Copyright
©The Author(s) 2024.
World J Clin Pediatr. Dec 9, 2024; 13(4): 98462
Published online Dec 9, 2024. doi: 10.5409/wjcp.v13.i4.98462
Published online Dec 9, 2024. doi: 10.5409/wjcp.v13.i4.98462
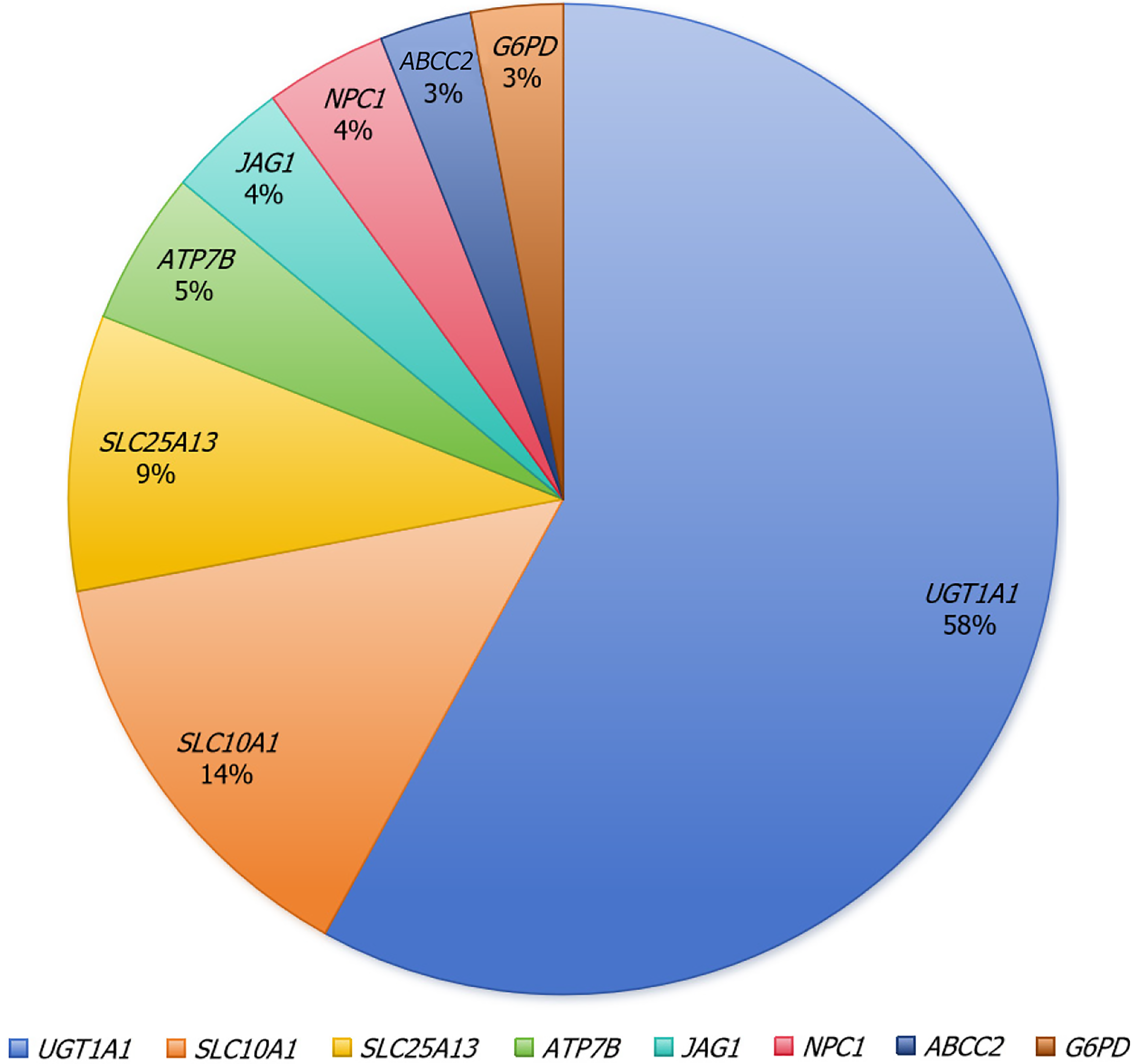
Figure 1 Results for the percentage of mutated genes in 105 patients.
UGT1A1: Uridine 5'-diphospho-glucuronosyltransferase 1A1; SLC10A1: Na+/taurocholate cotransporting polypeptide Ntcp; SLC25A13: Heterozygous 851del4 mutation; ATP7B: Adenosine triphosphatase 7B; JAG1: Jagged 1; NPC1: Niemann-Pick type C 1; ABCC2: Adenosine triphosphatase-binding cassette subfamily C member 2; G6PD: Glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase.
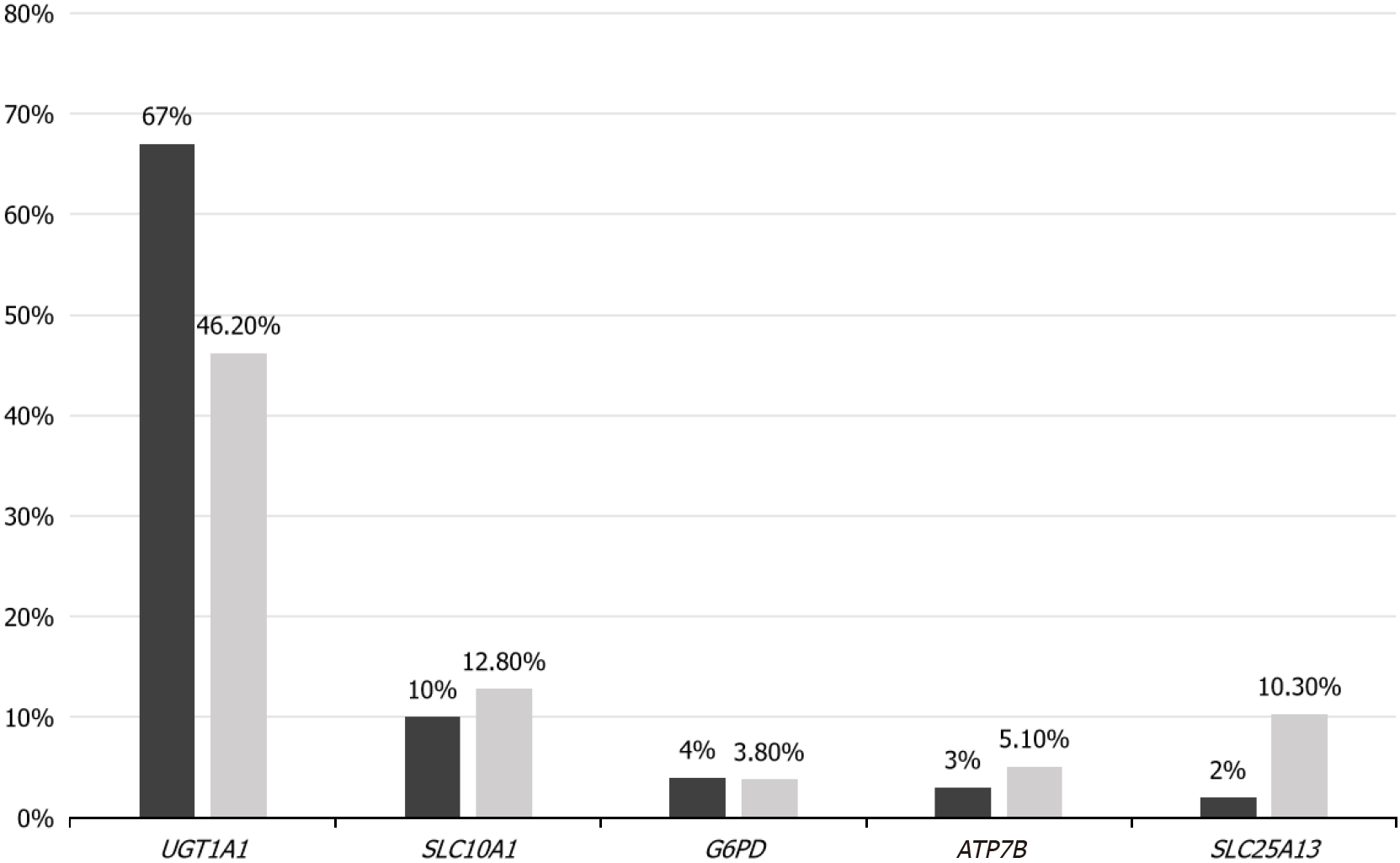
Figure 2 Analysis of the percentage of genes between the high and low total serum bilirubin groups.
The blue bars represent the high-risk group with a total bilirubin level greater than 342 μmol/L. The orange bars correspond to the high-risk group with a total bilirubin level of less than 342 μmol/L. UGT1A1: Uridine 5'-diphospho-glucuronosyltransferase 1A1; SLC10A1: Na+/taurocholate cotransporting polypeptide Ntcp; SLC25A13: Heterozygous 851del4 mutation; ATP7B: Adenosine triphosphatase 7B; G6PD: Glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase.
- Citation: You JY, Xiong LY, Wu MF, Fan JS, Fu QH, Qiu MH. Genetic variation features of neonatal hyperbilirubinemia caused by inherited diseases. World J Clin Pediatr 2024; 13(4): 98462
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2219-2808/full/v13/i4/98462.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5409/wjcp.v13.i4.98462