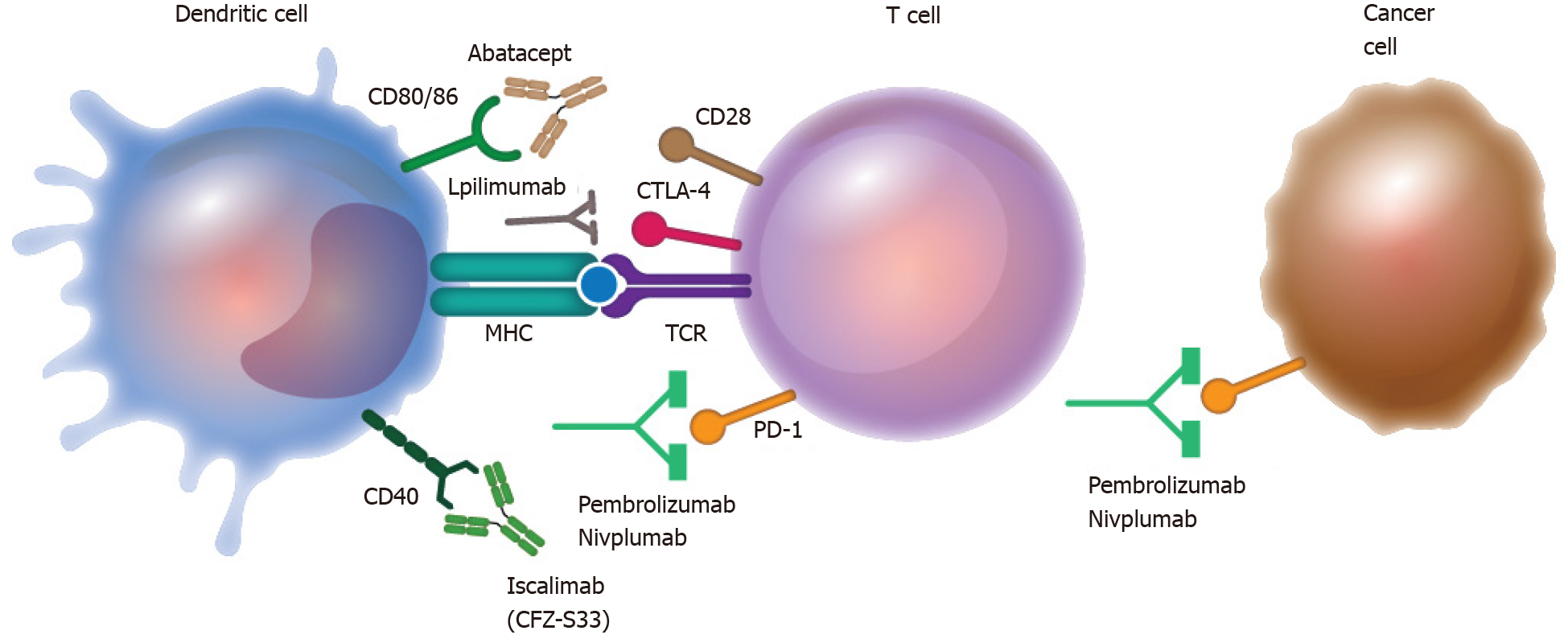
Figure 2 Therapeutical manipulation of co-stimulatory molecules.
Biological drugs have been developed to target co-stimulatory molecules and promote or inhibit their functions in distinct diseases. For example, the fusion protein abatacept blocks CD80/CD86 to prevent interaction with CD28; mAb iscalimab blocks CD40, ipilimumab blocks cytotoxic T lymphocyte antigen-4, and pembrolizumab blocks programmed death-1 (PD-1). These strategies have been implemented to modulate co-stimulatory molecule functions in immune and cancer cells. MHC: Major histocompatibility complex; TCR: T cell receptor.
- Citation: Velazquez-Soto H, Real F, Jiménez-Martínez MC. Historical evolution, overview, and therapeutic manipulation of co-stimulatory molecules. World J Immunol 2022; 12(1): 1-8
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2219-2824/full/v12/i1/1.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5411/wji.v12.i1.1