Copyright
©The Author(s) 2022.
World J Clin Pediatr. Nov 9, 2022; 11(6): 463-484
Published online Nov 9, 2022. doi: 10.5409/wjcp.v11.i6.463
Published online Nov 9, 2022. doi: 10.5409/wjcp.v11.i6.463
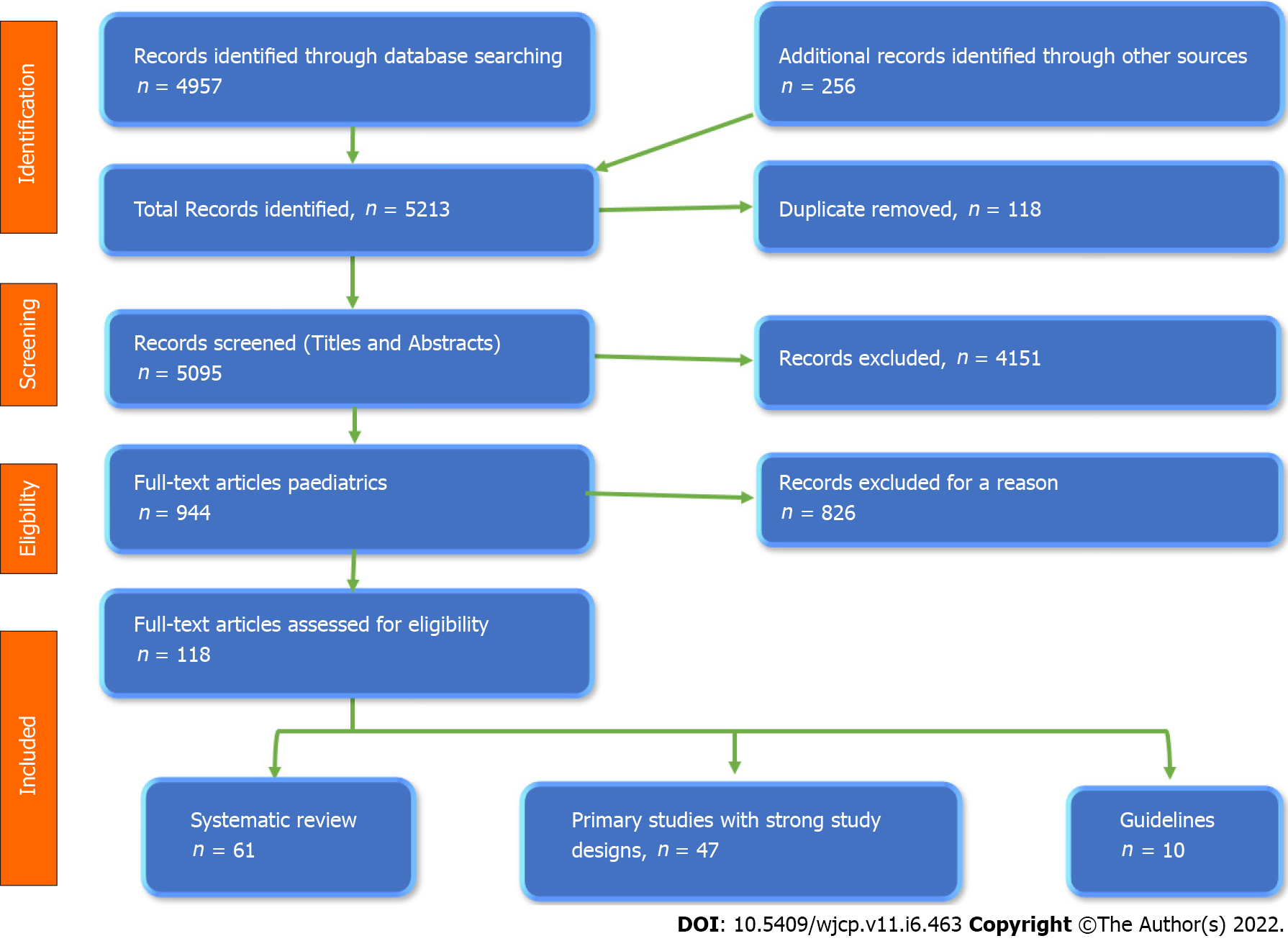
Figure 1
The flow chart of the study according to PRISMA 2009 guidelines.
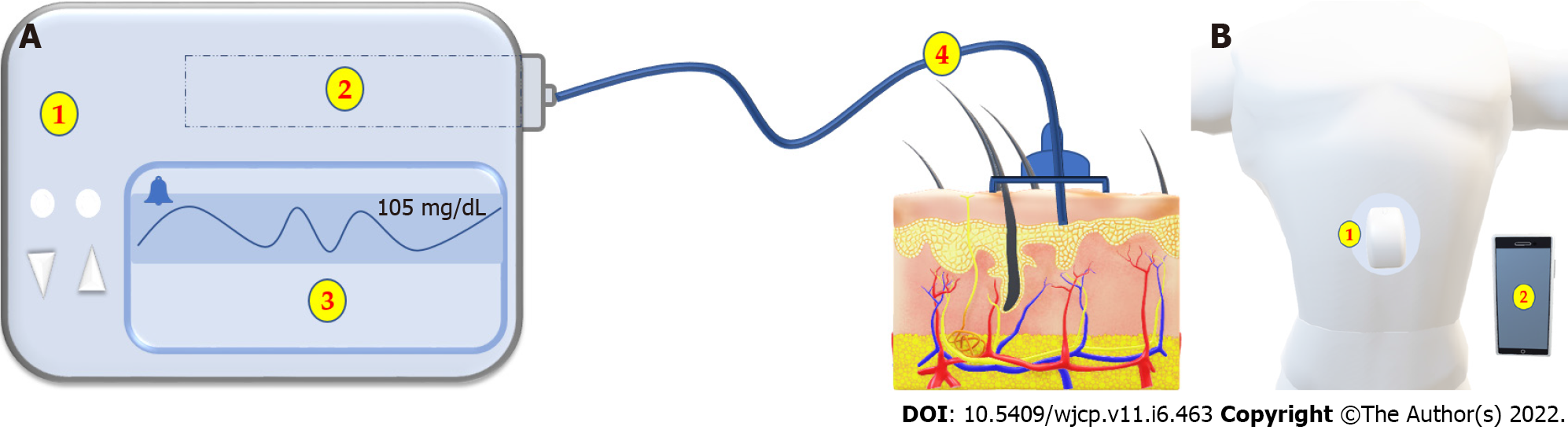
Figure 2 shows the two main types of Insulin Pumps.
A: Tethered pump formed of 1: Main pump. 2: Insulin Reservoir. 3: Monitor. 4: Infusion set; B: The patch pump formed of 1: A pump adherent to the skin with no or very short tube and 2: A wireless control unit.
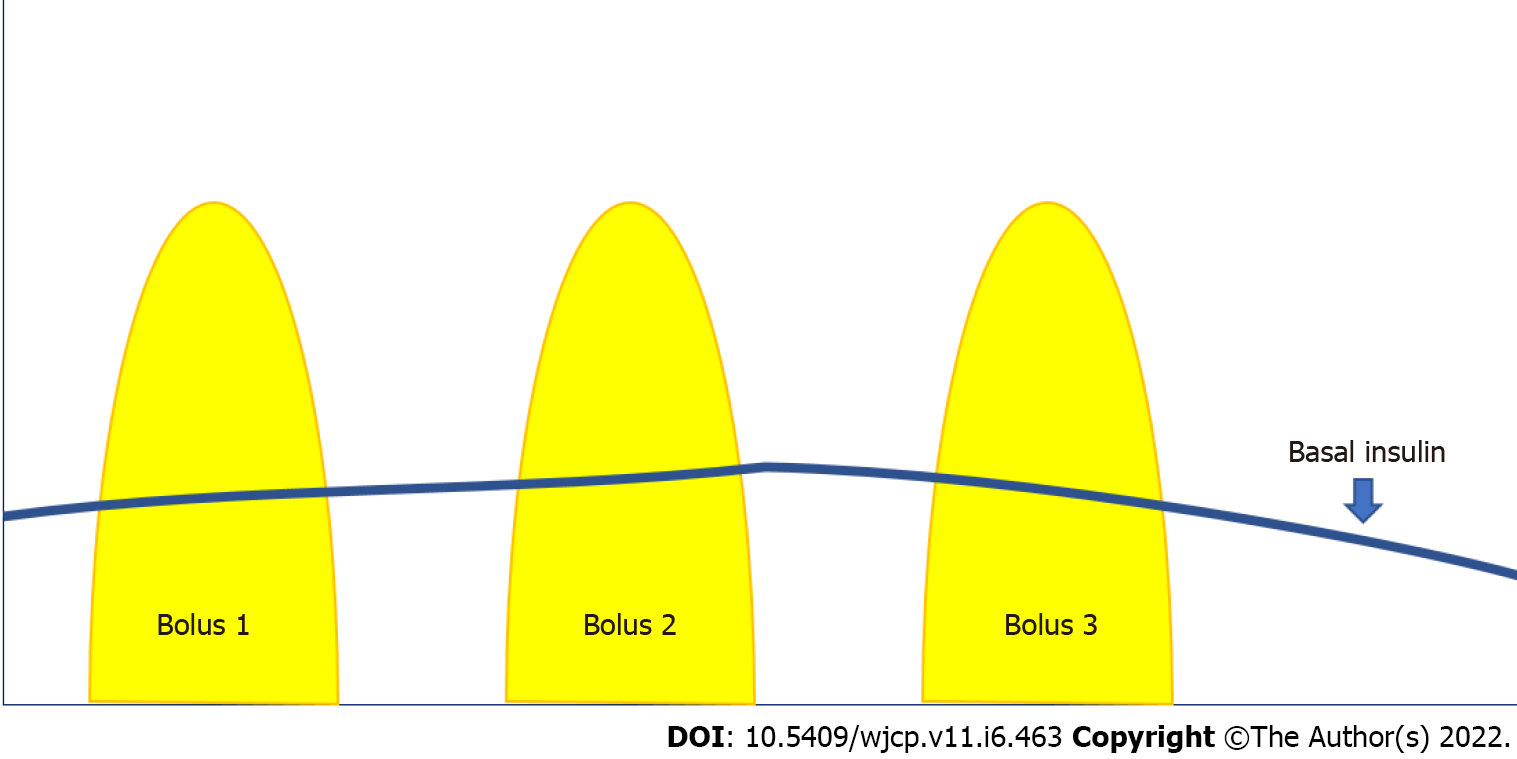
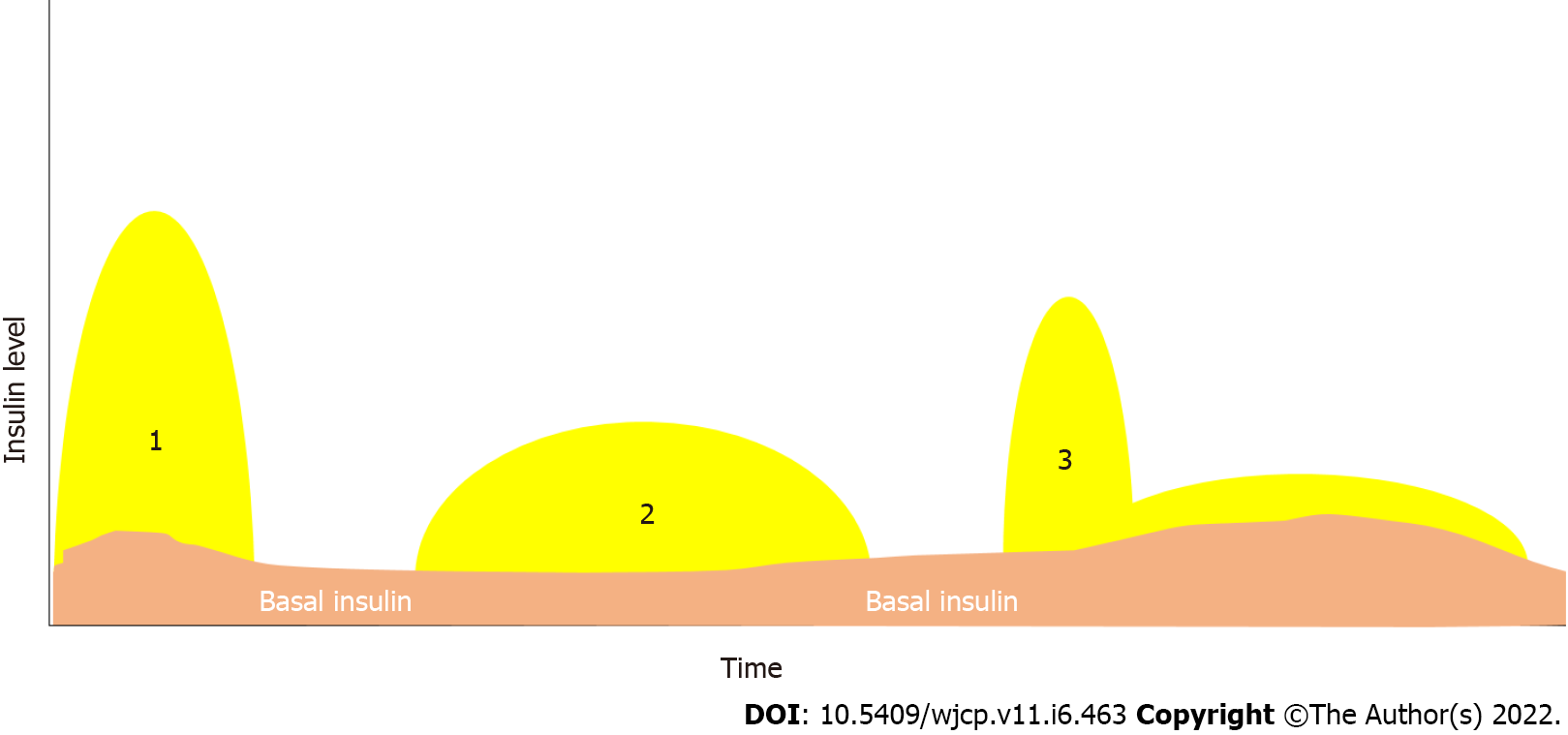
Figure 3 Basal and bolus insulin.
Basal insulin is delivered continuously in a small amount as a background to keep the blood glucose levels within the target between meals. The pump can be programmed to deliver at different rates within 24 h. Bolus insulin is a large amount delivered over a short period, which can be given at any time. The pre-meal bolus is given based on the number of carbohydrates in grams. The bolus can also be given to correct high blood glucose levels.
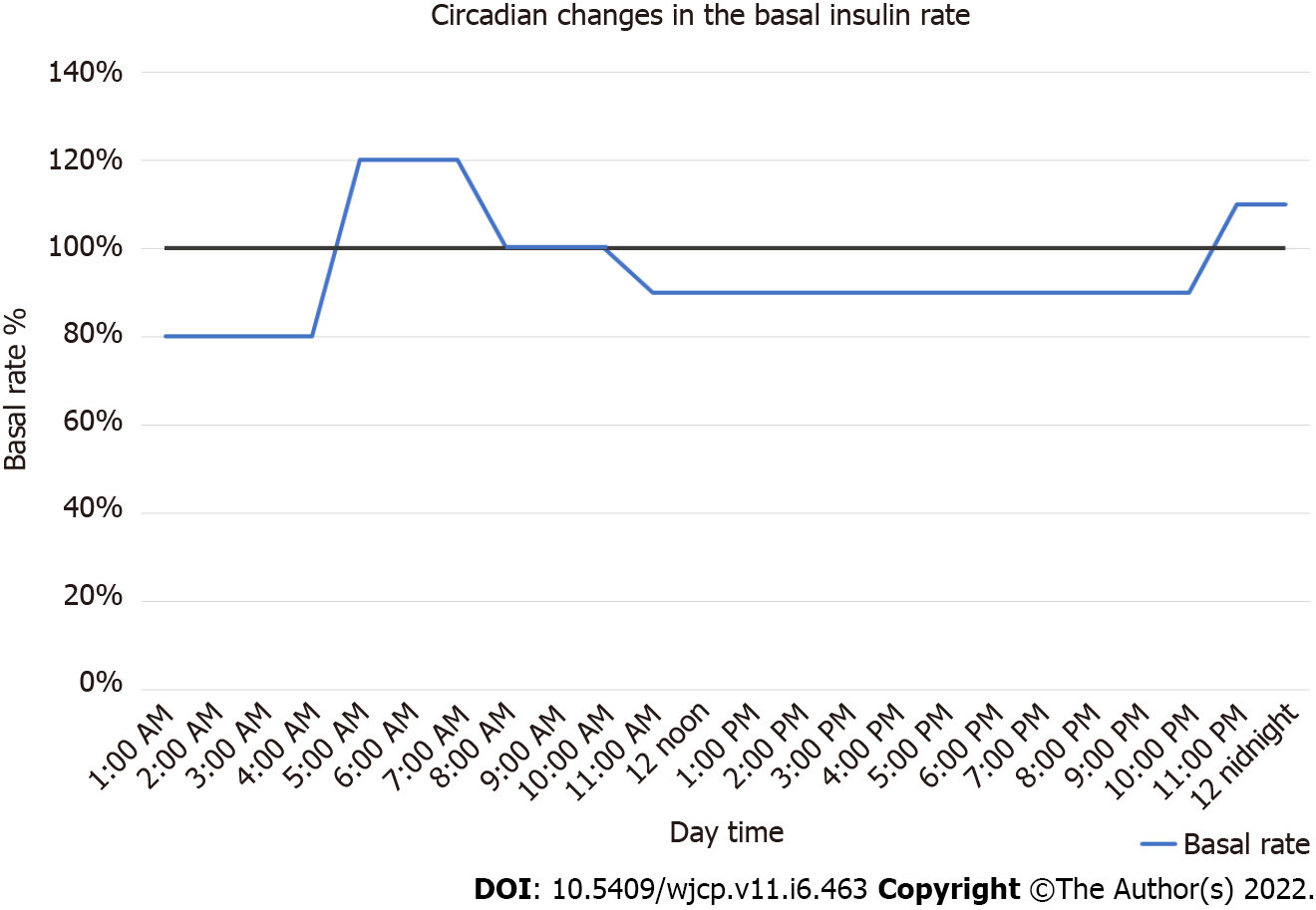
Figure 4 Circadian changes in the basal insulin profile.
An example of the circadian changes in the basal insulin profile. Between 12 midnight to 4:0 am, the basal rate is reduced by 20% to increase 20% between 4:0 am to 7:0 am, then will be 100% between 7:0 am to 10:0 am to be reduced by 10% between 10:0 am to 10:0 pm, then it increases again by 10% between 10:0 pm to 12 midnight.
Figure 5 The different insulin bolus types.
1: The typical bolus, 2: The extended bolus, 3: The dual bolus
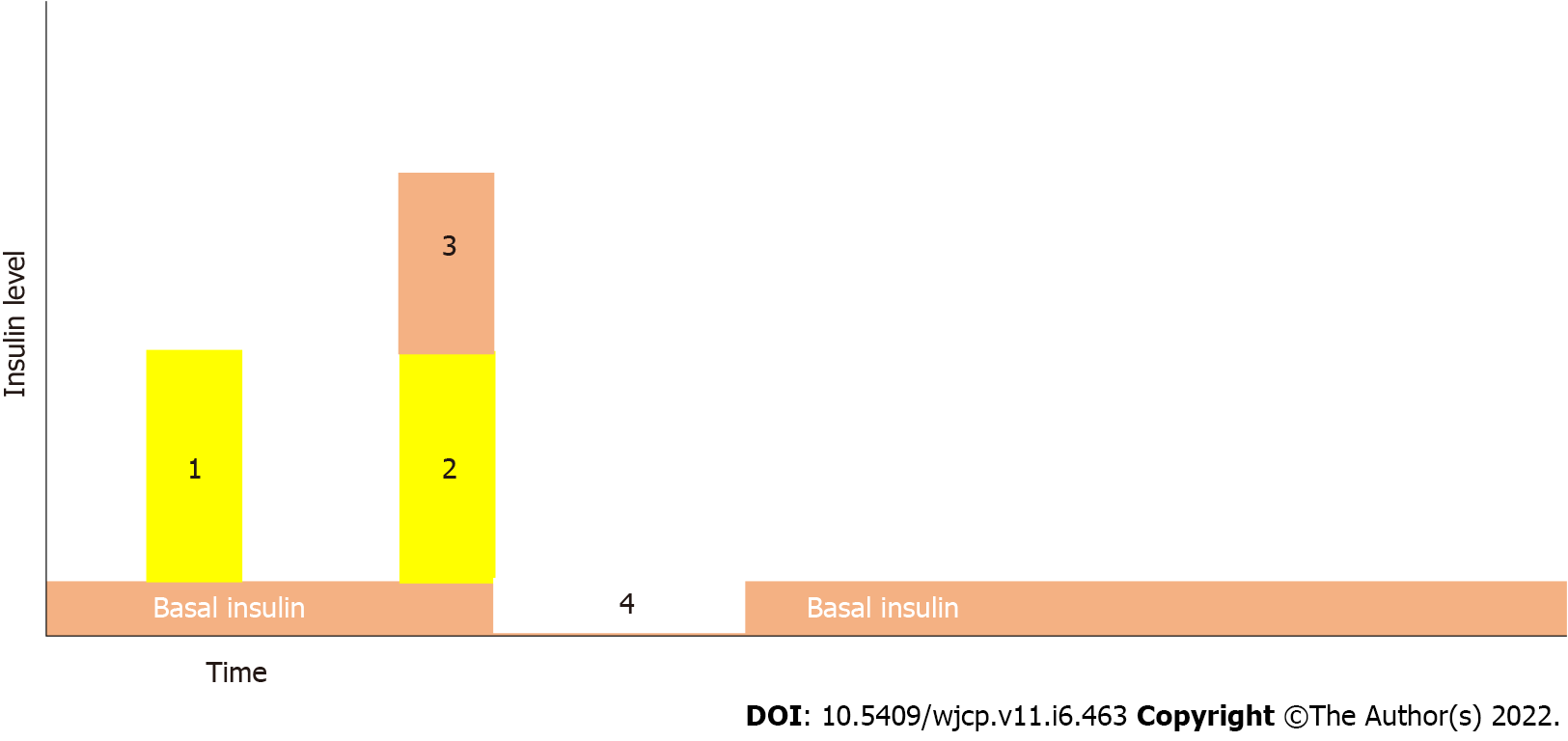
Figure 6 Different types of insulin bolus.
1: Typical insulin bolus, 2 and 3 super bolus equal to the calculated bolus plus the basal insulin for the coming one to four hours, 4: The basal insulin rate will be 0% for the remaining four hours.
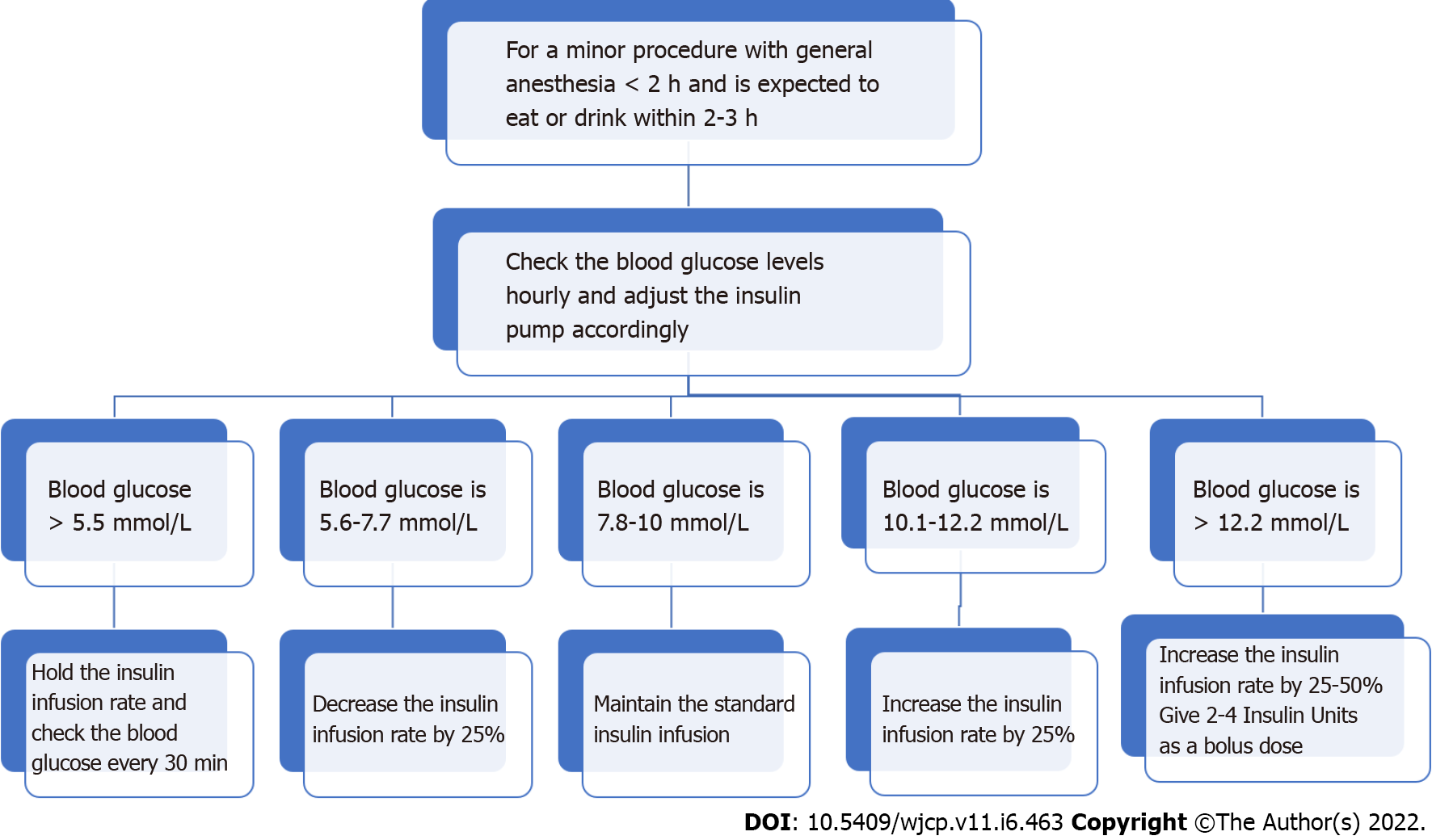
Figure 7
A flow chart for a minor procedure with general anesthesia for less than two hours.
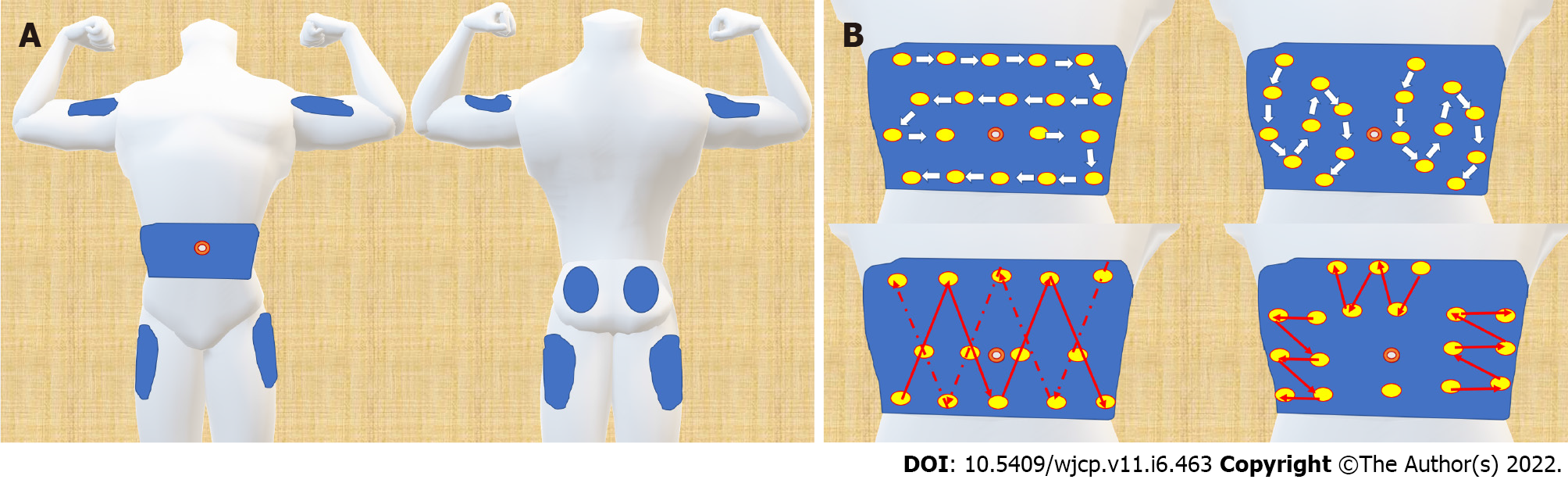
Figure 8 Approved insertion sites and different types of insertion site rotation.
A: There are four approved sites for the subcutaneous injection of insulin: Insulin Absorption Rate Fluctuation Depending on Injection Site; B: shows different types of insertion site rotation. Note that all the rotation patterns keep away from the umbilicus by at least one inch.
- Citation: Al-Beltagi M, Saeed NK, Bediwy AS, Elbeltagi R. Insulin pumps in children - a systematic review. World J Clin Pediatr 2022; 11(6): 463-484
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2219-2808/full/v11/i6/463.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5409/wjcp.v11.i6.463