Copyright
©2013 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
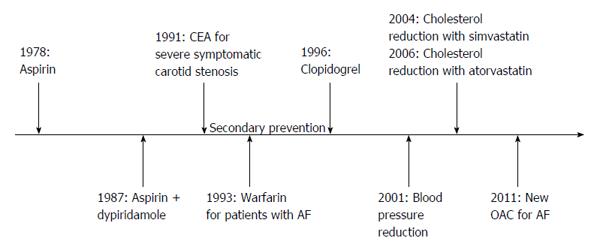
Figure 1 Medical and surgical treatments which have been proved to be effective for secondary prevention after stroke or transient ischaemic attacks in the last decades.
OAC: Oral anticoagulants; CEA: Carotid endarterectomy; AF: Atrial fibrillation.
Figure 2 Old and new antiplatelet agents and their mechanism of action.
PAR1: Proteinase activated receptor 1; ADP: Adenosine diphosphate; TXA2: Thromboxane A2; cAMP: Cyclic adenosine monophosphate; COX1: Cyclooxygenase-1; 5-HT2A: 5-hydroxytryptamine (serotinin) receptor 2A.
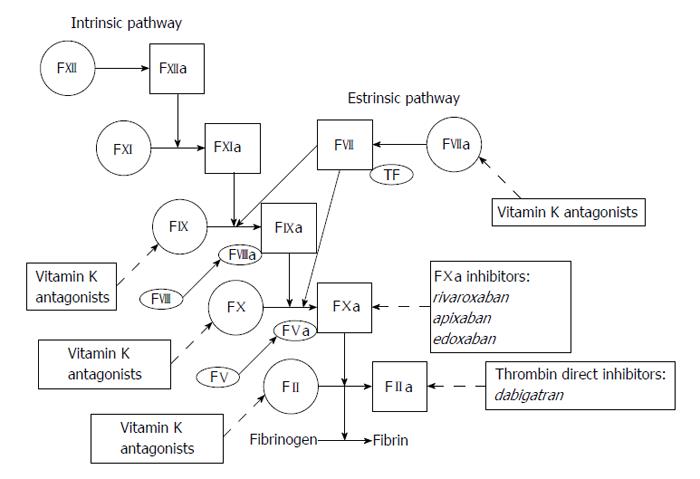
Figure 3 Vitamin K antagonist and new anticoagulant mechanism of action.
F: Factor.
- Citation: Volonghi I, Padovani A, Zotto ED, Giossi A, Costa P, Morotti A, Poli L, Pezzini A. Secondary prevention of ischaemic stroke. World J Neurol 2013; 3(4): 97-114
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2218-6212/full/v3/i4/97.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5316/wjn.v3.i4.97