Published online Jun 18, 2016. doi: 10.5312/wjo.v7.i6.376
Peer-review started: February 14, 2016
First decision: March 1, 2016
Revised: March 7, 2016
Accepted: March 24, 2016
Article in press: March 25, 2016
Published online: June 18, 2016
Processing time: 123 Days and 23.3 Hours
AIM: To determine the impact of different characteristics on postoperative outcomes for patients in a joint arthroplasty Perioperative Surgical Home (PSH) program.
METHODS: A retrospective review was performed for patients enrolled in a joint arthroplasty PSH program who had undergone primary total hip arthroplasty (THA) and total knee arthroplasty (TKA). Patients were preoperatively stratified based on specific procedure performed, age, gender, body mass index (BMI), American Society of Anesthesiologists Physical Classification System (ASA) score, and Charleston Comorbidity Index (CCI) score. The primary outcome criterion was hospital length of stay (LOS). Secondary criteria including operative room (OR) duration, transfusion rate, Post-Anesthesia Care Unit (PACU) stay, readmission rate, post-operative complications, and discharge disposition. For each outcome, the predictor variables were entered into a generalized linear model with appropriate response and assessed for predictive relationship to the dependent variable. Significance level was set to 0.05.
RESULTS: A total of 337 patients, 200 in the TKA cohort and 137 in the THA cohort, were eligible for the study. Nearly two-third of patients were female. Patient age averaged 64 years and preoperative BMI averaged 29 kg/m2. The majority of patients were ASA score III and CCI score 0. After analysis, ASA score was the only variable predictive for LOS (P = 0.0011) and each increase in ASA score above 2 increased LOS by approximately 0.5 d. ASA score was also the only variable predictive for readmission rate (P = 0.0332). BMI was the only variable predictive for PACU duration (P = 0.0136). Specific procedure performed, age, gender, and CCI score were not predictive for any of the outcome criteria. OR duration, transfusion rate, post-operative complications or discharge disposition were not significantly associated with any of the predictor variables.
CONCLUSION: The joint arthroplasty PSH model reduces postoperative outcome variability for patients with different preoperative characteristics and medical comorbidities.
Core tip: The Perioperative Surgical Home (PSH) model is designed to improve healthcare delivery and reduce medical costs. In this study, patients in a joint arthroplasty PSH program were stratified based on preoperative characteristics and comorbidities to determine if these variables would impact postoperative results. Our results suggest that a joint arthroplasty PSH program may improve postoperative consistency and limit the influence of different patient attributes on surgical outcome. Arthroplasty patients with preoperative characteristics traditionally considered risk factors for negative outcomes, such as a high body mass index or an elderly age, may benefit from enrollment in a PSH program.
- Citation: Phan DL, Ahn K, Rinehart JB, Calderon MD, Wu WD, Schwarzkopf R. Joint arthroplasty Perioperative Surgical Home: Impact of patient characteristics on postoperative outcomes. World J Orthop 2016; 7(6): 376-382
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2218-5836/full/v7/i6/376.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5312/wjo.v7.i6.376
The relative increase in the elderly population, combined with changing indications for younger patients, is predicted to result in a growing number of patients undergoing total joint arthroplasty (TJA)[1-3]. This will likely result in a diverse surgical population, with different medical comorbidities and characteristics, which can potentially lead to equally variable results. Standardizing and streamlining the operative experience and minimizing procedural and patient variables will thus be essential to ensure optimal and predictable outcomes.
The Perioperative Surgical Home (PSH) has been promoted as a patient-centered model to improve health, healthcare delivery, and reduce medical costs[4-6]. A multidisciplinary team led by the primary surgeon and anesthesiologist engages with the patient, starting from the moment the decision for surgery is made all the way through to the post-operative 30-d recovery phase, to yield the best possible results and optimize value for both the patient and the healthcare system. PSH is ideally designed to enhance the perioperative experience, regardless of preoperative patient conditions, and has been implemented in different patient populations with beneficial results[7].
The purpose of this study was to examine the results of a TJA PSH protocol designed and adopted at our institution. Preoperative stratification and postoperative outcomes for patients undergoing primary total knee (TKA) and primary total hip (THA) arthroplasty were analyzed to determine the effects of PSH. Our hypothesis was that the joint arthroplasty PSH will lead to equivalent or improved perioperative outcomes regardless of our patients’ preoperative comorbidity burden.
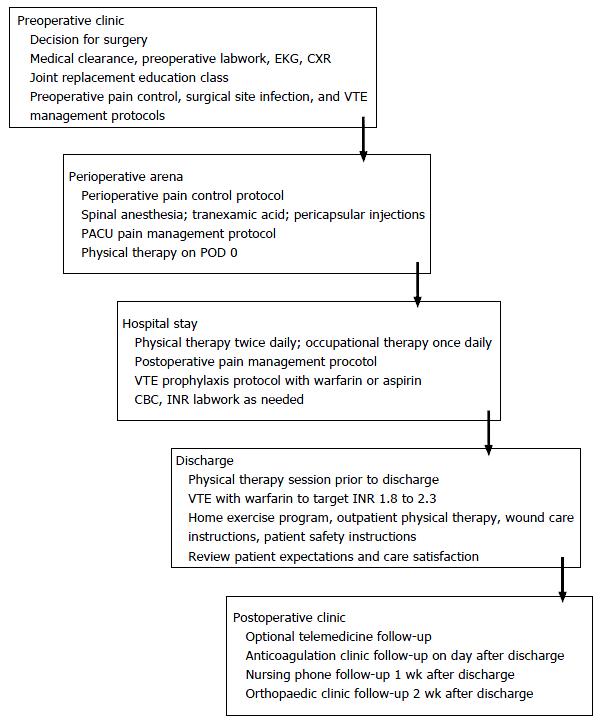
After institutional review board approval was obtained, a retrospective review was performed of joint arthroplasty PSH patients undergoing elective primary TKA and THA at our institution from October 2012 through February 2015. The structure of the PSH protocol is detailed in Figure 1. All surgeries were performed by the senior author. Exclusion criteria included revision, bilateral, and acute post-traumatic arthroplasty. During surgery, all TKA patients were supine and underwent a medial parapatellar approach with the use of a tourniquet, while THA patients were lateral decubitus and underwent either a posterolateral or modified lateral surgical approach.
Patient charts were pulled from the PSH data mart for analysis. Preoperative variables that were stratified included: Specific procedure, age, gender, body mass index (BMI), Charleston Comorbidity Index (CCI), and American Society of Anesthesiologists Physical Classification System score (ASA). The primary outcome criteria measured was length of stay (LOS); secondary outcomes included operating room (OR) duration, transfusion rate, Post-Anesthesia Care Unit (PACU) stay, readmission rate, post-operative complications, and discharge disposition up to 30-d post-surgery.
For the primary and secondary outcomes, the predictor variables were entered into a generalized linear model with appropriate response (Linear for scalar measures, Gamma for counts or time, logit for binary outcomes like readmissions) and assessed for predictive relationship to the dependent variable. Significance level was set to 0.01 to correct for multiple comparisons. Demographics and variable summaries were presented as mean ± SD, or as percentage for binary outcomes. Statistics were performed with Microsoft Excel (Microsoft, Redmond, WA); SPSS (IBM, Armonk NY), and R (R-Project, https://www.r-project.org/).
Our cohort included 337 patients, 200 undergoing TKA and 137 undergoing THA. The average age was slightly over 60 years of age and almost two-thirds of patients were female. The most common preoperative medical comorbidity was hypertension, while the majority of patients were rated as ASA III and CCI 0 when evaluating for overall medical condition. Complete patient demographics are shown in Table 1. The average total OR time was slightly over three hours and the average PACU stay was slightly over two hours. The average hospital length of stay was two and a half days. The rate of hospital readmission was minimal. Complete surgical outcomes are shown in Table 2.
| Number | 337 |
| Age (yr) | 63.7 ± 13.8 |
| Gender (M/F) | 123/214 |
| Procedure (THA/TKA) | 137/200 |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 29.4 ± 6.2 |
| Congestive heart failure | 6 (1.8%) |
| Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease | 25 (7.4%) |
| Diabetes mellitus | 59 (17.5%) |
| Hypertension | 198 (58.8%) |
| History of myocardial infarction | 17 (5.0%) |
| American Society of Anesthesiologist score | I-0 (0.0%) II-67 (19.9%) III-255 (75.7%) IV-15 (4.5%) |
| Charlson Comorbidity Index score | 0-226 (67.1%) 1-85 (25.2%) 2-24 (7.1%) 6-2 (0.6%) |
| OR duration (min) | 189 ± 60 |
| PACU duration (min) | 138 ± 80 |
| Transfusion rate | 32 (9.5%) |
| Length of stay (d) | 2.5 ± 0.8 |
| Severe postoperative nausea and vomiting | 15 (4.5%) |
| Emergency department visits | 7 (2.1%) |
| Readmissions | 2 (0.6%) |
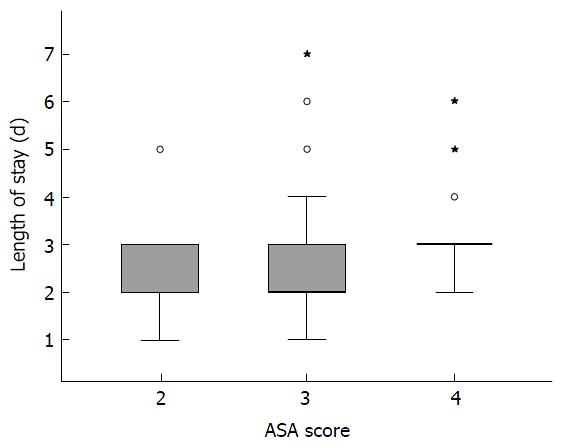
With regards to the primary outcome, age, BMI, and ASA score were all predictive of LOS. Specific procedure performed, gender, and CCI scores were non-significant. ASA score was strongly predictive of LOS (P = 0.0011) as shown in Figure 2; on average each increase in ASA score above 2 increased LOS by 0.5 d. Age was only weakly predictive (P = 0.0021), with older patients having a slightly shorter LOS. Similarly, BMI was weakly predictive (P = 0.0003), with higher BMI patients having slightly shorter LOS.
With regards to secondary outcomes, ASA score was the only variable predictive of readmission rate (P = 0.0332). With a 0.6% readmission rate, however, the power for this outcome was low. BMI was the only variable predictive of increased PACU duration (P = 0.0136), with higher BMI leading to slightly longer PACU stay. Specific procedure performed, age, gender, and CCI score were not predictive for any of the secondary outcome criteria. OR duration, transfusion rate, post-operative complications or discharge disposition were not significantly associated with any of the predictor variables.
TKA and THA are common orthopaedic procedures that provide reliable and beneficial outcomes for the majority of patients[8,9]. However, despite advancements in surgical implants, technique, and management, a minority of patients continue to do comparatively poorly[10,11]. The expected significant increase in the patient population eligible for TJA will only increase the overall number of patients that have suboptimal outcomes. The goal of this study was to examine if TJA patients, managed under a new surgical home care model, perioperative outcomes were equivalent or better as compared to national standards.
The PSH has been endorsed by the American Society of Anesthesiologists as a model to decrease the variability in perioperative care[4]. PSH starts in the office, where immediately after a decision for surgery is made, both surgical and anesthesiology teams are in constant communication with the patient. Perioperative factors such as surgical technique, anesthetic delivery, pain control, and discharge disposition are addressed to help formulate an operative plan and set expectations. During surgery, perioperative variables are minimized due to consistent protocol based surgical and anesthesiology performance; potential pitfalls are avoided by adhering to the operative plan and perioperative pathways and deviating only when necessary. After surgery, dedicated inpatient ancillary staff, including nurses and therapists, assist the surgical and anesthesiology teams to provide a smooth transition to discharge. Patients follow-up with the surgical and anesthesiology teams to ensure postoperative continuity of care. By having a patient-centered team assuring continuity of care throughout the surgical period and applying evidence-based medicine in a consistent and standardized manner, PSH is designed to minimize errors, reduce unnecessary costs, and improve patient outcomes. Studies examining the benefits of PSH are currently limited, likely due to only a recent increase in popularity. However, PSH has been implemented in cardiac and vascular patients[12] as well as in a Veterans Affairs population[13] with success, and results are expected to be forthcoming as more institutions adopt the PSH model.
In the current orthopaedic literature, only 2 significant studies have been published analyzing patients in a PSH model. Boraiah et al[14] recently published a study examining the utility of a scoring system, the Readmission Risk Assessment Tool, for TJA patients in their PSH model and noted that preoperative patient stratification could predict readmission rates. However, the benefits of PSH on patient outcomes were not directly examined. The results of PSH implementation have recently been published after adoption of a TJA protocol at our institution, with postoperative outcome measures comparable to national benchmarks[6]. However, this study did not stratify patients preoperatively to determine if the outcomes were due to PSH or if there was an inherent selection bias that played a role. The current study is a follow-up to that first initial analysis to examine if the benefits of the PSH model could be isolated and specified, and to predict if similar outcomes could be achieved among patients with a differing preoperative comorbidity burden.
Preoperative stratification took into account different variables, all of which have been examined previously in the literature. An increased patient age has been shown to result in higher hospital LOS[15-17], readmission rates[15,18-20], increased complication rate[16,21,22], and disposition to an extended care facility[16]. Interestingly, a relatively young age at time of surgery has also been shown to increase readmission rates[11,20]. Male gender resulted in a higher readmission rate in most studies[11,19,23,24] while female gender was the predictor of readmission in another[25], and associated with a longer LOS[26]. Male gender also predicted a higher complication rate[24]. Obesity resulted in a longer hospital LOS[17,27,28], readmission rate[19,20,23,27], and complication rate[21,22,28]. An underweight status has also been shown to increase the rate of readmission[20]. A higher ASA score predicted a longer LOS[26], higher rate of readmission[23,25,29], and complication rate[29]. A higher CCI score predicted higher rate of readmission[30] and a higher complication rate[31].
In the current study, the influence of preoperative variables appeared to be minimized as patients underwent TJA in a PSH care model. As contrasted to the previously mentioned studies, patient gender, procedure type, and CCI score did not have any significant correlation with peri-operative outcome criteria, including LOS, PACU duration, discharge disposition, complication rate, and readmission rate. This does not imply that these variables do not play a role in patient outcomes. Rather, it suggests that within a PSH care model, the effects of these variables on the outcomes in TJA patients are reduced. This is likely due to standardization of the entire continuum of perioperative care that includes close follow-up of patients by a dedicated PSH team, and incorporation of evidence-based clinical pathways. These processes help reduce the variability in the delivery and quality of care typically found within a traditional care model. The effect of age was also diminished. Similarly, preoperative BMI also had a diminished effect with outcome criteria, aside from PACU duration.
The effects of both age and BMI on LOS, while very weak, were the opposite of what has been previously reported in other studies (both increasing age and BMI led to marginally but statistically significant shorter LOS). We hypothesize that this may be because younger, thinner patients who are having total joint replacements are more likely to have other physical or social factors contributing to their need for replacement which may contribute to longer LOS (for example narcotic dependence), as opposed to older or heavier patients who are more likely to have uncomplicated primary osteoarthritis joint degeneration.
Higher ASA scores were strongly predictive for an increase in hospital LOS, with each point increase above 2 resulting in an increased stay of 0.5 d. Similarly, higher ASA scores were strongly predictive for patient readmission rates. There was not a strong correlation between ASA scores and other outcome criteria, which is surprising because a large number of readmissions are due to post-operative complications. Also surprising is that CCI scoring did not result in a similar correlation to LOS and readmission rates. Like the ASA model, CCI is designed to evaluate overall patient comorbidity and as such it would be expected that stratification of both would lead to comparable outcomes. It is possible that the ASA score intrinsically includes the information contained in CCI such that using both in the same model becomes redundant. The ASA score is also more discriminating between the full range of mild to severe comorbidity, whereas the CCI tends to discriminate better between moderate and severe comorbidity only.
There were several limitations to the study that may have affected the results. The study was retrospective in nature, which may have led to inadvertent biases. However, preoperative exclusion criteria and stratification was stringently designed in order to limit any bias. The surgeries were all performed by one surgeon, which may have skewed outcomes but also limited surgical variation. This was supported by using standard surgical approaches and the same implant system for all patients. Although samples sizes were not small, a larger patient population would have increased the power of the study. Patient outcomes were included only up to the 30-d postoperative period and changes afterwards were not incorporated into outcome analysis. Finally, patients readmitted elsewhere would not have been captured within our study, although such a limitation is not unique to our study. Our joint replacement PSH was designed to encompass perioperative patient care up to 30-d after surgery; as such we felt it appropriate to end data collection at this time point.
The PSH is a patient-centered care model designed to provide coordinated care through shared decision-making and standardization using evidence-based medicine. Through physician-led multidisciplinary care, this care model aims to add value and help achieve Institute for Healthcare’s Triple Aim of improving patient-care experience and population health at a reduced cost. Our study suggests that patient factors, which have historically influenced TJA results, such as age, gender, CCI scores, and BMI, may be minimized. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first study examining the outcomes of TJA patients in a PSH model. Further prospective studies are needed in order to support our results.
Perioperative Surgical Home (PSH) is a patient-centered program designed to improve clinical efficiency, optimize surgical results, and decrease the financial burden on healthcare. The increasing number of patients who will undergo total joint arthroplasty (TJA) makes this subset of the medical population ideal for enrollment in a PSH protocol.
PSH has been used selectively with beneficial results in different patient populations in the last decade. Optimizing patient outcome after TJA has been a focus of analysis since these surgeries were invented and recent studies have highlighted different factors, such as age, weight, gender, and procedure performed, that have an influence on outcomes.
To our knowledge, this study is the first of its kind stratifying TJA PSH patients preoperatively based on different characteristics and comorbidities and identifying associations with postoperative outcomes. The results suggest that a majority of patients with different preoperative variables may have equivalent outcomes due to perioperative optimization in a PSH protocol.
The study shows the efficacy and safety for TJA patients enrolled in a PSH protocol and suggests that preoperative differences may be minimized through this patient-centered model.
PSH: Patient-centered multidisciplinary team led by the lead surgeon and anesthesiologist.
The manuscript is well written and the use of English is good.
P- Reviewer: Malik H, Willis-Owen CA S- Editor: Ji FF L- Editor: A E- Editor: Li D
| 1. | Kurtz S, Ong K, Lau E, Mowat F, Halpern M. Projections of primary and revision hip and knee arthroplasty in the United States from 2005 to 2030. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2007;89:780-785. [PubMed] |
| 2. | Kurtz SM, Ong KL, Lau E, Bozic KJ. Impact of the economic downturn on total joint replacement demand in the United States: updated projections to 2021. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2014;96:624-630. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 623] [Cited by in RCA: 682] [Article Influence: 62.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 3. | Ravi B, Croxford R, Reichmann WM, Losina E, Katz JN, Hawker GA. The changing demographics of total joint arthroplasty recipients in the United States and Ontario from 2001 to 2007. Best Pract Res Clin Rheumatol. 2012;26:637-647. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 142] [Cited by in RCA: 174] [Article Influence: 14.5] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 4. | Cannesson M, Kain Z. The perioperative surgical home: an innovative clinical care delivery model. J Clin Anesth. 2015;27:185-187. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 18] [Cited by in RCA: 20] [Article Influence: 2.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 5. | Desebbe O, Lanz T, Kain Z, Cannesson M. The perioperative surgical home: An innovative, patient-centred and cost-effective perioperative care model. Anaesth Crit Care Pain Med. 2016;35:59-66. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 43] [Cited by in RCA: 48] [Article Influence: 4.8] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 6. | Garson L, Schwarzkopf R, Vakharia S, Alexander B, Stead S, Cannesson M, Kain Z. Implementation of a total joint replacement-focused perioperative surgical home: a management case report. Anesth Analg. 2014;118:1081-1089. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 91] [Cited by in RCA: 92] [Article Influence: 8.4] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 7. | Kash BA, Zhang Y, Cline KM, Menser T, Miller TR. The perioperative surgical home (PSH): a comprehensive review of US and non-US studies shows predominantly positive quality and cost outcomes. Milbank Q. 2014;92:796-821. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 85] [Cited by in RCA: 84] [Article Influence: 7.6] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 8. | Learmonth ID, Young C, Rorabeck C. The operation of the century: total hip replacement. Lancet. 2007;370:1508-1519. [PubMed] |
| 9. | Kane RL, Saleh KJ, Wilt TJ, Bershadsky B. The functional outcomes of total knee arthroplasty. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2005;87:1719-1724. [PubMed] |
| 10. | Pulido L, Parvizi J, Macgibeny M, Sharkey PF, Purtill JJ, Rothman RH, Hozack WJ. In hospital complications after total joint arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 2008;23:139-145. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 160] [Cited by in RCA: 192] [Article Influence: 11.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 11. | Zmistowski B, Restrepo C, Hess J, Adibi D, Cangoz S, Parvizi J. Unplanned readmission after total joint arthroplasty: rates, reasons, and risk factors. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2013;95:1869-1876. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 182] [Cited by in RCA: 212] [Article Influence: 17.7] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 12. | Silvay G, Zafirova Z. Ten Years Experiences With Preoperative Evaluation Clinic for Day Admission Cardiac and Major Vascular Surgical Patients: Model for “Perioperative Anesthesia and Surgical Home”. Semin Cardiothorac Vasc Anesth. 2016;20:120-132. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 14] [Cited by in RCA: 15] [Article Influence: 1.5] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 13. | Walters TL, Howard SK, Kou A, Bertaccini EJ, Harrison TK, Kim TE, Shafer A, Brun C, Funck N, Siegel LC. Design and Implementation of a Perioperative Surgical Home at a Veterans Affairs Hospital. Semin Cardiothorac Vasc Anesth. 2016;20:133-140. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 22] [Cited by in RCA: 24] [Article Influence: 2.4] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 14. | Boraiah S, Joo L, Inneh IA, Rathod P, Meftah M, Band P, Bosco JA, Iorio R. Management of Modifiable Risk Factors Prior to Primary Hip and Knee Arthroplasty: A Readmission Risk Assessment Tool. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2015;97:1921-1928. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 88] [Cited by in RCA: 97] [Article Influence: 9.7] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 15. | Jauregui JJ, Boylan MR, Kapadia BH, Naziri Q, Maheshwari AV, Mont MA. Total Joint Arthroplasty in Nonagenarians: What Are the Risks? J Arthroplasty. 2015;30:2102-2105.e1. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 31] [Cited by in RCA: 41] [Article Influence: 4.1] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 16. | Fang M, Noiseux N, Linson E, Cram P. The Effect of Advancing Age on Total Joint Replacement Outcomes. Geriatr Orthop Surg Rehabil. 2015;6:173-179. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 71] [Cited by in RCA: 114] [Article Influence: 11.4] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 17. | Bradley BM, Griffiths SN, Stewart KJ, Higgins GA, Hockings M, Isaac DL. The effect of obesity and increasing age on operative time and length of stay in primary hip and knee arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 2014;29:1906-1910. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 58] [Cited by in RCA: 65] [Article Influence: 5.9] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 18. | Avram V, Petruccelli D, Winemaker M, de Beer J. Total joint arthroplasty readmission rates and reasons for 30-day hospital readmission. J Arthroplasty. 2014;29:465-468. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 79] [Cited by in RCA: 95] [Article Influence: 8.6] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 19. | Paxton EW, Inacio MC, Singh JA, Love R, Bini SA, Namba RS. Are There Modifiable Risk Factors for Hospital Readmission After Total Hip Arthroplasty in a US Healthcare System? Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2015;473:3446-3455. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 89] [Cited by in RCA: 116] [Article Influence: 11.6] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 20. | Saucedo JM, Marecek GS, Wanke TR, Lee J, Stulberg SD, Puri L. Understanding readmission after primary total hip and knee arthroplasty: who’s at risk? J Arthroplasty. 2014;29:256-260. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 106] [Cited by in RCA: 136] [Article Influence: 12.4] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 21. | Belmont PJ, Goodman GP, Hamilton W, Waterman BR, Bader JO, Schoenfeld AJ. Morbidity and mortality in the thirty-day period following total hip arthroplasty: risk factors and incidence. J Arthroplasty. 2014;29:2025-2030. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 117] [Cited by in RCA: 131] [Article Influence: 11.9] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 22. | Belmont PJ, Goodman GP, Waterman BR, Bader JO, Schoenfeld AJ. Thirty-day postoperative complications and mortality following total knee arthroplasty: incidence and risk factors among a national sample of 15,321 patients. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2014;96:20-26. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 291] [Cited by in RCA: 340] [Article Influence: 30.9] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 23. | Pugely AJ, Callaghan JJ, Martin CT, Cram P, Gao Y. Incidence of and risk factors for 30-day readmission following elective primary total joint arthroplasty: analysis from the ACS-NSQIP. J Arthroplasty. 2013;28:1499-1504. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 178] [Cited by in RCA: 210] [Article Influence: 17.5] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 24. | Singh JA, Kwoh CK, Richardson D, Chen W, Ibrahim SA. Sex and surgical outcomes and mortality after primary total knee arthroplasty: a risk-adjusted analysis. Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken). 2013;65:1095-1102. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 38] [Cited by in RCA: 49] [Article Influence: 4.1] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 25. | Tayne S, Merrill CA, Smith EL, Mackey WC. Predictive risk factors for 30-day readmissions following primary total joint arthroplasty and modification of patient management. J Arthroplasty. 2014;29:1938-1942. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 49] [Cited by in RCA: 54] [Article Influence: 4.9] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 26. | Husted H, Holm G, Jacobsen S. Predictors of length of stay and patient satisfaction after hip and knee replacement surgery: fast-track experience in 712 patients. Acta Orthop. 2008;79:168-173. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 410] [Cited by in RCA: 428] [Article Influence: 25.2] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 27. | Schwarzkopf R, Thompson SL, Adwar SJ, Liublinska V, Slover JD. Postoperative complication rates in the “super-obese” hip and knee arthroplasty population. J Arthroplasty. 2012;27:397-401. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 101] [Cited by in RCA: 116] [Article Influence: 8.9] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 28. | Alvi HM, Mednick RE, Krishnan V, Kwasny MJ, Beal MD, Manning DW. The Effect of BMI on 30 Day Outcomes Following Total Joint Arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 2015;30:1113-1117. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 94] [Cited by in RCA: 109] [Article Influence: 10.9] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 29. | Schaeffer JF, Scott DJ, Godin JA, Attarian DE, Wellman SS, Mather RC. The Association of ASA Class on Total Knee and Total Hip Arthroplasty Readmission Rates in an Academic Hospital. J Arthroplasty. 2015;30:723-727. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 47] [Cited by in RCA: 63] [Article Influence: 6.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 30. | Mesko NW, Bachmann KR, Kovacevic D, LoGrasso ME, O’Rourke C, Froimson MI. Thirty-day readmission following total hip and knee arthroplasty - a preliminary single institution predictive model. J Arthroplasty. 2014;29:1532-1538. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 79] [Cited by in RCA: 94] [Article Influence: 8.5] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 31. | Rasouli MR, Restrepo C, Maltenfort MG, Purtill JJ, Parvizi J. Risk factors for surgical site infection following total joint arthroplasty. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2014;96:e158. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 90] [Cited by in RCA: 107] [Article Influence: 9.7] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |