Published online Nov 18, 2021. doi: 10.5312/wjo.v12.i11.891
Peer-review started: May 15, 2021
First decision: July 28, 2021
Revised: July 28, 2021
Accepted: September 19, 2021
Article in press: September 19, 2021
Published online: November 18, 2021
Processing time: 184 Days and 12.9 Hours
Work-related injuries have gained recent attention, especially in the orthopaedic literature. As upper extremity orthopaedic surgical tasks require repetitive and constant maneuvers, these surgeons can be at increased risk of acquiring work-related musculoskeletal (MSK) disorders during their years in practice.
To assess the prevalence, characteristics and impact of MSK disorders among upper extremity orthopaedic surgeons.
A modified version of the physical discomfort survey was sent to surgeons who were members of the American Shoulder and Elbow Surgeons and the Canadian shoulder and elbow society via e-mail. The collected data were analyzed using descriptive statistics, one-way analysis of variance, and Fisher's exact test. P values of < 0.05 were considered statistically significant.
Of the 142 respondents, 90.8% were males and the majority were younger than 55 years old (65.5%). A work-related MSK injury was reported by 89.4% of respondents, of which the most common diagnoses were low back pain (26.1%) and lateral elbow epicondylitis (18.3%). Among those that reported an injury, 82.7% required treatment and 26% required time off work as a direct result of their injury. The need to undergo treatment due to the injury was associated with increased number of injuries (P < 0.01). Moreover, surgeons were more likely to require time off work when they had been in practice for > 21 years (P < 0.05).
A high proportion of surgeons in our survey reported MSK injuries, with more than one quarter of surgeons reported requiring time off work due to an MSK injury. The high incidence of these disorders may place a financial and psychological burden on surgeons and affect their ability to provide patient care. Awareness of operative ergonomics, irrespective of surgical specialty may help to decrease or possibly prevent the occurrence of these disorders.
Core Tip: A high proportion of surgeons in our survey reported MSK injuries, with more than one quarter of surgeons reported requiring time off work due to an MSK injury. Awareness of operative ergonomics, irrespective of surgical specialty may help to decrease or possibly prevent the occurrence of these disorders.
- Citation: Alzahrani MM, Alqahtani SM, Pichora D, Bicknell R. Work-related musculoskeletal injuries among upper extremity surgeons: A web-based survey. World J Orthop 2021; 12(11): 891-898
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2218-5836/full/v12/i11/891.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5312/wjo.v12.i11.891
Healthcare professionals are exposed daily to occupational hazards in their work environment, which can be chemical, radiation, psychological or musculoskeletal (MSK)[1-3]. The latter has gained increased attention in the medical literature due to its high prevalence in physicians, especially surgeons, in addition to its significant impact both physically and psychologically on the physician and thus health care system in general[4-6].
While all surgeons have been found to have an increased risk of sustaining work related MSK disorders, recent studies have shown that the orthopaedic surgeon is at an even increased risk[2,6-8]. Repetitive and constantly forceful surgical tasks have been identified as the major contributing factor to their increased prevalence in orthopaedic surgeons. In addition, these MSK disorders can involve multiple regions, including the lower back and both upper and lower extremities.
Improving operative room setup and ergonomics, in addition to implementing safe workplace recommendations can lead to a decrease in the incidence of these injuries[9-11]. Multiple hurdles have been identified that prevent specific ergonomic setups or hinder executing work space recommendations, which may contribute to the lack of decline of these MSK disorders in the healthcare profession population[12-13].
We performed a study to investigate the prevalence and characteristics of MSK disorders among upper extremity orthopaedic surgeons. In addition, we assessed for any associated risk factors and explored the impact of these injuries on the upper extremity surgeon’s practice.
A modified version of the physical discomfort survey was sent to surgeons who were members of the American Shoulder and Elbow Surgeons and the Canadian shoulder and elbow society via e-mail. The initial email was sent in June 2016, followed by a reminder email in December 2016, and survey collection was ended in June 2017.
The survey contained questions related to the surgeons demographics (e.g., age, gender, hand-dominance, type of practice, number of years in practice and annual caseload), which were divided into groups guided by previously published similar studies. Also, the survey contained questions exploring work related MSK injuries, these were divided into anatomical regions, including neck, shoulder, elbow/forearm, wrist/hand, hip, knee, foot and ankle, low back. In addition, participants were asked about both treatments required and time off work required due to the reported injuries, if any.
The collected data were analyzed using descriptive statistics, one-way analysis of variance, and Fisher’s exact test. P values of < 0.05 were considered statistically significant.
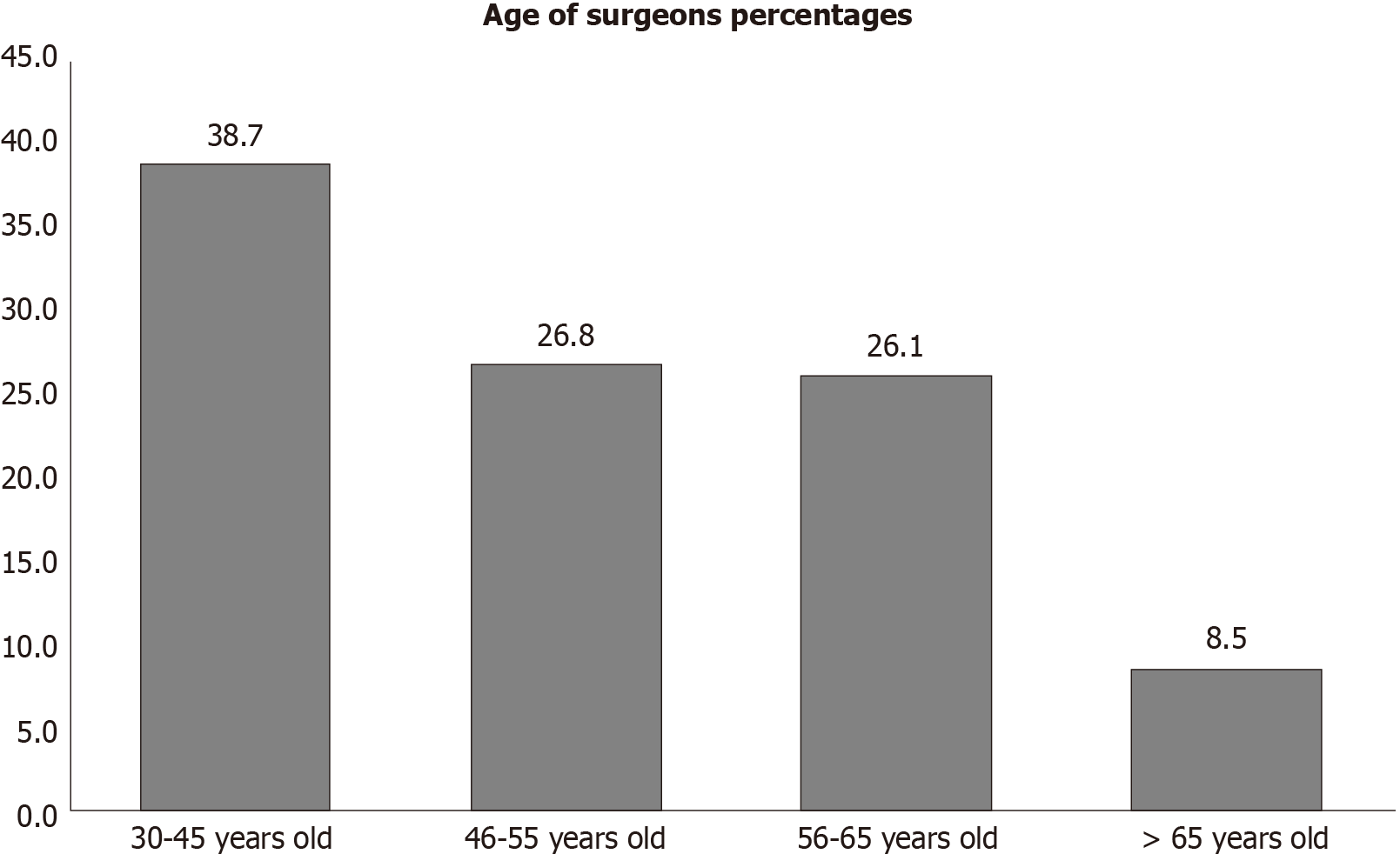
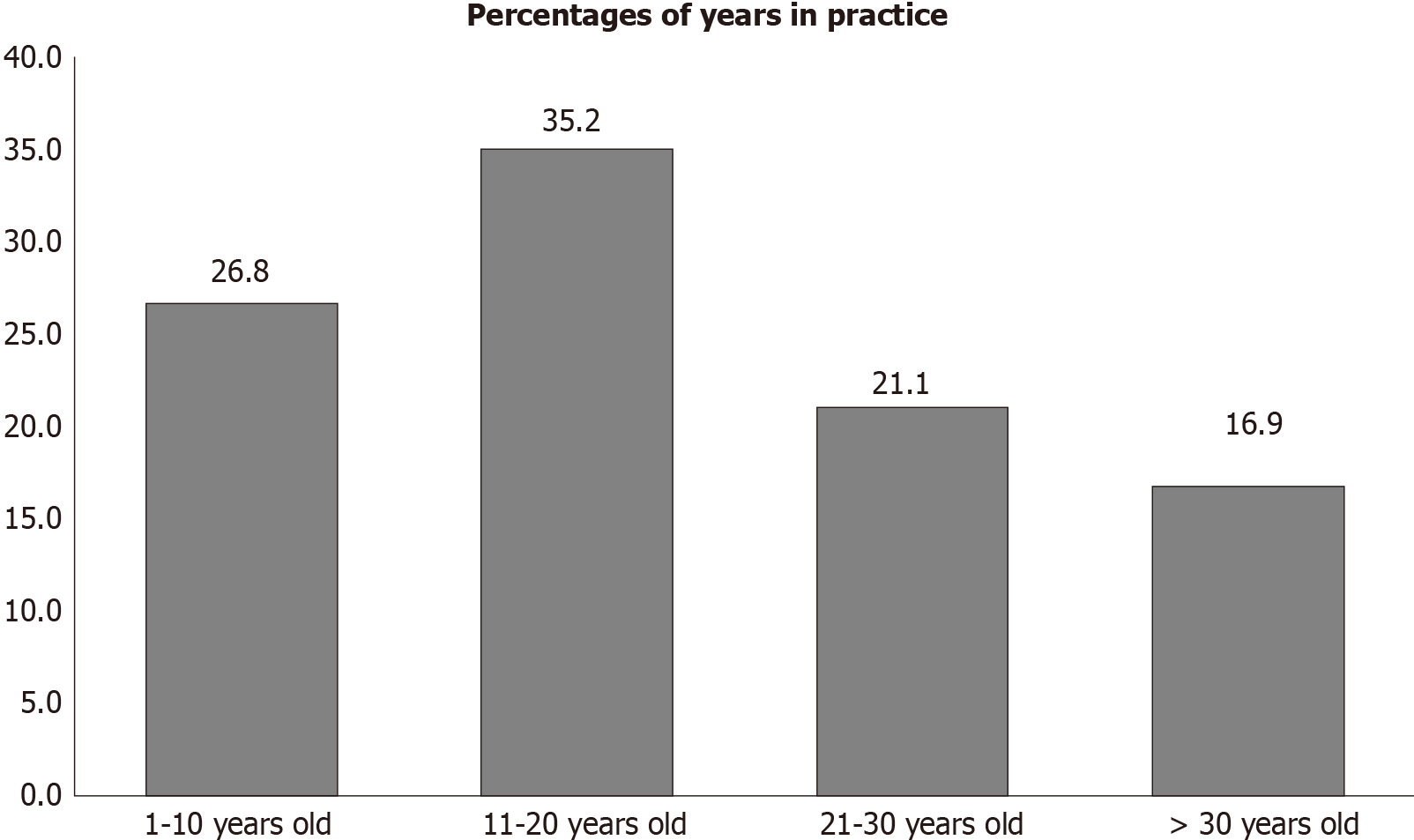
One hundred and forty-two surgeons responded to the survey, with a respondent rate of 12.5%. Of the 142 respondents, 90.8% were males and 9.2% were females (Table 1). Hand dominance was right in 122 and left in 20 respondents (Table 1). More than 60% of the respondents were younger than 55 years old (Figure 1). The majority of responding surgeons were within their first 20 years of practice (Figure 2). We found that above half of the respondents were in academic practice, 23.2% in community practice, 18.3% in private practice.
| Number | Percentage (%) | |
| Total respondents | 142 | 100 |
| Sex | ||
| Male | 129 | 90.8 |
| Female | 13 | 9.2 |
| Hand dominance | ||
| Right | 122 | 85.9 |
| Left | 20 | 14.1 |
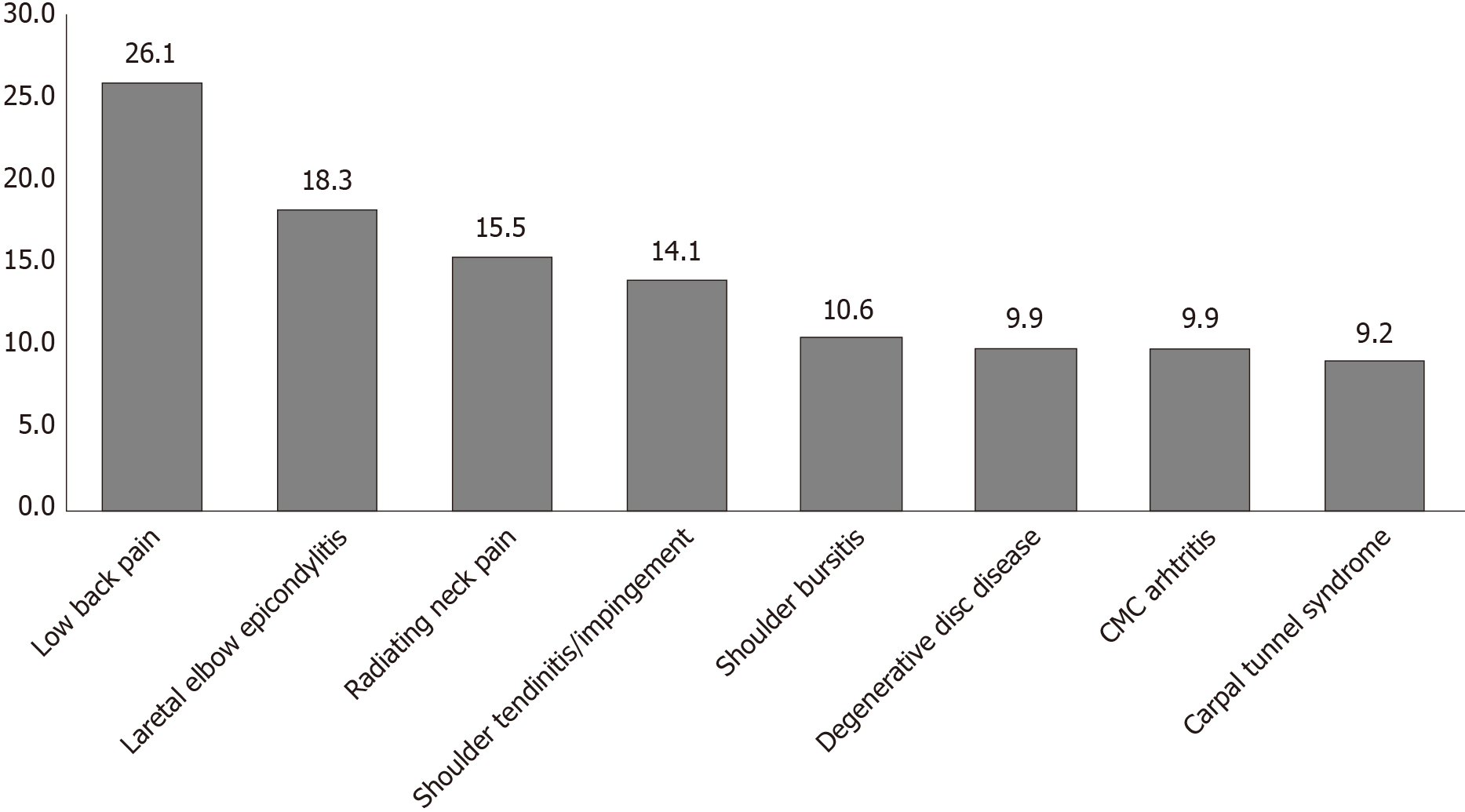
Work-related MSK injuries were reported by 89.4% of respondents (Table 2), of which the most common diagnoses were low back pain (26%), lateral elbow epicondylitis (18%), and neck pain (15.5%) (Figure 3). We found no association between the number of work-related injuries incurred and age, type of practice nor years in practice.
| Number of respondents (%) | Number of respondents with injuries (%) | Number of injured requiring time off work (%) | |
| Age (yr) | |||
| ≤ 45 | 38.7 | 81.8 | 14.5 |
| 46-55 | 26.8 | 92.1 | 34.2 |
| 56-65 | 26.1 | 70.3 | 29.7 |
| > 65 | 8.4 | 91.7 | 8.3 |
| Sex | |||
| Male | 90.8 | 92.2 | 24 |
| Female | 9.2 | 61.5 | 15.4 |
| Hand dominance | |||
| Right | 85.9 | 88.5 | 26.2 |
| Left | 14.1 | 95 | 5 |
| Type of practice | |||
| Academic | 50.7 | 88.9 | 23.6 |
| Community | 23.2 | 87.9 | 21.2 |
| Private | 18.3 | 88.5 | 26.9 |
| Other | 7.8 | 100 | 18.2 |
| Number of institutes | |||
| 1 | 92.3 | 88.5 | 23.7 |
| > 1 | 7.7 | 100 | 18.2 |
| Year in practice | |||
| ≤ 10 | 26.7 | 78.9 | 15.8 |
| 11-20 | 35.2 | 90 | 26 |
| 21-30 | 21.2 | 100 | 30 |
| > 30 | 16.9 | 91.7 | 20.8 |
| Annual caseload | |||
| ≤ 250 | 15.5 | 90.9 | 18.2 |
| 251-500 | 64.1 | 87.9 | 22 |
| 501-750 | 16.9 | 91.7 | 33.3 |
| > 750 | 3.5 | 100 | 20 |
Of the surgeons that reported an injury, 82.7% required treatment, with 65.7% requiring medical treatment, 20% requiring surgical treatment and 14.3% requiring both (Table 3). The need to undergo treatment due to the injury was associated with increased number of injuries (P < 0.01). Age and number of years in practice were not associated with the requirement of treatment for sustained injuries. More than a quarter of the surgeons required time off work as a direct result of their injury, which was associated with being in practice for > 21 years (P < 0.05), but not with the surgeon’s age (Table 2).
| Region | Percentage of respondents with injuries | Percentage of injured respondents requiring treatment | Percentage of treated respondents requiring surgical treatment | Percentage of treated respondents requiring time-off work |
| Neck | 32.3 | 17.7 | 5.9 | 4.4 |
| Shoulder | 36.0 | 22.8 | 6.6 | 7.4 |
| Elbow | 27.2 | 14.0 | 2.2 | 1.5 |
| Forearm, wrist and hand | 32.3 | 13.2 | 4.4 | 3.7 |
| Hip and thigh | 6.8 | 3.0 | 3.0 | 2.3 |
| Knee and lower leg | 15.9 | 9.1 | 6.1 | 4.6 |
| Foot and ankle | 10.6 | 4.6 | 0 | 0 |
| Lower back | 43.9 | 26.5 | 3.0 | 5.3 |
A number of studies in the current literature have assessed the prevalence of work-related hazards, both on a general healthcare worker scale and specific medical and surgical specialties[1,2,14,15]. Our current study explored the prevalence of MSK injuries in the orthopaedic upper extremity surgeon population, who share with other orthopaedic surgeons’ exposure to forceful and repetitive operative task that put this cohort at an increased risk for sustaining these injuries during their career.
More than 89% of our studied cohort reported a work related MSK injury at some time in their career, with spine and elbow injuries being the most common. This prevalence was found to be higher than the findings in previously published studies in other orthopaedic specialties, as in a study of 183 arthroplasty surgeons, 66% reported a work-related MSK injury[14]. Similarly, in the orthopaedic trauma surgeon and pediatric orthopaedic surgeon cohorts the prevalence was 66% and 67%, respectively[6,7]. Concerning the most commonly reported regions, cervical and lumbar spine disease and rotator cuff pathology were identified as the most common work-related musculoskeletal disorders in a recent meta-analysis of 5828 physicians[4]. In the orthopaedic literature, low back and elbow injuries (especially lateral epicondylitis) were the most common regions involved in the majority of these studies, similar to our findings[6,7]. This may be attributed to the sometime long operative procedures associated with a standing posture, in addition to the frequent pronation/supination movements required during these procedures.
Interestingly, we found no association between the age nor number of years in practice and the risk for sustaining a work-related MSK injury. This is in agreement with the study by Alqahtani et al[14] on 183 arthroplasty surgeons, that also found no association. In contrast, a study on the orthopaedic trauma surgeon population identified an association between the number of MSK disorders and the surgeons age and number of years in practice. Alzahrani et al[6,7]. also found the same association in a study of 402 pediatric orthopaedic surgeons, where increasing age, working in more than one institute and being in practice more than 21 years was associated with increased number of work-related MSK injuries.
Our current study and previously published literature indicate that the risk of work-related musculoskeletal disorders is high, especially in orthopaedic surgeons. Specific attention should be directed towards improving operative room ergonomics and surgeon education on the adequate and safe postures and movements while in the operating room[10,16]. In addition, utilizing instruments that decrease the requirement of repetitive forceful movements in the operating room (e.g., power for inserting screws) may help protect these surgeons during their long career[13].
Our study has some limitations, including recall bias of these reported injuries. In addition, similar to previously used surveys which include self-reported measures, our current survey has not had its reliability and validity established. Also, due to the low response rate, selection bias may also be another limitation. But we believe that this sample size is truly representative of the population in study as the sample size is similar to a number of previously published similar studies.
MSK injuries were reported by a high proportion of our surveyed cohort of upper extremity surgeons, with more than a quarter of them requiring time off work. As these injuries may place a psychological burden on the surgeon and affect the healthcare system, specific attention should be directed towards improving ergonomics and safety in the operative room to help decrease the high prevalence of these injuries in the future.
Upper extremity orthopaedic surgical tasks require repetitive and constant maneuvers, which can put them at increased risk of acquiring work-related musculoskeletal disorders during their years in practice.
As these injuries may place a psychological burden on the surgeon and affect the healthcare system, attention should be directed at studying their prevalence and associated factors.
To assess the prevalence, characteristics and impact of musculoskeletal disorders among upper extremity orthopaedic surgeons.
A modified version of the physical discomfort survey was sent to surgeons who were members of the American Shoulder and Elbow Surgeons and the Canadian shoulder and elbow society via e-mail. The collected data were analyzed using descriptive statistics, one-way analysis of variance, and Fisher's exact test. P values of <0.05 were considered statistically significant.
A work-related musculoskeletal injury was reported by 89.4% of respondents, of which the most common diagnoses were low back pain and lateral elbow epicondylitis.
Musculoskeletal injuries were reported by a high proportion of our surveyed cohort of upper extremity surgeons, with more than a quarter of them requiring time off work.
Specific attention should be directed towards improving ergonomics and safety in the operative room to help decrease the high prevalence of these injuries in the future.
Provenance and peer review: Unsolicited article; Externally peer reviewed
Specialty type: Orthopedics
Country/Territory of origin: Canada
Peer-review report’s scientific quality classification
Grade A (Excellent): 0
Grade B (Very good): 0
Grade C (Good): C, C
Grade D (Fair): 0
Grade E (Poor): 0
P-Reviewer: Guo F S-Editor: Wang LL L-Editor: A P-Editor: Wang LYT
| 1. | Auerbach JD, Weidner ZD, Milby AH, Diab M, Lonner BS. Musculoskeletal disorders among spine surgeons: results of a survey of the Scoliosis Research Society membership. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2011;36:E1715-E1721. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 66] [Cited by in RCA: 93] [Article Influence: 6.6] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 2. | Davis WT, Sathiyakumar V, Jahangir AA, Obremskey WT, Sethi MK. Occupational injury among orthopaedic surgeons. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2013;95:e107. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 48] [Cited by in RCA: 72] [Article Influence: 6.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 3. | Vajapey SP, Li M, Glassman AH. Occupational hazards of orthopaedic surgery and adult reconstruction: A cross-sectional study. J Orthop. 2021;25:23-30. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 3] [Cited by in RCA: 15] [Article Influence: 3.8] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 4. | Epstein S, Sparer EH, Tran BN, Ruan QZ, Dennerlein JT, Singhal D, Lee BT. Prevalence of Work-Related Musculoskeletal Disorders Among Surgeons and Interventionalists: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. JAMA Surg. 2018;153:e174947. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 145] [Cited by in RCA: 309] [Article Influence: 44.1] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 5. | Vijendren A, Yung M. An overview of occupational hazards amongst UK Otolaryngologists. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2016;273:2825-2832. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 4] [Cited by in RCA: 9] [Article Influence: 1.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 6. | AlQahtani SM, Alzahrani MM, Harvey EJ. Prevalence of musculoskeletal disorders among orthopedic trauma surgeons: an OTA survey. Can J Surg. 2016;59:42-47. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 43] [Cited by in RCA: 57] [Article Influence: 6.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 7. | Alzahrani MM, Alqahtani SM, Tanzer M, Hamdy RC. Musculoskeletal disorders among orthopedic pediatric surgeons: an overlooked entity. J Child Orthop. 2016;10:461-466. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 32] [Cited by in RCA: 38] [Article Influence: 4.2] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 8. | Wyatt RW, Lin CC, Norheim EP, Przepiorski D, Navarro RA. Occupation-related Cervical Spine Disease in Orthopaedic Surgeons. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2020;28:730-736. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 6] [Cited by in RCA: 18] [Article Influence: 3.6] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 9. | Esser AC, Koshy JG, Randle HW. Ergonomics in office-based surgery: a survey-guided observational study. Dermatol Surg. 2007;33:1304-13; discussion 1313. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 10] [Cited by in RCA: 20] [Article Influence: 1.1] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 10. | van Veelen MA, Kazemier G, Koopman J, Goossens RH, Meijer DW. Assessment of the ergonomically optimal operating surface height for laparoscopic surgery. J Laparoendosc Adv Surg Tech A. 2002;12:47-52. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 82] [Cited by in RCA: 87] [Article Influence: 3.8] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 11. | Alaqeel M, Tanzer M. Improving ergonomics in the operating room for orthopaedic surgeons in order to reduce work-related musculoskeletal injuries. Ann Med Surg (Lond). 2020;56:133-138. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 8] [Cited by in RCA: 33] [Article Influence: 6.6] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 12. | Lin DW, Bush RW, Earle DB, Seymour NE. Performance and ergonomic characteristics of expert surgeons using a face-mounted display during virtual reality-simulated laparoscopic surgery: an electromyographically based study. Surg Endosc. 2007;21:1135-1141. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 14] [Cited by in RCA: 15] [Article Influence: 0.8] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 13. | Albayrak A, van Veelen MA, Prins JF, Snijders CJ, de Ridder H, Kazemier G. A newly designed ergonomic body support for surgeons. Surg Endosc. 2007;21:1835-1840. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 85] [Cited by in RCA: 69] [Article Influence: 3.8] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 14. | Alqahtani SM, Alzahrani MM, Tanzer M. Adult Reconstructive Surgery: A High-Risk Profession for Work-Related Injuries. J Arthroplasty.. 2016;31 1194-1198. [PMID:26791046 DOI: 10.1016/j.arth.2015.12.025]. |
| 15. | 15 Capone AC, Parikh PM, Gatti ME, Davidson BJ, Davison SP. Occupational injury in plastic surgeons. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2010;125:1555-1561. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 61] [Cited by in RCA: 83] [Article Influence: 5.5] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 16. | Park A, Lee G, Seagull FJ, Meenaghan N, Dexter D. Patients benefit while surgeons suffer: an impending epidemic. J Am Coll Surg. 2010;210:306-313. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 310] [Cited by in RCA: 347] [Article Influence: 23.1] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |