Copyright
©2014 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Anesthesiol. Mar 27, 2014; 3(1): 124-128
Published online Mar 27, 2014. doi: 10.5313/wja.v3.i1.124
Published online Mar 27, 2014. doi: 10.5313/wja.v3.i1.124
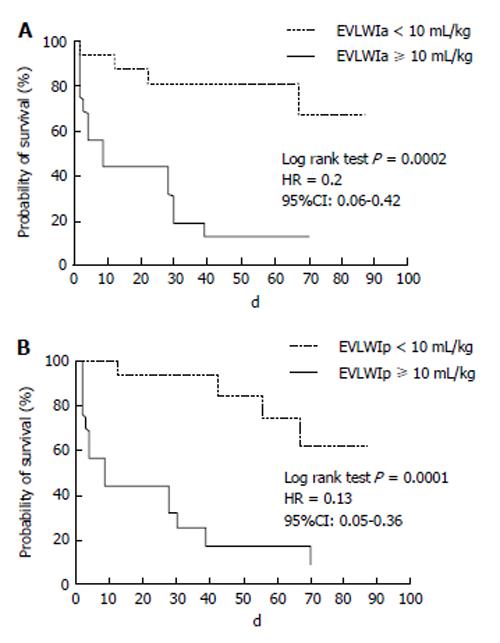
Figure 1 Proportion of patients surviving with a low extravascular lung water.
The proportion of patients surviving with a low EVLW (EVLWI < 10 mL/kg) was better than that of those patients with a higher EVLW whether indexed by actual (EVLWIa) (A) or predicted body weight (EVLWIp) (B) during their hospital stay with the Kaplan-Meier method (76% vs 12.5%, respectively). ELVMI: Extravascular lung water index.
- Citation: Chung FT, Lin SM, Lin HC, Yu CT, Hsieh MH, Fang YF, Liu CY, Kuo CH, Wang TY. Predictive value of extravascular lung water indexed to predicted body weight. World J Anesthesiol 2014; 3(1): 124-128
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2218-6182/full/v3/i1/124.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5313/wja.v3.i1.124