Copyright
©2013 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Otorhinolaryngol. Nov 28, 2013; 3(4): 114-133
Published online Nov 28, 2013. doi: 10.5319/wjo.v3.i4.114
Published online Nov 28, 2013. doi: 10.5319/wjo.v3.i4.114
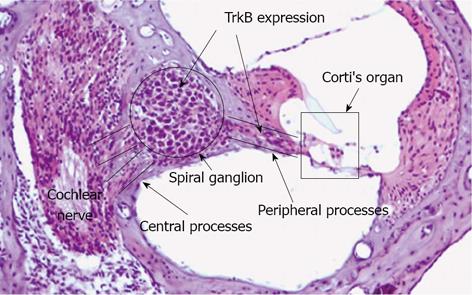
Figure 1 Histology of cochlea and targets for cell specific pharmaco-/gene therapy.
Three fluid filled compartments characterize the mammalian hearing organ. Nerve fibres and neurons (Spiral ganglion, peripheral processes and central processes), sensory epithelium (Corti’s organ). Tyrosine kinease B receptor (TrkB) is indicated as a target for therapy.
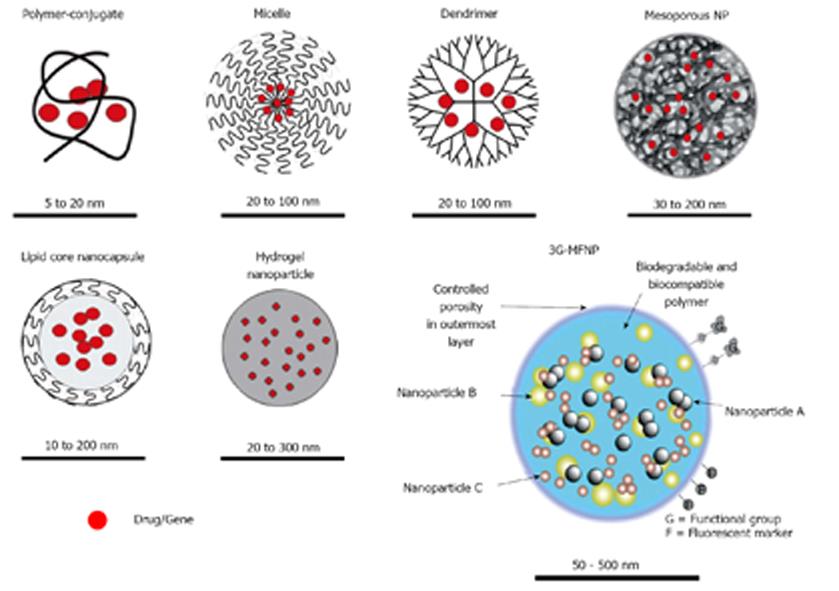
Figure 2 Examples of nanoparticles.
The 3G-multifunctional nanoparticle (MNFP) indicates the functionalized third generation multifunctional nanoparticle. The red dots indicate drug/gene incorporation. The respective nanoparticle sizes are shown for each nanoparticle (NP).
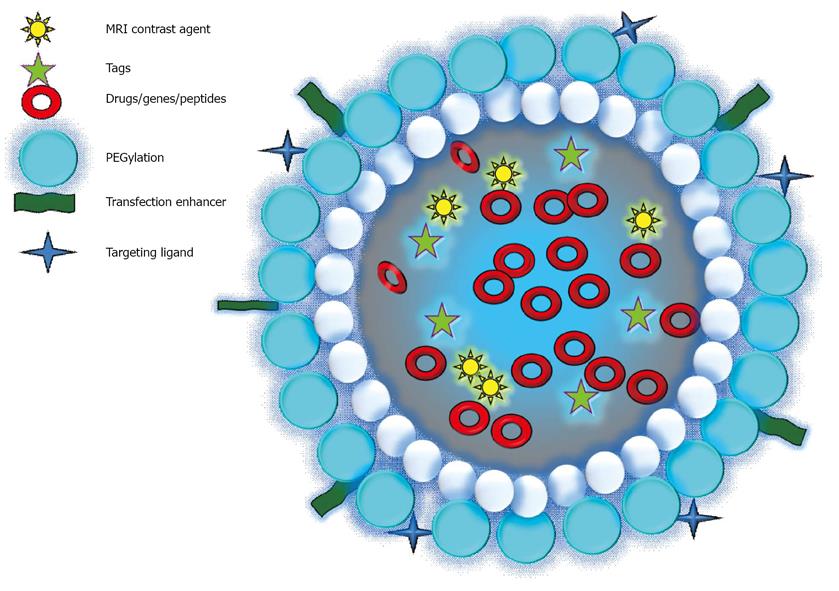
Figure 3 Composition of a targeted nanoparticle.
MRI: Magnetic resonance imaging.
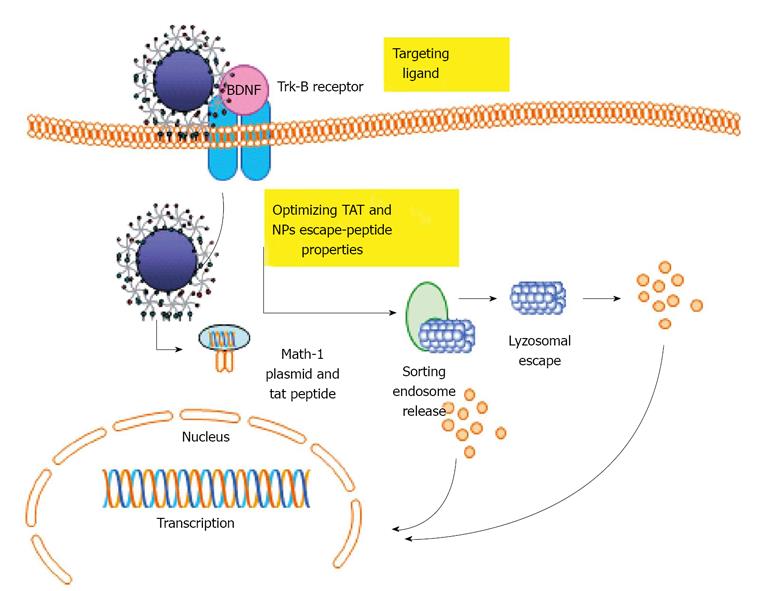
Figure 4 Internalization and cellular trafficking of nanoparticles.
TrkB: Tyrosine kinease B receptor; BDNF: Brain derived neurotrophic factor; TAT: Tactical arrival time.
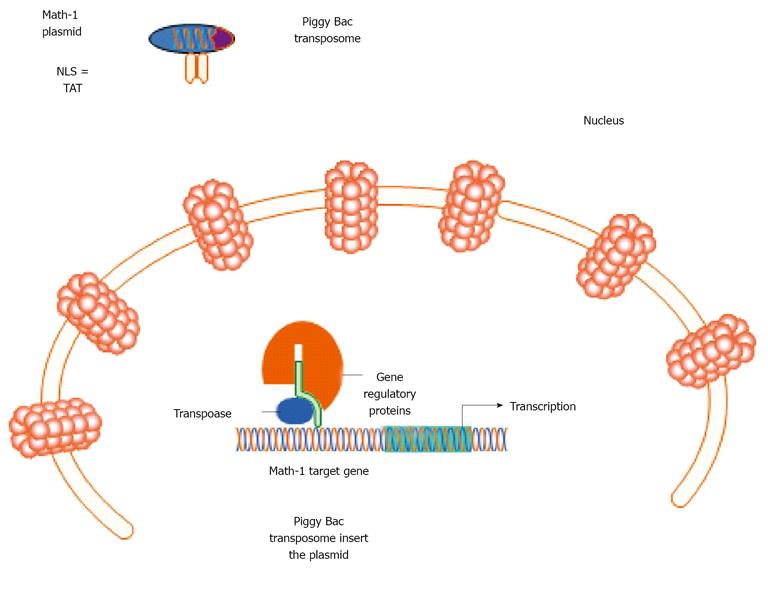
Figure 5 Example showing nuclear pore complexes targeted Tat-coated nanoparticle containing Math-1 plasmid and PiggyBac transposome.
NLS: Nuclear import signal; TAT: Tactical arrival time.
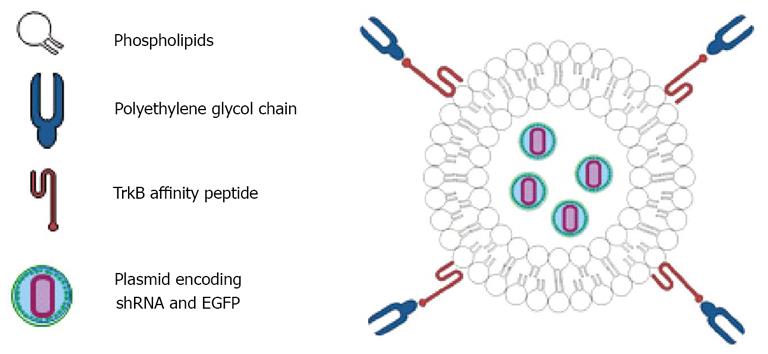
Figure 6 Illustration of the tyrosine kinease B receptor-targeting liposome nanoparticles that express short hairpin RNA to silence inhibitor of differentiation and DNA binding-2 and a reporter enhanced green fluorescent protein.
shRNA: Short hairpin RNA; EGFP: Enhanced green fluorescent protein; TrkB: Tyrosine kinease B receptor.
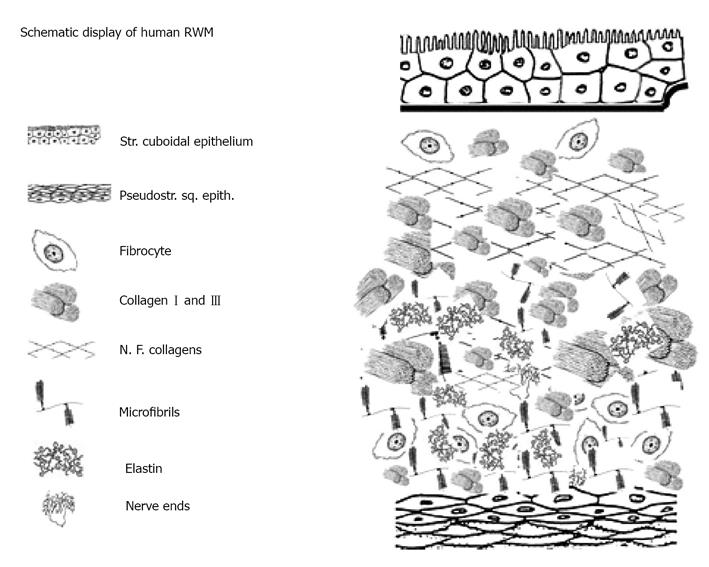
Figure 7 Human round window membrane and inner ear with different layers.
RWM: Round window membrane.
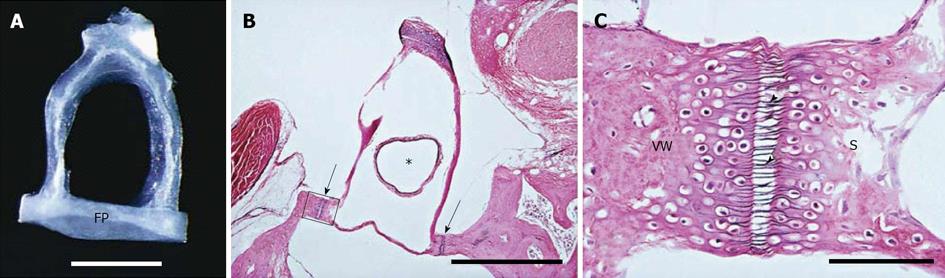
Figure 8 Porous annular ligament between the stapes footplate and vestibular window.
Source: Reference[141], with permission. VW: Vestibular window; S: Stapes.
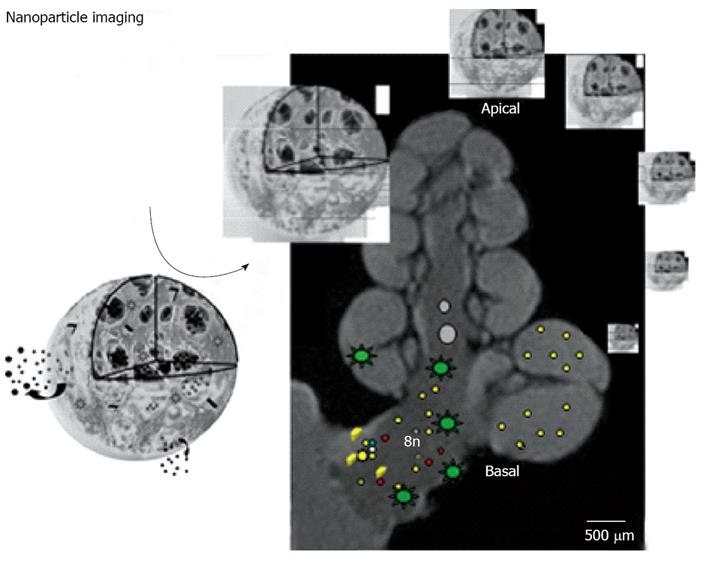
Figure 9 Schematic representation of imaging of nanoparticles in the inner ear of guinea pig with magnetic resonance imaging.
The cochlear nerve (8n) and cochlear basal turn (basal) are indicated. As nanoparticle transmission electron microscopy of multifunctional poly-lactic-co-glycolic acid -nanoparticle is shown. The star-like dots in the fluid spaces of the cochlea and the cochlear nerve demonstrate the distribution of gadolinium chelate used for visualization. The small dots indicate nanoparticles, their ingredients and dye for histological confirmation of targeting.
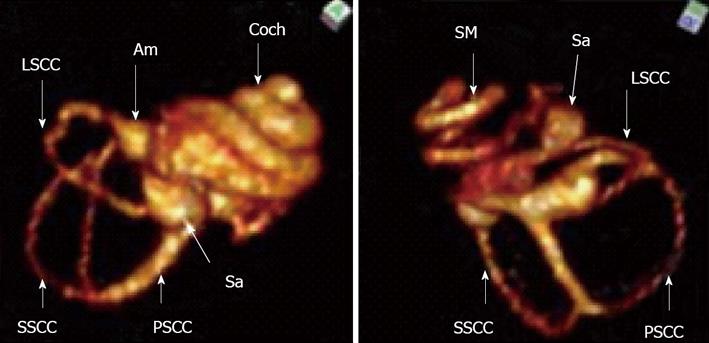
Figure 10 Magnetic resonance imaging of the inner ear of rat using SPION as contrast agent.
The upper figure shows T1 weighted imaging where all cochlear fluid spaces are visible. The lower figure shows T2 weighted image where SPION injected into the perilymphatic space will reduce the T2 signal and the perilymphatic space signal is extinguished. Only the fluid in scala media (endolymph) is visible. Am: Ampulla; Coch: Cochlea; Sa: Saccus; LSCC: Lateral semicircular canal; SSCC: Superior semicircular cananal; PSCC: Posterior semicicrcular canal; SM: Scala media.
- Citation: Pyykkö I, Zou J, Zhang Y, Zhang W, Feng H, Kinnunen P. Nanoparticle based inner ear therapy. World J Otorhinolaryngol 2013; 3(4): 114-133
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2218-6247/full/v3/i4/114.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5319/wjo.v3.i4.114