Copyright
©2014 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
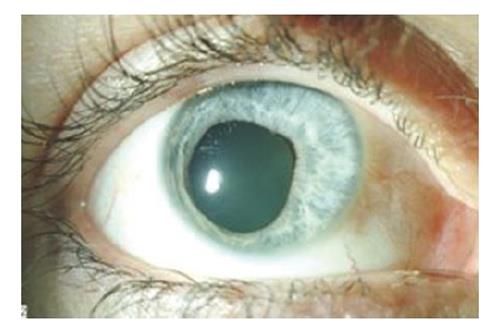
Figure 1 Anterior view of the right eye of a patient with pharmacologic pupillary dilation showing iris atrophy and pupillary distortion secondary to posterior synechia following inadvertent ocular intense pulsed light injury.
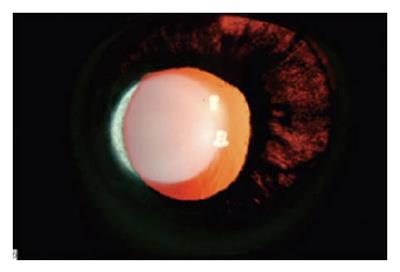
Figure 2 Slit lamp photograph of the right eye of the patient in Figure 1 showing iris transillumination defects.
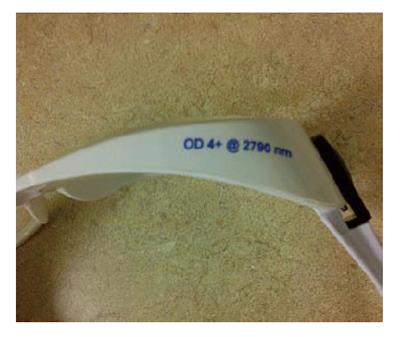
Figure 3 Optical density engraved on laser safety eyewear.
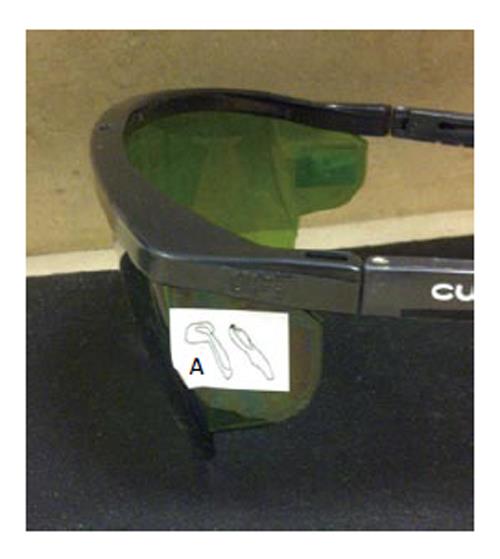
Figure 4 Drawing of the hand-held delivery system is placed on the side of the goggle.
Figure 5 Shutter glasses used for intense pulsed light.
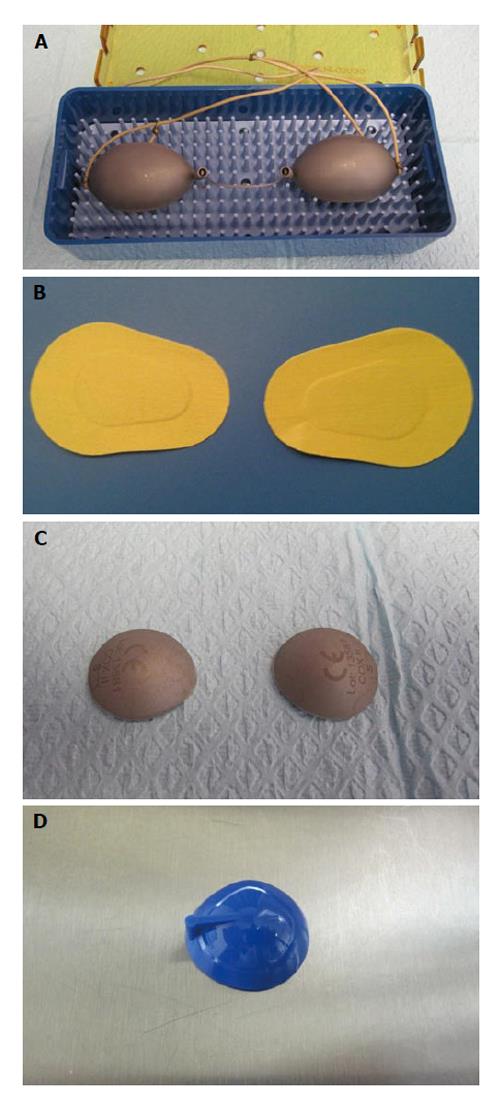
Figure 6 Shields.
A: Stainless steel external shield; B: Stick-on fabric external eye shield; C: Stainless steel corneal shields; D: Methyl methacrylate corneal shields.
- Citation: Sayed MS, Ko MJ, Ko AC, Lee WW. Ocular damage secondary to lights and lasers: How to avoid and treat if necessary. World J Ophthalmol 2014; 4(1): 1-6
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2218-6239/full/v4/i1/1.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5318/wjo.v4.i1.1