Copyright
©The Author(s) 2018.
Figure 1 Knee rotation jig prior to mounting of specimen.
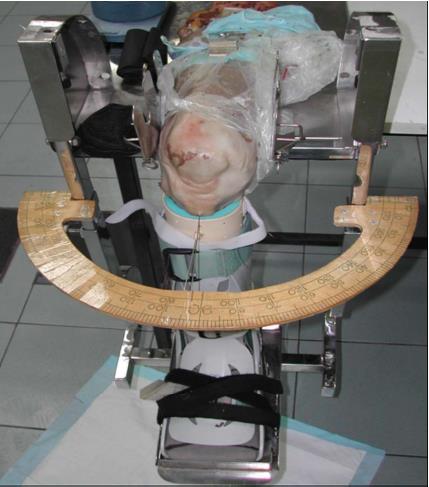
Figure 2 Knee rotation jig with specimen mounted with nail though tibial tuberosity and skin pointer in place.
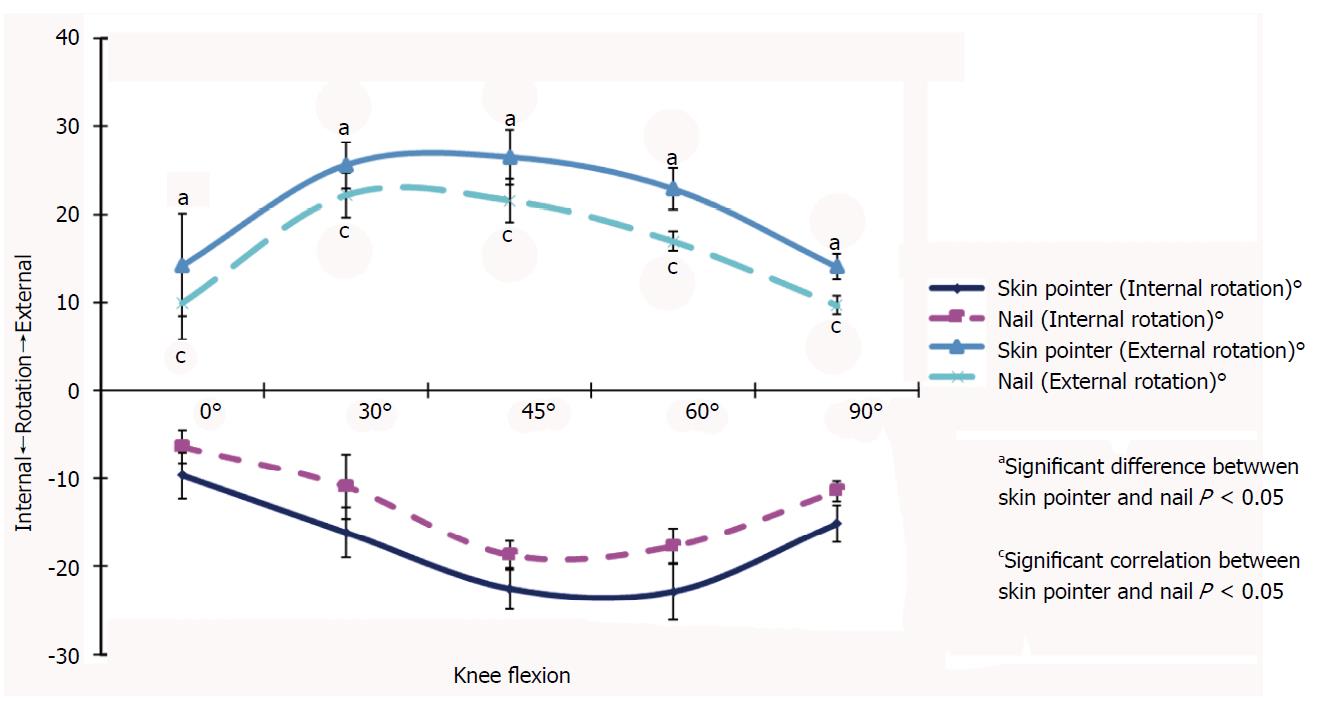
Figure 3 Knee rotation measured at 0°, 30°, 45°, 60° and 90° of knee flexion with 3 nm of torque.
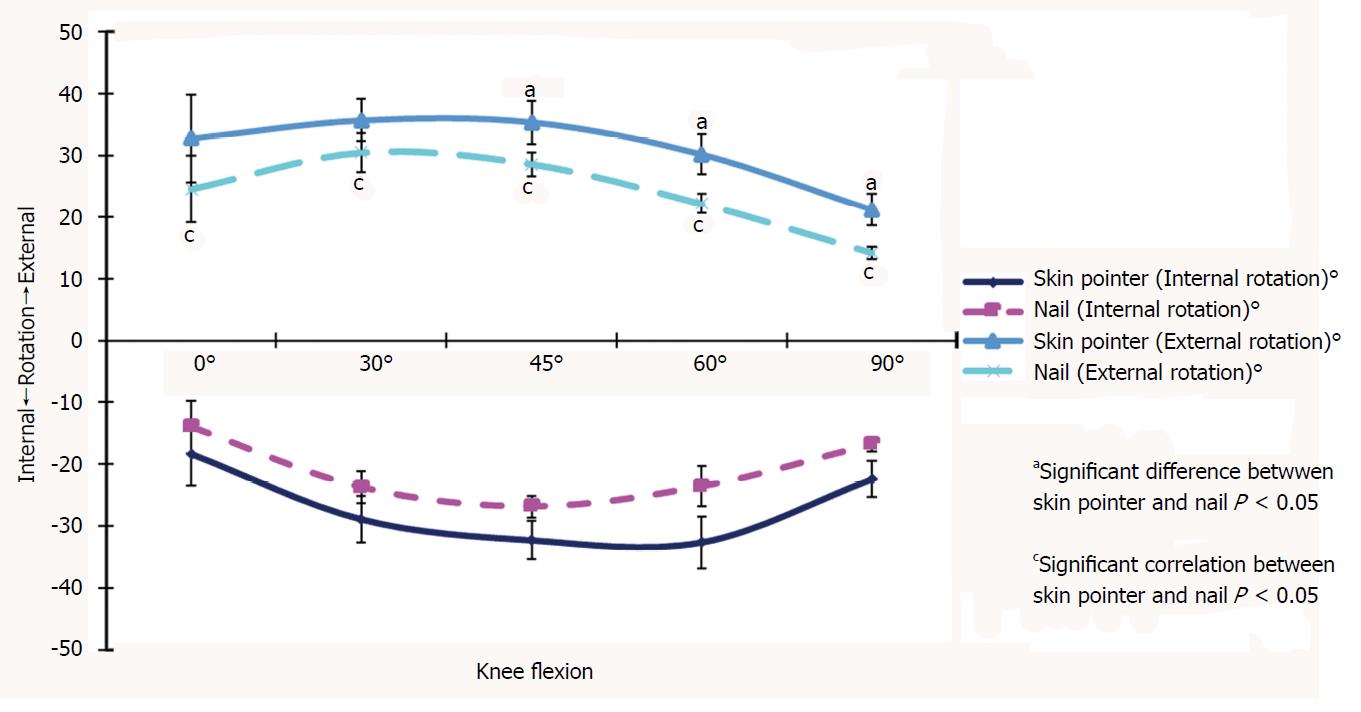
Figure 4 Knee rotation measured at 0°, 30°, 45°, 60° and 90° of knee flexion with 6 nm of torque.
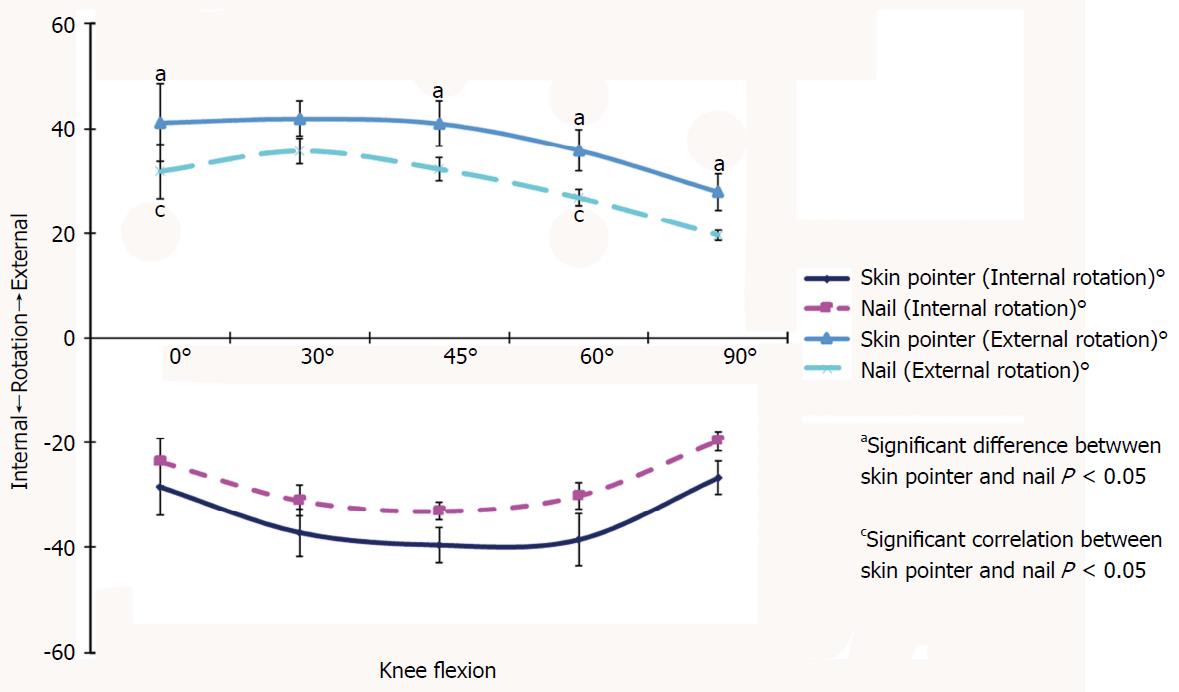
Figure 5 Knee rotation measured at 0°, 30°, 45°, 60° and 90° of knee flexion with 9 nm of torque.
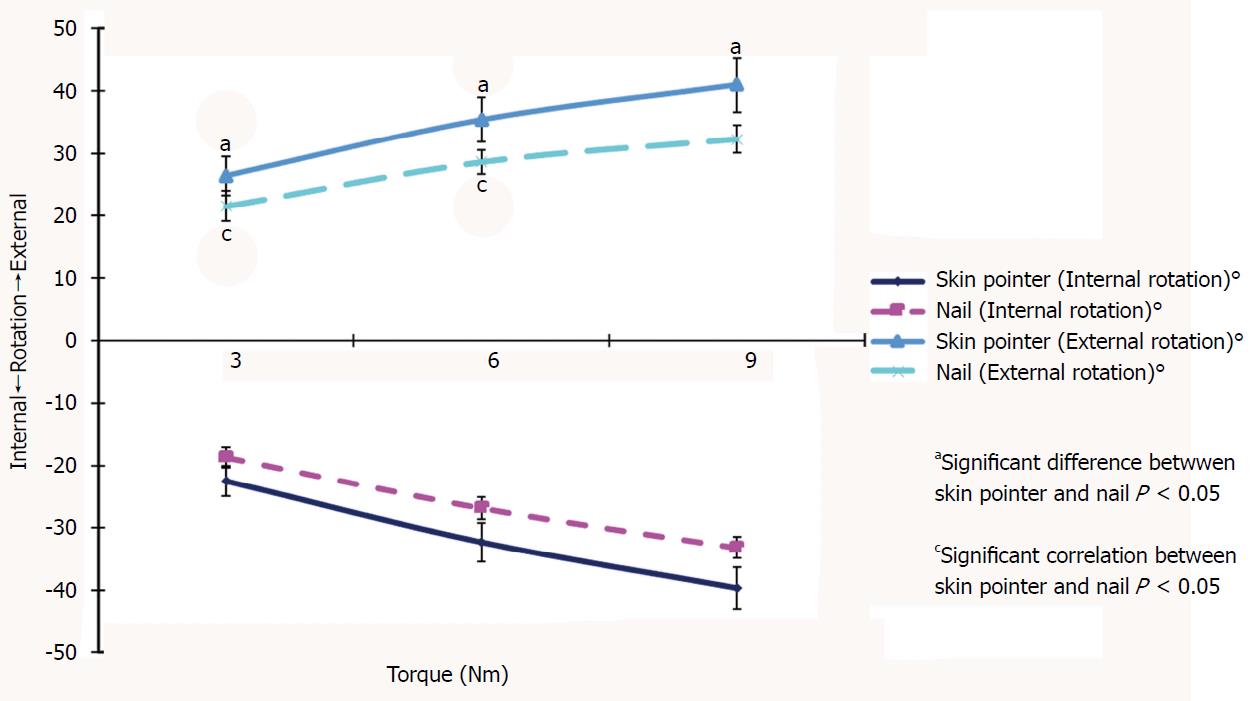
Figure 6 Knee rotation at 45° of flexion with 3, 6, and 9 nm of torque.
- Citation: Puah KL, Yew AKS, Chou SM, Lie DTT. Comparison of a simplified skin pointer device compared with a skeletal marker for knee rotation laxity: A cadaveric study using a rotation-meter. World J Orthop 2018; 9(6): 85-91
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2218-5836/full/v9/i6/85.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5312/wjo.v9.i6.85