Copyright
©2014 Baishideng Publishing Group Inc.
World J Otorhinolaryngol. May 28, 2014; 4(2): 6-11
Published online May 28, 2014. doi: 10.5319/wjo.v4.i2.6
Published online May 28, 2014. doi: 10.5319/wjo.v4.i2.6
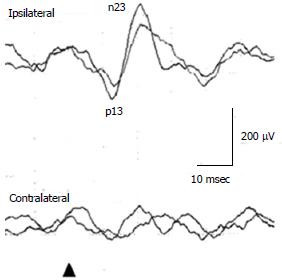
Figure 1 Cervical vestibular evoked myogenic potential waveforms in a healthy subject.
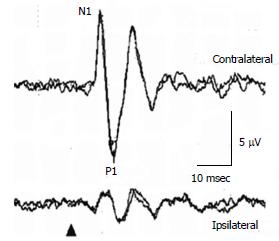
Figure 2 Ocular vestibular evoked myogenic potential waveforms in a healthy subject.
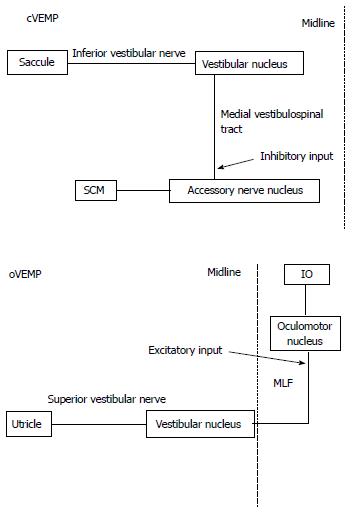
Figure 3 Supposed neural pathway of Cervical vestibular evoked myogenic potential and ocular vestibular evoked myogenic potential.
cVEMP : Cervical vestibular evoked myogenic potential; oVEMP: Ocular vestibular evoked myogenic potential; SCM: Sternocleidomastoid muscle; IO: Inferior oblique muscle; MLF: Medial longitudinal fasciculus.
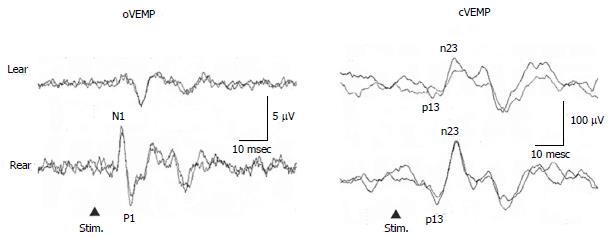
Figure 4 Vestibular evoked myogenic potential responses of a 57-year-old man with episodic lateral tilt sensation diagnosed as having idiopathic otolithic vertigo.
He showed absent oVEMP to the left ear stimulation. cVEMP : Cervical vestibular evoked myogenic potential; oVEMP: Ocular vestibular evoked myogenic potential.
- Citation: Murofushi T. Vestibular evoked myogenic potential. World J Otorhinolaryngol 2014; 4(2): 6-11
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2218-6247/full/v4/i2/6.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5319/wjo.v4.i2.6