Published online Oct 18, 2018. doi: 10.5312/wjo.v9.i10.220
Peer-review started: April 28, 2018
First decision: June 15, 2018
Revised: June 22, 2018
Accepted: June 27, 2018
Article in press: June 27, 2018
Published online: October 18, 2018
Processing time: 173 Days and 1.6 Hours
To investigate whether minority ethnicity and the duration of education influence preoperative disability and expectations in patients undergoing total knee arthroplasty.
We prospectively included 829 patients undergoing primary unilateral total knee arthroplasty (TKA) from April 2013 to December 2014 at a single centre. Patients filled in pre-operative questionnaires with information regarding place of birth, duration of education, expectations for outcome of surgery and baseline characteristics. Patients were stratified based on ethnicity. Majority ethnicity was defined as born in the study country and minority ethnicity was defined as born in any other country. Similarly, patients were stratified based on duration of education in groups defined as < 9 years, 9-12 years and > 12 years, respectively.
We found that 92.2% of patients were of majority ethnicity. We found that 24.5%, 44.8% and 30.8% of patients had an education of < 9 years, 9-12 years and > 12 years, respectively. The mean preoperative (pre-OP) oxford knee score (OKS) in the total population was 23.6. Patients of minority ethnicity had lower mean pre-OP OKS (18.6 vs 23.9, P < 0.001), higher pain levels (VAS 73.0 vs 58.7, P < 0.001), expected higher levels of post-OP pain (VAS 14.1 vs 6.1, P = 0.02) and of overall symptoms (VAS 16.6 vs 6.4, P = 0.006). Patients with > 12 years education had lower mean pre-OP OKS (21.5 vs 23.8 and 24.6, P < 0.001) and higher pre-OP VAS pain (65.4 vs 59.2 and 56.4, P < 0.001) compared to groups with shorter education. One year post-operative (post-OP) patients of minority ethnicity had lower mean OKS, higher pain and lower QoL. One year post-OP patients with > 12 years education reported higher pain compared to patients with shorter educations. However, the response-rate was low (44.6%), and therefore post-OP results were not considered to be significant.
Minority ethnicity and the duration of education influence preoperative disability and expectation in patients undergoing TKA. This should be taken into account when patients are advised pre-operatively.
Core tip: We investigated whether minority ethnicity and duration of education influence preoperative disability and expectations in patients undergoing total knee arthroplasty. We prospectively included 829 patients scheduled to undergo primary total knee arthroplasty in a single centre. We found that patients of minority ethnicity suffer from more severe preoperative symptoms and expect a poorer post-operative outcome compared to patients of majority ethnicity. We also found that patients with > 12 years education have more severe preoperative symptoms compared to patients with shorter educations. This information can assist surgeons in appropriate treatment plans and preoperative consultation for all patients.
- Citation: Kudibal MT, Kallemose T, Troelsen A, Husted H, Gromov K. Does ethnicity and education influence preoperative disability and expectations in patients undergoing total knee arthroplasty? World J Orthop 2018; 9(10): 220-228
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2218-5836/full/v9/i10/220.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5312/wjo.v9.i10.220
Thousands of patients undergo total knee arthroplasty (TKA) every year worldwide. In recent years, pre-operative (pre-OP) planning and patient information has been streamlined by using the fast-track concept[1]. This operation has excellent results in terms of survival, with a reported ten-year prosthetic survival of close to 95% (National Hospital Discharge Survey 2010); however, patient satisfaction remains a challenge, with up to 20% of patients being dissatisfied with their one-year post-operative (post-OP) outcomes[2,3].
Outcome is known to be influenced by patient-related factors that include age, pre-OP symptoms[4-6], comorbidities and mental health status, such as depression and anxiety[7]. Previous studies have shown that patient satisfaction can be influenced by both surgery-related factors, such as implant alignment[8-10], implant brand and hospital type[8], as well as patient-related factors including age, pre-OP symptoms and expectations[2]. Other less well-defined factors have also been shown to influence outcome following TKA and THA, such as socioeconomic factors[11,12] and duration of education[13]. Understanding the way that ethnicity and the duration of education influence both pre-OP symptoms and post-OP outcome in TKA patients will assist healthcare providers in determining specific areas of possible improvement and adjusting treatment options appropriately. Furthermore, it will assist in more accurate comparisons of study populations in future research.
The purpose of the study was to investigate whether minority ethnicity and duration of education influence pre-OP disability and expectations in patients undergoing TKA.
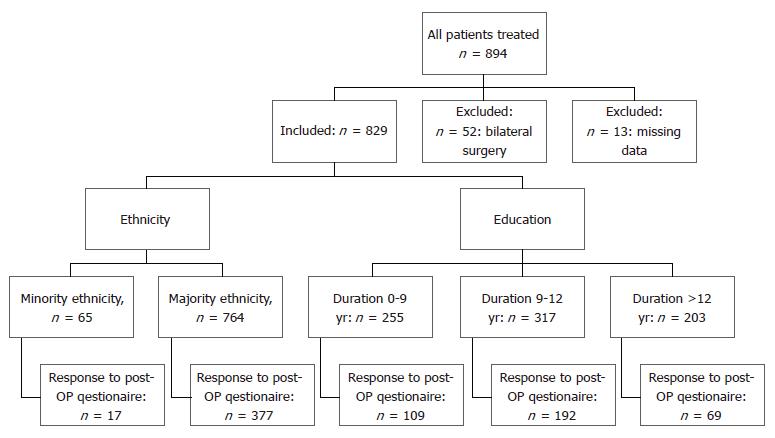
We conducted a prospective cohort study that included all patients undergoing primary TKA at our institution from April 1st 2013 to December 8th 2014. Exclusion criteria were simultaneous bilateral TKA and missing data on education/country of origin. Prior to surgery, patients were asked to fill in a questionnaire regarding patient demographics, pre-OP symptoms and expectations about surgery outcome. All patients were asked to fill in another questionnaire one year post-OP via email or regular mail, and 370 patients completed a one-year follow-up questionnaire (Figure 1). A clinical control was not conducted. Patients filled in the questionnaire independently or with help from family members. All surgeries were performed in a standardized fast-track setup[1] by experienced surgeons specializing in arthroplasty surgery, each having performed > 100 primary TKAs annually. The standard surgical protocol for TKA includes spinal analgesia, standardized fluid management, use of preoperative intravenous tranexamic acid, preoperative single-shot high-dose methylprednisolone[14] and absence of drains. All TKAs were performed with a standard medial parapatellar approach without the use of tourniquet, with an application of local infiltration analgesia (LIA)[15] and postoperative compression bandaging[16]. Post-operative opioid-sparing pain treatment consisted of celecoxib 200 mg/12 h and paracetamol 1 g/6 h with rescue analgesics [administered if visual analogue scale (VAS) > 50 mm at rest] consisting of 10 mg oral morphine as needed. Physiotherapy was started on the day of surgery and continued until discharge. Rivaroxaban (Bayer, Denmark) was used as oral thromboprophylaxis starting 6 to 8 h postoperatively and continued daily until discharge[17]. Mechanical thromboprophylaxis and extended oral thromboprophylaxis were not used. Patients were discharged to their own home upon fulfilling functional discharge criteria[18].
Preoperative disability was measured by Oxford knee score (OKS), self-reported quality of life (QoL)[19], knee pain during activity measured on VAS, and overall symptoms and expectations. OKS ranges from 0 to 48, with lower numbers indicating more severe symptomatic disease. All VAS scales in this study range from 0 to 100. For pain and symptoms, higher values represent the worst conditions, while high values on the scale for QoL represent the best conditions. Patients were stratified based on duration of education and place of birth. Ethnicity was divided into two groups, majority and minority ethnicity. Majority ethnicity was defined as patients born in Denmark (the study country), and minority ethnicity was defined as all patients born outside Denmark. As the level of education varies between countries, education was stratified based on duration (< 9 years, 9-12 years and > 12 years of education). Preoperatively, we registered baseline-characteristics including alcohol consumption, smoking, BMI and comorbidity. Comorbidity was registered as heart disease, lung disease, previous stroke, kidney disease, liver disease, diabetes and autoimmune disease. We also registered symptoms (OKS, use of walking aids, walking distance, pain on VAS score during rest and activity) self-reported QoL, and expectations for post-OP symptoms and QoL. Finally, we registered self-reported post-OP symptoms and self-reported QoL using the one-year post-op questionnaire.
As all our results are based on patient reported outcome measures, we take into account the minimal clinically important difference (MCID). For OKS, this is acknowledged to be four-five[20,21]. For VAS scales in knee arthritis patients, MCID has been reported to be around 20 points[22].
All data were processed in R 3.2.2. All measurements were reported as mean with standard deviation (SD) for continues variables and number with percent for categorical variables. Tests for association of minority ethnicity with continues interest variables was done by t-test or for non-normal distributed variables by Wilcoxon sum rank test. Association with categorical interest variables was done by chi-squared or, in cases with expected values below 5, Fishers exact test. Associations between education duration groups and the interest variables were done for continues variables by uni-variable linear regression with TYPE III test or Kruskal-Wallis sum rank test for non-normal distributed variables, and for categorical variables chi-square and Fishers exact test. Additionally, to adjust for multiple testing, a Bonferroni correction was done for all P-values, and the correction scale was given by the number of tests performed within each outcome group. The adjusted P-value was calculated by multiplying the original P-values by the given scale. P < 0.05 was considered significant.
We included 894 consecutive and unselected patients undergoing TKA at our institution. The following were excluded: simultaneous bilateral TKA (n = 52) and missing data on education/country of origin (n = 13), thus leaving 829 patients for analysis.
For the total population, mean ± SD at time of surgery was 66.8 (10) years, 63.4% were female and 764 (92.2%) of patients were of majority ethnicity. Specifically, 24.5% of patients had an education of < 9 years, 44.8% of 9-12 years and 30.8% > 12 years (Table 1). Mean pre-OP OKS (SD) was 23.6 (8). Patients of minority ethnicity were younger compared to patients of majority ethnicity (P = 0.045) and had a shorter education (72.3% had an education of 0-9 years while only 20.4% of patients with majority ethnicity had an education of this length (P < 0.001) (Table 2). Patients of minority ethnicity had a lower pre-OP OKS (P < 0.005), higher knee pain during activity (P < 0.001), and a significantly larger proportion were dependent on a walking aid (P = 0.026) (Table 2). Furthermore, this patient group had a significantly lower expectation to their post-OP pain during activity (P = 0.016) and overall symptoms (P = 0.016). Patients with an education of > 12 years were older at the time of surgery, with a mean age of 67.7 years compared to 64.8 years for patients with an education of 0-9 years (P < 0.001). Patients with an education > 12 years reported a lower pre-OP OKS compared to the groups with 9-12 years and < 9 years of education (P < 0.001). Concurrent to this, patients with an education > 12 years had a higher pre-OP VAS for knee pain during activity compared to the other groups (P = 0.002, expectation measures also differed between the education groups (all P ≤ 0.008)). Women composed a higher proportion of the highly educated group, with 73.4% compared to 57.1% and 63.0% in the middle and low education groups, respectively (P = 0.003) (Table 3).
| All patients | |
| Baseline characteristics | |
| BMI (mean ± SD) | 29.7 ± 5 |
| Age (mean ± SD) | 66.8 ± 10 |
| Gender | |
| Male | 308 (36.6) |
| Female | 534 (63.4) |
| Smoking | |
| Non-smoker | 492 (58.6) |
| Former smoker | 213 (25.4) |
| Active smoker | 134 (16) |
| Duration of education | |
| More than 12 yr | 255 (30.8) |
| 9-12 yr | 371 (44.8) |
| 0-9 yr | 203 (24.5) |
| Ethnicity | |
| Born in Denmark | 764 (92.2) |
| Born outside Denmark | 65 (7.8) |
| Preoperative level of function and symptoms | |
| Walking aid outside the home: | |
| None | 597 (71.2) |
| One cane | 133 (15.9) |
| Two canes | 34 (4.1) |
| Wheeled walker | 69 (8.2) |
| Do not leave the home | 6 (0.7) |
| Oxford knee score (mean ± SD) | 23.6 ± 8 |
| Knee pain during activity1, median (range) | 63 (0:100) |
| Quality of life1, median (range) | 47 (0:100) |
| Level of symptoms1, median (range) | 50 (0:100) |
| Preoperative expectations | |
| Knee pain 1 yr after surgery1, median (range) | 2 (0:100) |
| Quality of life 1 yr post-OP1, median (range) | 94 (0:100) |
| Level of symptoms. 1 yr post-OP1, median (range) | 3 (0:99) |
| Majority ethnicity | Minority ethnicity | P value (adjusted) | ||
| Baseline characteristics | ||||
| BMI (mean ± SD) | 29.7 ± 5 | 29.9 ± 4 | 0.702 (3.508) | |
| Age (mean ± SD) | 67.0 ± 10 | 64.0 ± 9 | 0.009 (0.045) | |
| Gender | ||||
| Male | 294 (37.36) | 11 (15.22) | < 0.001 (0.004) | |
| Female | 470 (62.64) | 54 (84.78) | ||
| Smoking | ||||
| Non-smoker | 430 (56.3) | 55 (84.6) | < 0.001 (< 0.001) | |
| Former smoker | 207 (27.1) | 4 (6.5) | ||
| Active smoker | 127 (16.6) | 6 (9.2) | ||
| Duration of education | ||||
| More than 12 yr | 248 (32.5) | 7 (10.8) | < 0.001 (< 0.001) | |
| 9-12 yr | 369 (47.1) | 11 (16.9) | ||
| 0-9 yr | 156 (20.4) | 47 (72.3) | ||
| Preoperative level of function and symptoms | ||||
| Walking aid outside the home: | ||||
| None | 556 (72.8) | 34 (52.3) | 0.005 (0.026) | |
| One cane | 111 (14.9) | 20 (30.8) | ||
| Two canes | 30 (3.9) | 3 (4.6) | ||
| Wheeled walker | 61 (8) | 8 (12.3) | ||
| Do not leave the home | 6 (0.8) | 0 (0) | ||
| Oxford knee score (mean ± SD) | 23.9 ± 7 | 18.6 ± 8 | < 0.001 (< 0.001) | |
| Knee pain during activity1, median (range) | 61.0 (0:100) | 76 (13:100) | < 0.001 (< 0.001) | |
| Quality of life before surgery1, median (range) | 47.0 (0:100) | 38 (0:100) | 0.388 (1.938) | |
| Level of symptoms before surgery1, median (range) | 50.0 (0:100) | 61 (0:100) | 0.276 (1.380) | |
| Preoperative expectations | ||||
| Expectations to knee pain caused by use of hip 1 yr after surgery1, median (range) | 2.0 (0:100) | 4 (0:99) | 0.005 (0.016) | |
| Expectations to quality of life 1 yr after surgery1, median (range) | 94.0 (0:100) | 92 (0:100) | 0.296 (0.888) | |
| Expectations to level of symptoms 1 yr after surgery1, median (range) | 3.0 (0:99) | 6 (0:99) | 0.005 (0.016) | |
| Postoperative level of function and symptoms: | ||||
| Oxford knee score, median (range) | 39.0 (3.0:48.0) | 24.0 (10.0:47.0) | < 0.001 (0.002) | |
| Knee pain during act1, median (range) | 18.0 (0.0:100.0) | 62.0 (5.0:90.0) | < 0.001 (< 0.001) | |
| Quality of life1, median (range) | 71.5 (0.0:100.0) | 40.0 (0.0:95.0) | < 0.001 (0.001) | |
| Level of symptoms1, median (range) | 21.0 (0.0:100.0) | 62.0 (10.0:90.0) | < 0.001 (0.001) | |
| Difference in outcome parameters: | ||||
| Difference in Pain1, median (range) | 13.0 (90.0:100.0) | 47.0 (37.0:90.0) | 0.008 (0.0499) | |
| Difference in Quality of life after surgery1, median (range) | 15.0 (100.0:98.0) | 44.0 (99.0:38.0) | 0.013 (0.078) | |
| Difference in level of symptoms1, median (range) | 17 (56.0:100.0) | 46.0 (36.0:88.0) | 0.299 (1.796) | |
| Education 0-9 yr | Education 9-12 yr | Education > 12 yr | P value (adjusted) | |
| Baseline characteristics | ||||
| BMI, mean ± SD | 28.7± 5 | 30.0 ± 6 | 30.5 ± 5 | < 0.001 (0.007) |
| Age, mean ± SD | 64.8 ± 10 | 67.8 ± 10 | 67.7 ± 11 | < 0.001 (0.005) |
| Gender | ||||
| Male | 92 (36.1) | 159 (42.9) | 54 (26.6) | < 0.001 (0.003) |
| Female | 163 (63.9) | 212 (57.1) | 149 (73.4) | |
| Ethnicity | ||||
| Majority ethnicity | 248 (97.3) | 360 (97) | 156 (76.8) | < 0.001 (< 0.001) |
| Minority ethnicity | 7 (2.7) | 11 (3) | 47 (23.2) | |
| Smoking: | ||||
| Non-smoker | 155 (60.8) | 207 (55.8) | 123 (60.6) | 0.003 (0.017) |
| Former smoker | 74 (29) | 100 (27) | 37 (18.2) | |
| Active smoker | 26 (10.2) | 64 (17.3) | 43 (21.2) | |
| Preoperative level of function and symptoms | ||||
| Walking aid outside the home | 198 (77.6) | 273 (73.6) | 119 (58.6) | 0.005 (0.002) |
| None | 35 (13.7) | 55 (14.8) | 41 (20.2) | |
| One cane | 11 (4.3) | 12 (3.2) | 10 (4.9) | |
| Two canes | 10 (3.9) | 27 (7.3) | 32 (15.8) | |
| Wheeled walker housebound | 1 (0.4) | 4 (1.1) | 1 (0.5) | |
| Oxford knee score, mean ± SD | 24.6 ± 8 | 23.8 ± 7 | 21.5 ± 8 | < 0.001 (< 0.001) |
| Knee pain during activity1, median (range) | 59 (0:99) | 63 (0:100) | 67 (6:100) | < 0.001 (0.002) |
| Quality of life before surgery1, median (range) | 45 (0:100) | 47 (0:100) | 50 (0:100) | 0.634 (3.170) |
| Level of symptoms before surgery1, median (range) | 51 (0:100) | 50 (0:100) | 50 (0:100) | 0.634 (3.171) |
| Preoperative expectations | ||||
| Expectations to knee pain caused by use of hip 1 yr after surgery1, median (range) | 4 (0:95) | 2 (0:96) | 2 (0:100) | 0.003 (0.008) |
| Expectations to quality of life 1 yr after surgery1, median (range) | 90 (0:100) | 94 (0:100) | 96 (0:100) | < 0.001 (0.002) |
| Expectations to level of symptoms 1 yr after surgery1, median (range) | 4 (0:82) | 2 (0:99) | 2 (0:99) | < 0.001 (0.001) |
| Postoperative level of function and symptoms: | ||||
| Oxford knee score, median (range) | 40 (8.0:47.0) | 37 (3.0:48.0) | 37.5 (7.0:48.0) | 0.240 (0.960) |
| Knee pain during activity, Post-OP1, median (range) | 12 (0.0:90.0) | 20 (0.0:100.0) | 26 (0.0:97.0) | 0.002 (0.006) |
| Quality of life after surgery1, median (range) | 77.5 (13.0:98.0) | 70 (0.0:100.0) | 69 (0.0:100.0) | 0.055 (0.219) |
| Level of symptoms after surgery1, median (range) | 21 (0.0:94.0) | 23 (0.0:100.0) | 31 (0.0:95.0) | 0.182 (0.728) |
| Difference in outcome parameters: | ||||
| Difference in Pain1, median (range) | 8 (-11.0:84.0) | 15 (-90.0:100.0) | 21 (-48.0:97.0) | 0.012 (0.069) |
| Difference in Quality of life Post-OP1, median (range) | -7 (-67.0:95.0) | -20 (-100.0:98.0) | -18 (-99.0:98.0) | 0.003 (0.017) |
| Difference in level of symptoms1, median (range) | 15 (-14.0:89.0) | 17 (-56.0:100.0) | 18 (-41.0:95.0) | 0.532 (3.193) |
Response-rates to the post-OP questionnaire were 44.6% (n = 370). We found a higher response-rate for patients of majority ethnicity (46.2% vs 26.2% for minority ethnicity patients). We also found that responders overall had a longer duration of education, the biggest difference seen in education of 0-9 years (29.2% for non-responders vs 18.6% for responders, P < 0.001). The differences between responders and non-responders for other parameters was not statistically significant.
Patients of minority ethnicity had significantly lower mean OKS one year post-OP compared with patients of majority ethnicity (P = 0.002). Patients of minority ethnicity also reported higher pain during activity (P = 0.001), a significantly lower QoL (P = 0.001) and significantly higher overall symptom score (P = 0.001) compared with patients of majority ethnicity. Although patients of minority ethnicity had higher post-OP pain, we also found a larger difference between pre-OP and post-OP pain compared to patients of majority ethnicity (P = 0.049) (Table 2). Patients with educations > 12 years had significantly higher knee pain post-OP (P = 0.006), however there was also a larger difference between pre-OP and post-OP pain during activity (P = 0.069) and QoL (P = 0.017) (Table 3).
In this prospective study, we found that patients of minority ethnicity report more severe pre-OP symptoms (lower OKS and higher overall pain level) and have lower expectations for post-OP outcome compared to patients of majority ethnicity. Patients of minority ethnicity also report more severe symptoms post-OP, however our response rate was too low to regard the results as significant. Patients with an education > 12 years report more severe pre-OP symptoms (OKS and overall pain level) compared to patients with both < 9 years and 9-12 years of education. Post-OP, we found that patients with an education > 12 years reported higher overall pain.
It is generally acknowledged that patient’s overall health is associated with socioeconomic factors[23]. Recently, Lavernia et al[11] showed that expectations and the knowledge of prosthetic surgery in patients with knee and hip arthritis depend on ethnicity. The same observation was made by Krupic et al[12], who showed that patients born outside of Sweden had a poorer outcome after total hip replacement than patients born within Sweden. This is concurrent with our results, as we find that patients born outside the country have greater preoperative disability (lower OKS and higher VAS for pain). However, the studies describing the correlations between ethnicity and surgery are few and based on short-term observation.
In general, minority groups in western countries are less likely to undergo knee replacement than their locally-born counterparts[24-26]. Our data show that patients of minority ethnicity have lower expectations for surgery and suffer from more severe symptoms pre-OP than patients of majority ethnicity. The reason for this difference is unknown, but we could speculate that patients of minority ethnicity might seek doctors at a more progressed stage of the disease compared to patients of majority ethnicity due to cultural or language barriers. Shahid et al[25] reports that racial disparities in African Americans compared to Caucasian Americans are caused by patient preferences, patients education/knowledge of osteoarthritis (OA) and expectations for post-OP outcome. Minority Americans were found to have lower expectations of the overall effect of OA surgery and higher expectations of post-OP pain[24,27-29]. This supports our findings that patients of minority ethnicity have lower pre-OP expectations. African Americans have been found to be less knowledgeable regarding OA, to have a lesser understanding of the risks and benefits of surgery compared to White Americans[30,31], and to have a lower preference for surgical treatment[25]. This could explain our finding of more severe pre-OP symptoms in patients of minority ethnicity, as patient preference has been associated with referral from GP to orthopaedic evaluation in OA patients[25]. Many American-based studies report that minorities are more likely to undergo surgery at low volume hospitals and that this is a cause for poorer outcome. This does not apply in Denmark, as most patients are treated in the public system and all our data are based on patients treated in one high-volume public institution. Severity of pre-OP symptoms has been shown to influence outcome[4-6]. Although our post-OP response rate was too low to make any conclusions, we did find that the overall outcome for patients born outside the country was poorer compared to patients born in the country, which is concurrent with the reportings of Krupic et al[12]. Similar findings have been reported in American patients, where minorities are reported to have a higher post-OP complication rate, mortality and longer hospital stay compared to white Americans[25,26].
The duration of education is key to how individuals seek and handle information[32], and therefore important with regard to how patients cope with medical treatment. We found that patients with > 12 years of education had more severe pre-OP symptoms than those with shorter educations. This result is not concurrent with findings in previous studies, as these have found more severe symptoms in patients with shorter education; an educational level less than high school in the United States has been associated with greater pre-OP pain and lower function in TKA patients by Lopez-Olivo et al[33]. Although we found significant P-values for these parameters, the differences of OKS was only three, two and nine on VAS, thus both below MCID and not convincingly clinically-relevant. High education has previously been found to be a predictor for better post-OP outcomes by Greene et al[13], while others report no significance[34]. We found that patients with short educations reported a lower post-OP pain severity (MCID below cut-off level), and could find no other significant influence of education on other outcome parameters. Although statistically significant, Greene et al[13] also found very small differences that were not clinically relevant. It is thus uncertain whether education can be used as an outcome predictor for TKA patients. Combined with our low response rate, no findings regarding education and post-OP outcome were convincing.
Our study has several limitations, as this is a purely descriptive and hypothesis-generating study. External validation is a major limitation for our study, as both ethnicity and education differ between countries. Education differs greatly across the world; we have, however, tried to accommodate this by dividing patients into three groups based on their number of education years rather than completed degrees. Ethnic minority groups within a country are of course different across the world. In this study, we try to address the issues that arise in healthcare for people born outside their residential country and not the health care behaviour of specific ethnic groups. We believe that our results can contribute to the knowledge base for how to approach racial disparities within a population.
Our results are based on regression analysis, adjusting for patient-related factors such as gender, smoking, alcohol consumption, co-morbidities, symptoms, self-reported QoL and expectations as shown in the Tables. Residual confounders include the missing evaluation of radiologic status/alignment. Surgical factors have been shown to influence patient satisfaction in other studies, and this is unaccounted for in our study; however, all patients were treated by the same high-volume surgeons in a well-defined fast-track setup with standardized treatment for pain, mobilisation and post-OP care, as described in the Methods section[1]. All treatments in Denmark are free of charge, and therefore socioeconomic factors do not affect the choice of implant in our population. Only 44.6% of patients responded to our post-OP questionnaire, and response rate was even lower for patients born outside the country (26.2% vs 46.2% for patients born in the country). We therefore make no conclusions regarding significance of either ethnicity or education on post-OP measurements. In this study, we have only evaluated results based on patient-reported outcome measures, and not other outcome measures such as the length of hospital stay, infection rate or other complication rates.
In conclusion, minority ethnicity and duration of education influence pre-OP disability and expectations in patients undergoing TKA. This should be taken into account when patients are advised pre-operatively.
The background, present status, and significance of the study should be described in detail. It is known that patient-related factors, socioeconomic factors and education influence patient outcomes in general, however this area is difficult to investigate and thus these factors are often confounding in scientific work. These factors are also known to be of significance in patients scheduled to undergo total knee arthroplasty (TKA), and this study provides information regarding the significance of education and ethnicity in these patients.
During recent years, a trend towards optimized care, standardized patient evaluations and fast-track surgery has been influencing orthopaedic surgery. Although beneficial in many ways, this concept may not be appropriate for all patients. Levels of education and ethnicity is known to influence patients, and understanding the significance of these factors in TKA patients will assist healthcare providers in optimizing treatment plans for individual patients.
The objectives of this study were to determine if level of education and ethnicity influence the preoperative status of patients undergoing primary TKA or patient expectations for surgery. The significance of ethnicity and level of education on outcome following TKA is still uncertain and should be an objective for future research.
We prospectively included 829 patients undergoing TKA. Patients filled in pre-operative questionnaires with information regarding place of birth, duration of education, expectations for outcome of surgery and baseline characteristics. Statistical analyses were performed to identify the significance of ethnicity and level of education.
We find that patients undergoing TKA in a country different to where they were born report more severe preoperative symptoms and lower expectations for postoperative outcome. We also found that patients with a longer duration of education report more severe pre-operative symptoms. We found that patients of minority ethnicity and with an education > 12 years had more severe symptoms post-operatively. However, due to a low response rate, we cannot draw generalizable conclusions about these results. The significance of ethnicity and education on post-operative results remain to be sufficiently described.
Minority ethnicity and duration of education influence preoperative disability and expectations in patients undergoing TKA. Patients undergoing TKA in a country different to where they were born need individualised evaluation to accommodate potential differences from the general patient population. Patients of minority ethnicity report more severe pro-operative symptoms before undergoing TKA and lower expectations for post-operative outcome. Patients with educations longer than 12 years report more severe symptoms before undergoing TKA. Minority ethnicity and duration of education influence preoperative disability and expectations in patients undergoing TKA. Ethnicity and education influence patients’ perception of disease. Socioeconomic factors should be considered when evaluating patients.
Our study provides knowledge regarding the significance of ethnicity and education on preoperative disability and expectations of outcome. This information is key for healthcare professionals when evaluating patients prior to TKA, as it allows for the identification of individuals who may not be suitable for a standardized information regimen. It is important to investigate the significance of socioeconomic factors on outcome following TKA.
Manuscript source: Unsolicited manuscript
Specialty type: Orthopedics
Country of origin: Denmark
Peer-review report classification
Grade A (Excellent): 0
Grade B (Very good): 0
Grade C (Good): C, C
Grade D (Fair): 0
Grade E (Poor): 0
P- Reviewer: Lin JA, Surace MF S- Editor: Cui LJ L- Editor: Filipodia E- Editor: Song H
| 1. | Husted H. Fast-track hip and knee arthroplasty: clinical and organizational aspects. Acta Orthop Suppl. 2012;83:1-39. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 174] [Cited by in RCA: 193] [Article Influence: 14.8] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 2. | Bourne RB, Chesworth BM, Davis AM, Mahomed NN, Charron KD. Patient satisfaction after total knee arthroplasty: who is satisfied and who is not? Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2010;468:57-63. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 1654] [Cited by in RCA: 1851] [Article Influence: 123.4] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 3. | Klit J, Jacobsen S, Rosenlund S, Sonne-Holm S, Troelsen A. Total knee arthroplasty in younger patients evaluated by alternative outcome measures. J Arthroplasty. 2014;29:912-917. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 33] [Cited by in RCA: 43] [Article Influence: 3.9] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 4. | Núñez M, Núñez E, Segur JM, Maculé F, Sanchez A, Hernández MV, Vilalta C. Health-related quality of life and costs in patients with osteoarthritis on waiting list for total knee replacement. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2007;15:258-265. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 45] [Cited by in RCA: 41] [Article Influence: 2.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 5. | Petersen KK, Simonsen O, Laursen MB, Nielsen TA, Rasmussen S, Arendt-Nielsen L. Chronic postoperative pain after primary and revision total knee arthroplasty. Clin J Pain. 2015;31:1-6. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 63] [Cited by in RCA: 100] [Article Influence: 10.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 6. | Sakellariou VI, Poultsides LA, Ma Y, Bae J, Liu S, Sculco TP. Risk Assessment for Chronic Pain and Patient Satisfaction After Total Knee Arthroplasty. Orthopedics. 2016;39:55-62. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 41] [Cited by in RCA: 52] [Article Influence: 5.8] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 7. | Alattas SA, Smith T, Bhatti M, Wilson-Nunn D, Donell S. Greater pre-operative anxiety, pain and poorer function predict a worse outcome of a total knee arthroplasty. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2017;25:3403-3410. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 72] [Cited by in RCA: 102] [Article Influence: 12.8] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 8. | Baker PN, van der Meulen JH, Lewsey J, Gregg PJ; National Joint Registry for England and Wales. The role of pain and function in determining patient satisfaction after total knee replacement. Data from the National Joint Registry for England and Wales. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2007;89:893-900. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 604] [Cited by in RCA: 711] [Article Influence: 39.5] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 9. | Choong PF, Dowsey MM, Stoney JD. Does accurate anatomical alignment result in better function and quality of life? Comparing conventional and computer-assisted total knee arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 2009;24:560-569. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 313] [Cited by in RCA: 338] [Article Influence: 21.1] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 10. | Longstaff LM, Sloan K, Stamp N, Scaddan M, Beaver R. Good alignment after total knee arthroplasty leads to faster rehabilitation and better function. J Arthroplasty. 2009;24:570-578. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 266] [Cited by in RCA: 295] [Article Influence: 18.4] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 11. | Lavernia CJ, Contreras JS, Parvizi J, Sharkey PF, Barrack R, Rossi MD. Do patient expectations about arthroplasty at initial presentation for hip or knee pain differ by sex and ethnicity? Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2012;470:2843-2853. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 14] [Cited by in RCA: 17] [Article Influence: 1.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 12. | Krupic F, Eisler T, Garellick G, Kärrholm J. Influence of ethnicity and socioeconomic factors on outcome after total hip replacement. Scand J Caring Sci. 2013;27:139-146. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 17] [Cited by in RCA: 20] [Article Influence: 1.5] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 13. | Greene ME, Rolfson O, Nemes S, Gordon M, Malchau H, Garellick G. Education attainment is associated with patient-reported outcomes: findings from the Swedish Hip Arthroplasty Register. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2014;472:1868-1876. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 44] [Cited by in RCA: 64] [Article Influence: 5.8] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 14. | Bugada D, Allegri M, Gemma M, Ambrosoli AL, Gazzerro G, Chiumiento F, Dongu D, Nobili F, Fanelli A, Ferrua P. Effects of anaesthesia and analgesia on long-term outcome after total knee replacement: A prospective, observational, multicentre study. Eur J Anaesthesiol. 2017;34:665-672. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 178] [Cited by in RCA: 208] [Article Influence: 29.7] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 15. | Andersen LØ, Husted H, Otte KS, Kristensen BB, Kehlet H. High-volume infiltration analgesia in total knee arthroplasty: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Acta Anaesthesiol Scand. 2008;52:1331-1335. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 126] [Cited by in RCA: 125] [Article Influence: 7.4] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 16. | Andersen LØ, Husted H, Otte KS, Kristensen BB, Kehlet H. A compression bandage improves local infiltration analgesia in total knee arthroplasty. Acta Orthop. 2008;79:806-811. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 81] [Cited by in RCA: 77] [Article Influence: 4.5] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 17. | Jørgensen CC, Jacobsen MK, Soeballe K, Hansen TB, Husted H, Kjærsgaard-Andersen P, Hansen LT, Laursen MB, Kehlet H. Thromboprophylaxis only during hospitalisation in fast-track hip and knee arthroplasty, a prospective cohort study. BMJ Open. 2013;3:e003965. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 80] [Cited by in RCA: 75] [Article Influence: 6.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 18. | Husted H, Lunn TH, Troelsen A, Gaarn-Larsen L, Kristensen BB, Kehlet H. Why still in hospital after fast-track hip and knee arthroplasty? Acta Orthop. 2011;82:679-684. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 290] [Cited by in RCA: 291] [Article Influence: 20.8] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 19. | Berliner JL, Brodke DJ, Chan V, SooHoo NF, Bozic KJ. Can Preoperative Patient-reported Outcome Measures Be Used to Predict Meaningful Improvement in Function After TKA? Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2017;475:149-157. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 152] [Cited by in RCA: 223] [Article Influence: 27.9] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 20. | Clement ND, MacDonald D, Simpson AH. The minimal clinically important difference in the Oxford knee score and Short Form 12 score after total knee arthroplasty. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2014;22:1933-1939. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 254] [Cited by in RCA: 349] [Article Influence: 31.7] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 21. | Beard DJ, Harris K, Dawson J, Doll H, Murray DW, Carr AJ, Price AJ. Meaningful changes for the Oxford hip and knee scores after joint replacement surgery. J Clin Epidemiol. 2015;68:73-79. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 338] [Cited by in RCA: 375] [Article Influence: 37.5] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 22. | Tubach F, Ravaud P, Baron G, Falissard B, Logeart I, Bellamy N, Bombardier C, Felson D, Hochberg M, van der Heijde D. Evaluation of clinically relevant changes in patient reported outcomes in knee and hip osteoarthritis: the minimal clinically important improvement. Ann Rheum Dis. 2005;64:29-33. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 779] [Cited by in RCA: 808] [Article Influence: 40.4] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 23. | Costa-Font J, Hernández-Quevedo C. Measuring inequalities in health: what do we know? What do we need to know? Health Policy. 2012;106:195-206. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 63] [Cited by in RCA: 60] [Article Influence: 4.6] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 24. | Katz JN. Persistence of Racial and Ethnic Differences in Utilization and Adverse Outcomes of Total Joint Replacement. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2016;98:1241-1242. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 13] [Cited by in RCA: 14] [Article Influence: 1.6] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 25. | Shahid H, Singh JA. Racial/Ethnic Disparity in Rates and Outcomes of Total Joint Arthroplasty. Curr Rheumatol Rep. 2016;18:20. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 60] [Cited by in RCA: 91] [Article Influence: 10.1] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 26. | Zhang W, Lyman S, Boutin-Foster C, Parks ML, Pan TJ, Lan A, Ma Y. Racial and Ethnic Disparities in Utilization Rate, Hospital Volume, and Perioperative Outcomes After Total Knee Arthroplasty. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2016;98:1243-1252. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 125] [Cited by in RCA: 184] [Article Influence: 20.4] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 27. | Groeneveld PW, Kwoh CK, Mor MK, Appelt CJ, Geng M, Gutierrez JC, Wessel DS, Ibrahim SA. Racial differences in expectations of joint replacement surgery outcomes. Arthritis Rheum. 2008;59:730-737. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 111] [Cited by in RCA: 123] [Article Influence: 7.2] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 28. | Lavernia CJ, Alcerro JC, Rossi MD. Fear in arthroplasty surgery: the role of race. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2010;468:547-554. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 47] [Cited by in RCA: 71] [Article Influence: 4.7] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 29. | Weng HH, Kaplan RM, Boscardin WJ, Maclean CH, Lee IY, Chen W, Fitzgerald JD. Development of a decision aid to address racial disparities in utilization of knee replacement surgery. Arthritis Rheum. 2007;57:568-575. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 58] [Cited by in RCA: 69] [Article Influence: 3.8] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 30. | Figaro MK, Williams-Russo P, Allegrante JP. Expectation and outlook: the impact of patient preference on arthritis care among African Americans. J Ambul Care Manage. 2005;28:41-48. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 36] [Cited by in RCA: 42] [Article Influence: 2.1] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 31. | Ibrahim SA. Racial and ethnic disparities in hip and knee joint replacement: a review of research in the Veterans Affairs Health Care System. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2007;15 Suppl 1:S87-S94. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 34] [Cited by in RCA: 44] [Article Influence: 2.4] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 32. | Hankins FH, American Sociological Association WC-L, American Sociological Society. American Sociological Review. Vol 60. American Sociological Society;. 1995;. |
| 33. | Lopez-Olivo MA, Landon GC, Siff SJ, Edelstein D, Pak C, Kallen MA, Stanley M, Zhang H, Robinson KC, Suarez-Almazor ME. Psychosocial determinants of outcomes in knee replacement. Ann Rheum Dis. 2011;70:1775-1781. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 132] [Cited by in RCA: 130] [Article Influence: 9.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 34. | Noiseux NO, Callaghan JJ, Clark CR, Zimmerman MB, Sluka KA, Rakel BA. Preoperative predictors of pain following total knee arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 2014;29:1383-1387. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 71] [Cited by in RCA: 87] [Article Influence: 7.9] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |