Copyright
©The Author(s) 2016.
World J Clin Pediatr. Nov 8, 2016; 5(4): 365-369
Published online Nov 8, 2016. doi: 10.5409/wjcp.v5.i4.365
Published online Nov 8, 2016. doi: 10.5409/wjcp.v5.i4.365
Figure 1 The number of patients that reached peak direct bilirubin ≥ 2.
0 (black bar) or direct bilirubin < 2.0 (grey bar). They are shown for both the low transfusion (total PRBC volume < 75 mL) and the high transfusion (total blood volume ≥ 75 mL) groups (high transfusion vs low transfusion P < 0.01). db: Direct bilirubin.
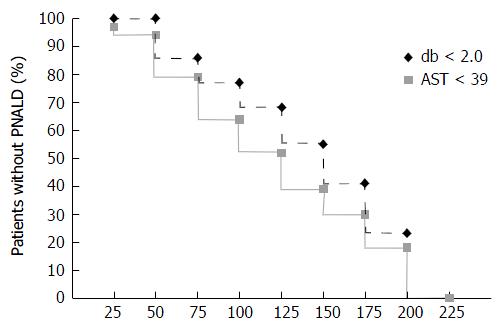
Figure 2 Kaplan-Meier plots tracking the onset of parenteral nutrition associated liver disease by the direct bilirubin and aspartate transaminase criteria as a function of total packed red blood cell transfused.
PNALD: Parenteral nutrition-associated liver disease; db: Direct bilirubin; AST: Aspartate transaminase.
- Citation: D’Souza A, Algotar A, Pan L, Schwarz SM, Treem WR, Valencia G, Rabinowitz SS. Packed red blood cell transfusions as a risk factor for parenteral nutrition associated liver disease in premature infants. World J Clin Pediatr 2016; 5(4): 365-369
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2219-2808/full/v5/i4/365.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5409/wjcp.v5.i4.365