Copyright
©The Author(s) 2023.
World J Otorhinolaryngol. May 9, 2023; 10(2): 23-29
Published online May 9, 2023. doi: 10.5319/wjo.v10.i2.23
Published online May 9, 2023. doi: 10.5319/wjo.v10.i2.23
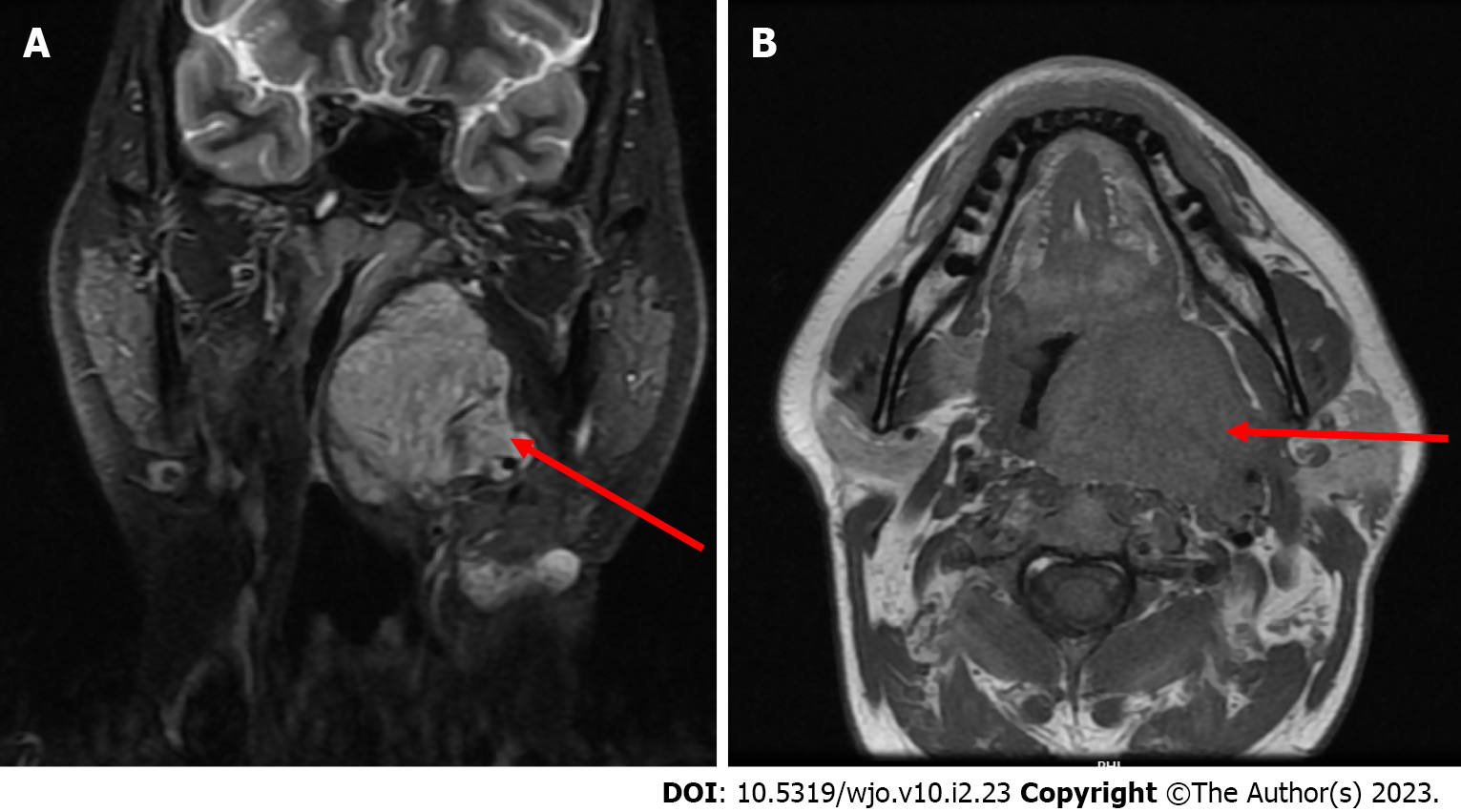
Figure 1 Magnetic resonance images (with contrast and plain) depicting a heterogeneous well enhancing lobulated lesion in the left parapharyngeal space as marked with a red arrow.
A: Axial; B: Coronal.
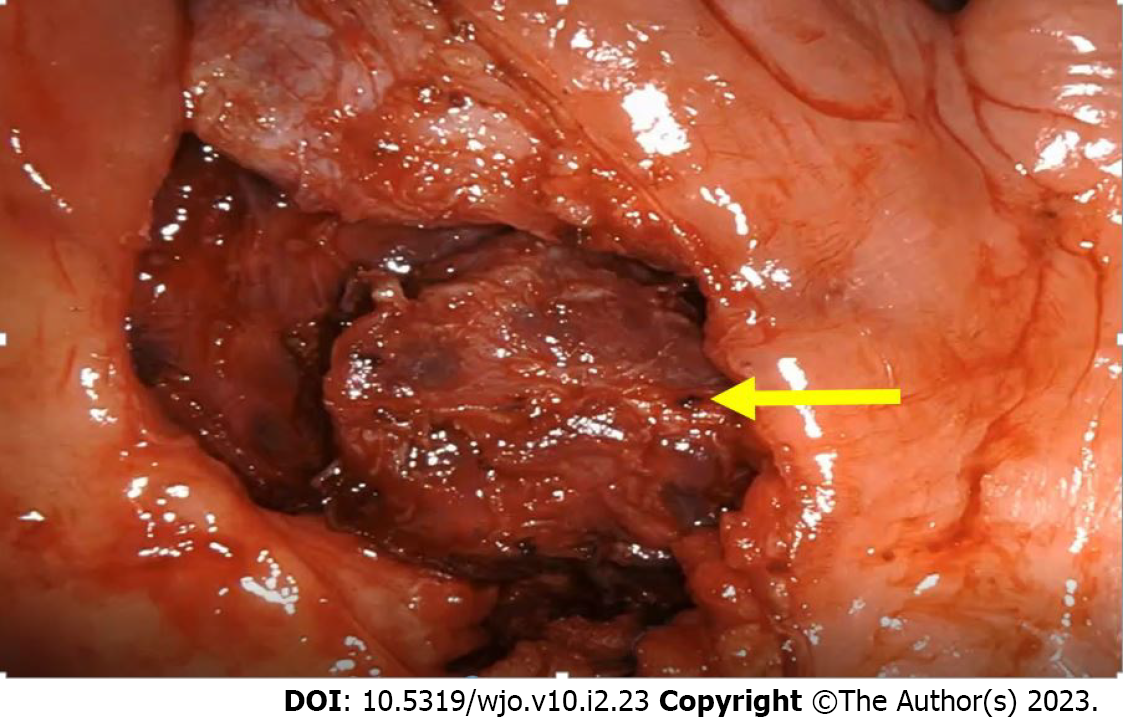
Figure 2 Partly excised parapharyngeal mass visualized with a 30-degree endoscope indicated with a yellow arrow.
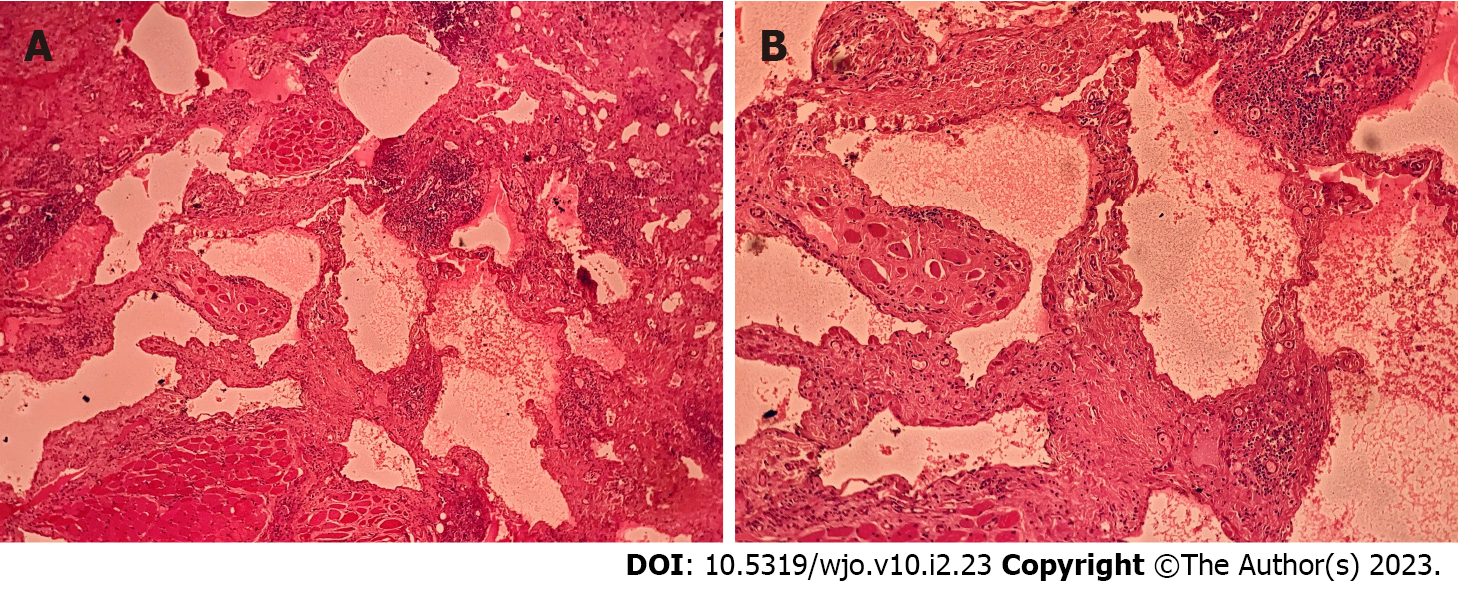
Figure 3 Hematoxylin-eosin staining.
A: Hematoxylin-eosin (HE), 40 ×, section examined shows a benign vascular tumour in the soft tissue and skeletal muscle fibres with morphological feature consistent with a lymphangioma; B: HE, 100 ×, section shows vascular spaces lined by a single layer of benign endothelial cells.
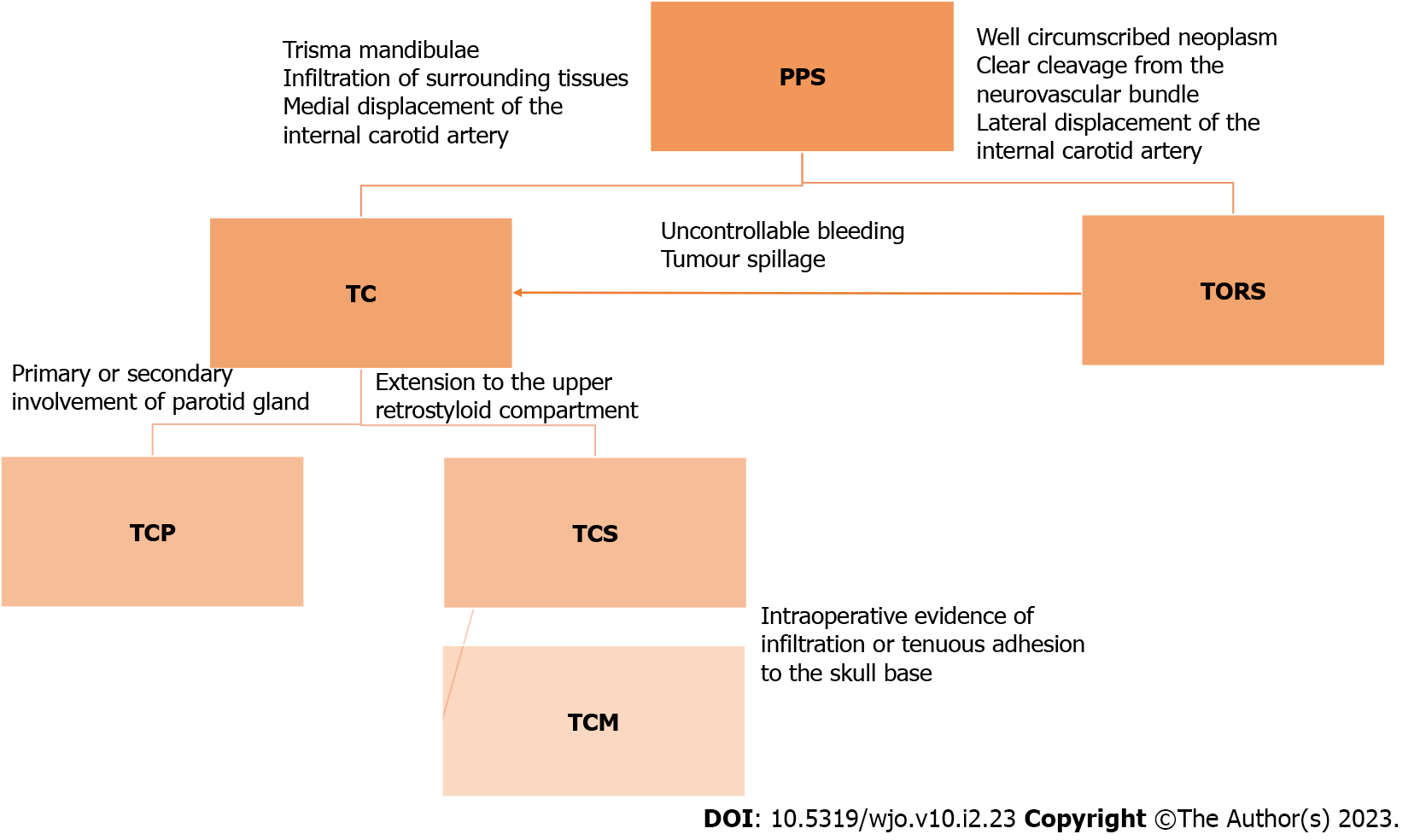
Figure 4 Surgical algorithm for approach to parapharyngeal tumors including transcervical approach, transoral robotic surgery, transcervical approach with parotidectomy, transcervical approach with styloid excision, transmandibular approach.
PPS: Parapharyngeal space; TC: Transcervical approach; TORS: Transoral robotic surgery; TCP: Transcervical approach with parotidectomy; TCS: Transcervical approach with styloid excision; TCM: Transmandibular approach.
- Citation: Dabas S, Menon NN, Ranjan R, Gurung B, Shukla H, Sharma AK, Tiwari S, Sinha A, Bhatti SS, Sangal R. Transoral robotic surgery for adult parapharyngeal lymphangioma: A case report. World J Otorhinolaryngol 2023; 10(2): 23-29
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2218-6247/full/v10/i2/23.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5319/wjo.v10.i2.23