Copyright
©2014 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Obstet Gynecol. May 10, 2014; 3(2): 78-84
Published online May 10, 2014. doi: 10.5317/wjog.v3.i2.78
Published online May 10, 2014. doi: 10.5317/wjog.v3.i2.78
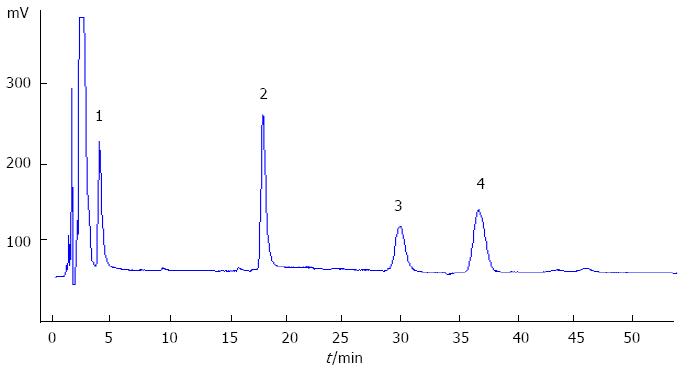
Figure 1 Chromatogram of phospholipids.
High-performance liquid chromatography was used for phospholipids measurement. Peaks represent the phospholipids extracted from amniotic fluids. Peaks refer to the following components: 1: Phosphatidylinositol; 2: Phosphatidylcholine; 3: Lysolecithin; 4: Sphingomyelin.
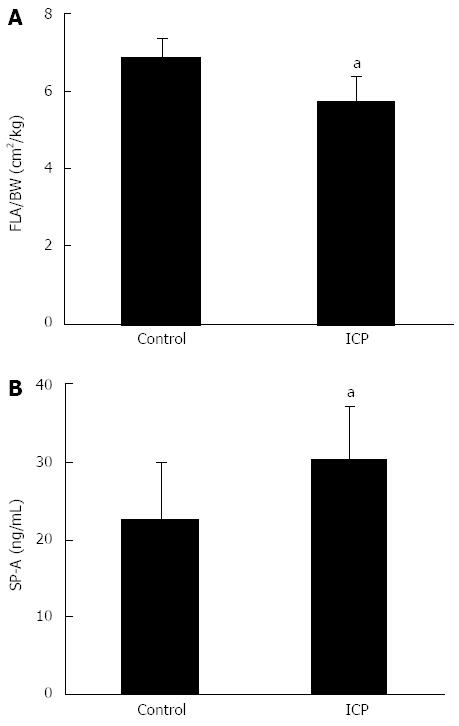
Figure 2 Fetal lung area/body weight ratio and fetal surfactant protein A.
A: Ratio between fetal lung area (FLA) and fetal body weight (BW). aP < 0.05 vs control; B: Fetal surfactant protein A (SP-A) concentration. Intrahepatic cholestasis of pregnancy (ICP) has a higher SP-A than that in the control group, aP < 0.05 vs control.
- Citation: Ding YL, Zhang LJ, Wang X, Zhou QC, Li N, Wang CX, Zhang XQ. Fetal lung surfactant and development alterations in intrahepatic cholestasis of pregnancy. World J Obstet Gynecol 2014; 3(2): 78-84
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2218-6220/full/v3/i2/78.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5317/wjog.v3.i2.78