Copyright
©The Author(s) 2017.
World J Orthop. Dec 18, 2017; 8(12): 913-921
Published online Dec 18, 2017. doi: 10.5312/wjo.v8.i12.913
Published online Dec 18, 2017. doi: 10.5312/wjo.v8.i12.913
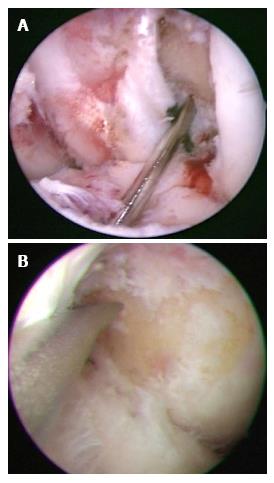
Figure 1 Arthroscopic techniques for creating the femoral tunnel.
A: Arthroscopic view of trans-tibial technique in left knee is shown. The femoral guide wire was centered at the 1:30-2:00 o’clock position; B: Left knee. In trans-portal technique, the anteromedial portal was used to visualize the lateral wall of the intercondylar notch. The far medial accessory portal was used to directly access to the center of the anterior cruciate ligament femoral insertion site.
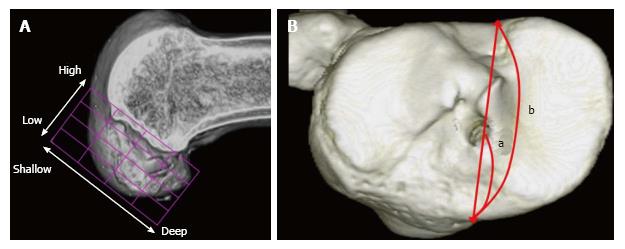
Figure 2 Evaluation of tunnel positions in femur and tibia.
A: 3D CT-based model of a femoral bone tunnel after an ACL reconstruction. Tunnel position was assessed according to the quadrant method[46]. Depth = (distance from the posterior edge to tunnel center along Blumensaat’s line/total length of the lateral condyle) × 100%. Height = (distance from Blumensaat’s line to tunnel center/total height of the intercondylar roof) × 100%; B: For tibial side, Staubli’s technique was used[47]. Anterior-posterior position = (a/b) × 100%. a: Distance from anterior edge to tunnel center; b: Anteroposterior length of the tibia plateau. ACL: Anterior cruciate ligament.
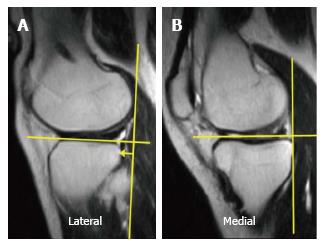
Figure 3 The anterior translation of the tibia with respect to the femoral condyle was measured on sagittal MR images of the (A) lateral compartment and (B) medial compartment, respectively.
As a landmark for the center of the lateral compartment, slices that included the medial edge of the fibula were selected. For the center of the medial compartment, slices with the attachment of the medial head of the gastrocnemius were selected.
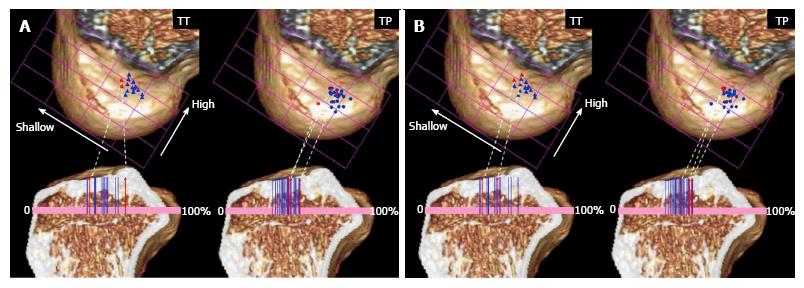
Figure 4 Tunnel positions in trans-tibial and trans-portal group are plotted for the femur and the tibia.
A: Blue and red markers mean the side-to-side differences of Kneelax3 arthrometer of the case were under 3 mm (blue) and over 3 mm (red), respectively; B: Blue and red markers mean the side-to-side differences of anterolateral tibial translation were under 3 mm (blue) and over 3 mm (red), respectively. TT: Trans-tibial; TP: Trans-portal.
- Citation: Tashiro Y, Okazaki K, Murakami K, Matsubara H, Osaki K, Iwamoto Y, Nakashima Y. Anterolateral rotatory instability in vivo correlates tunnel position after anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction using bone-patellar tendon-bone graft. World J Orthop 2017; 8(12): 913-921
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2218-5836/full/v8/i12/913.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5312/wjo.v8.i12.913