Copyright
©The Author(s) 2024.
World J Clin Pediatr. Dec 9, 2024; 13(4): 100493
Published online Dec 9, 2024. doi: 10.5409/wjcp.v13.i4.100493
Published online Dec 9, 2024. doi: 10.5409/wjcp.v13.i4.100493
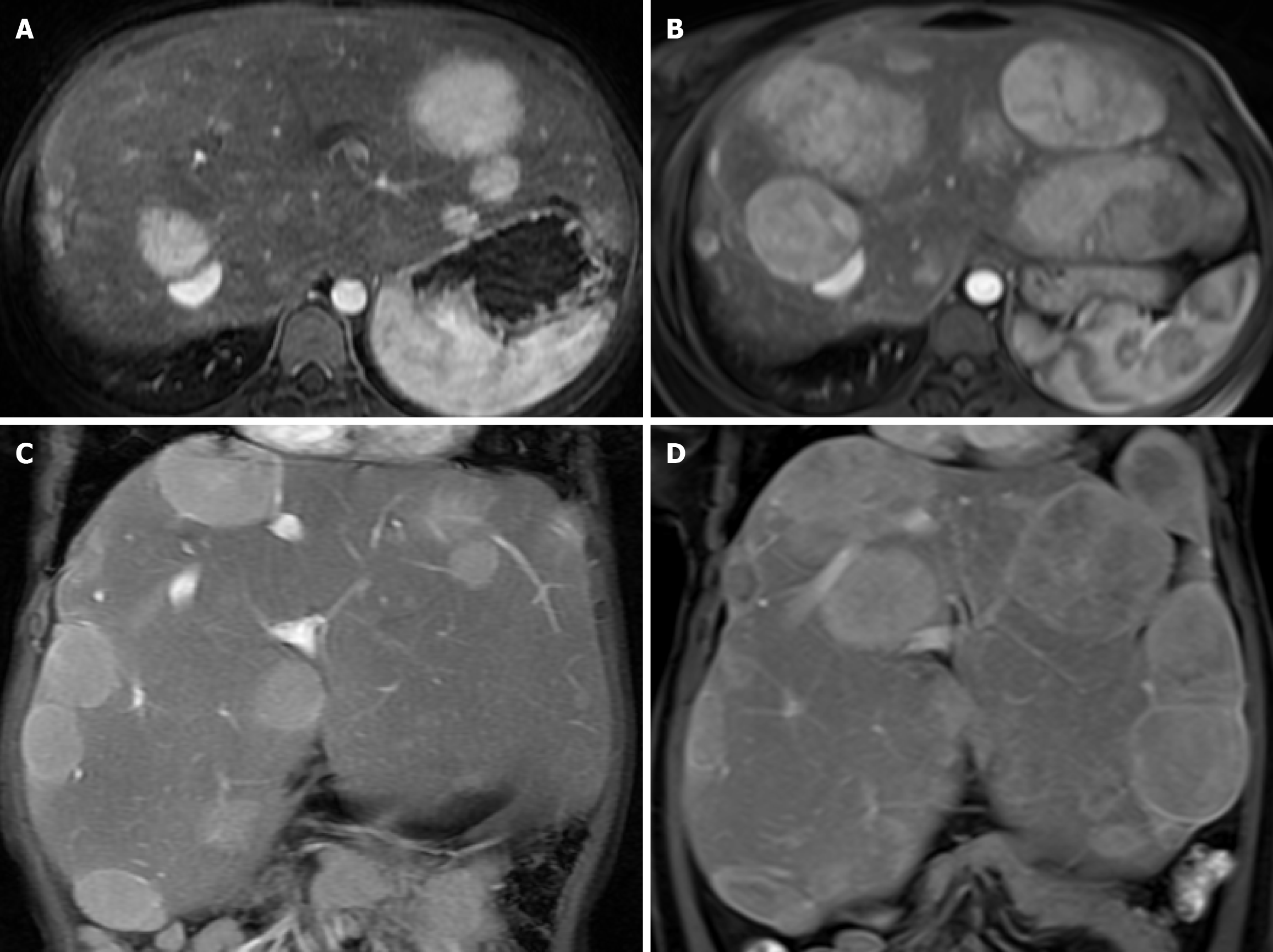
Figure 1 Axial post contrast arterial phase and coronal post contrast 3-minute delayed phase of a 15-year-old girl revealed multiple arterial and delayed enhancing nodules and masses scattering in both hepatic lobes with subsequent pathological proven hepatic adenomatosis.
Thirteen years later; overall increasing sizes and numbers of multiple known hepatic adenomatosis scattering in both hepatic lobes, showing heterogeneous arterial enhancement and heterogeneous delayed enhancement. Noted some nodules in the right hepatic lobe decreased in sizes. A: Initial axial post contrast arterial phase; B: Thirteen-year-follow-up axial arterial enhancement; C: Initial coronal post contrast delayed phase; D: Thirteen-year-follow-up coronal delayed phase.
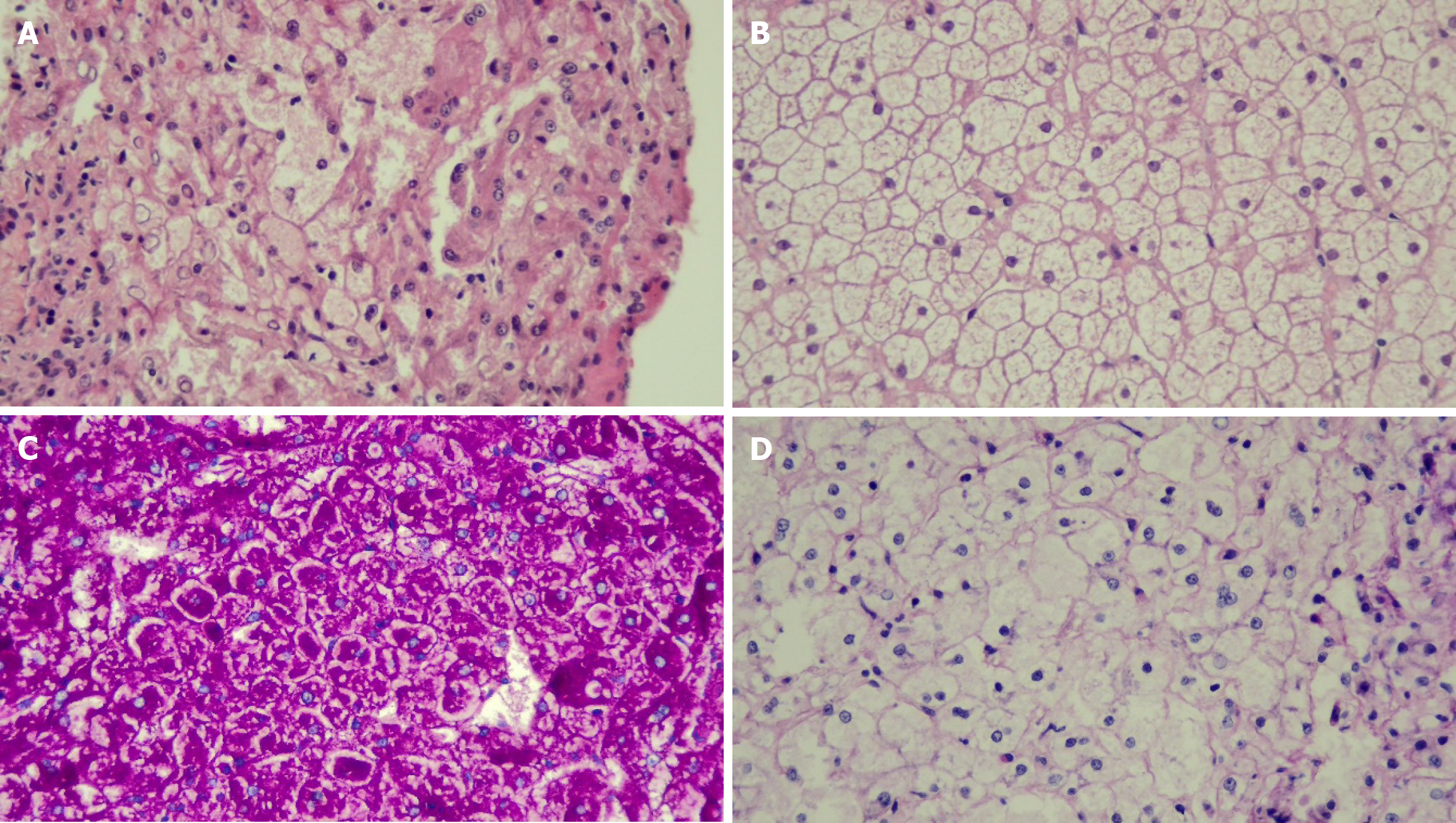
Figure 2 Light microscopy of liver histopathology with high-power magnification (× 40).
A: Patient 6 [glycogen storage disease (GSD) type III] hematoxylin and eosin stain (HE) shows swelling of hepatocytes; B: Patient 7 (GSD type VI) HE stain shows swelling of hepatolcytes with some material deposit inside; C: Patient 7 with periodic acid-Schiff (PAS) staining; D: Patient 7 with PAS-diastase (PAS-D) staining. Hepatocytes were stained with PAS and were mostly digested by PAS-D.
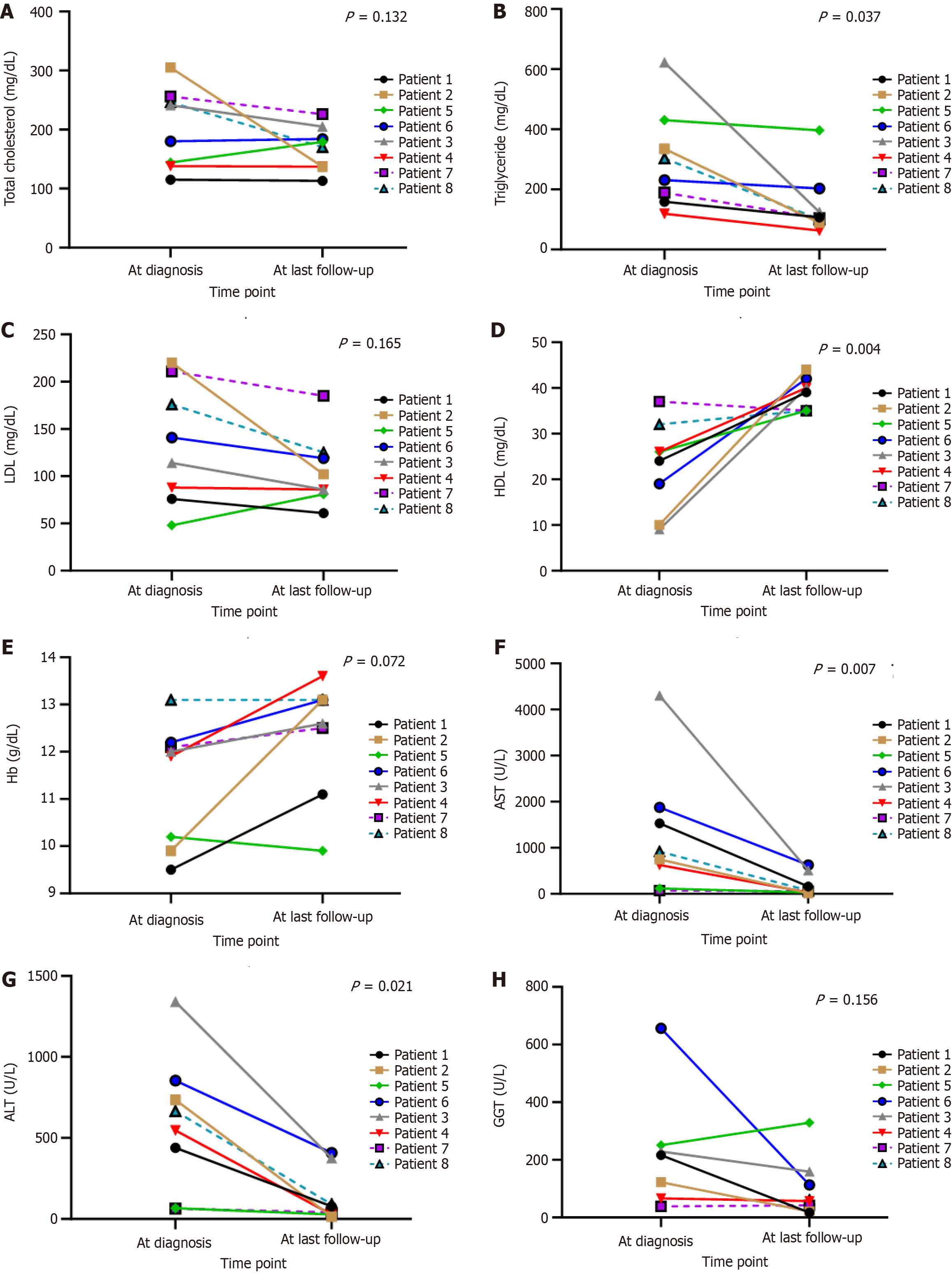
Figure 3 Biological profiles at diagnosis and the last follow-up.
A: Total cholesterol; B: Triglyceride; C: Low density lipoprotein; D: High density lipoprotein; E: Hemoglobin; F: Aspartate aminotransferase; G: Alanine aminotransferase; H: Gamma-glutamyl transferase. Hb: Hemoglobin; LDL: Low density lipoprotein; HDL: High density lipoprotein; ALT: Alanine aminotransferase; AST: Aspartate aminotransferase; GGT: Gamma-glutamyl transferase.
- Citation: Vanduangden J, Ittiwut R, Ittiwut C, Phewplung T, Sanpavat A, Sintusek P, Suphapeetiporn K. Molecular profiles and long-term outcomes of Thai children with hepatic glycogen storage disease in Thailand. World J Clin Pediatr 2024; 13(4): 100493
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2219-2808/full/v13/i4/100493.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5409/wjcp.v13.i4.100493