Copyright
©The Author(s) 2016.
World J Orthop. Jun 18, 2016; 7(6): 361-369
Published online Jun 18, 2016. doi: 10.5312/wjo.v7.i6.361
Published online Jun 18, 2016. doi: 10.5312/wjo.v7.i6.361
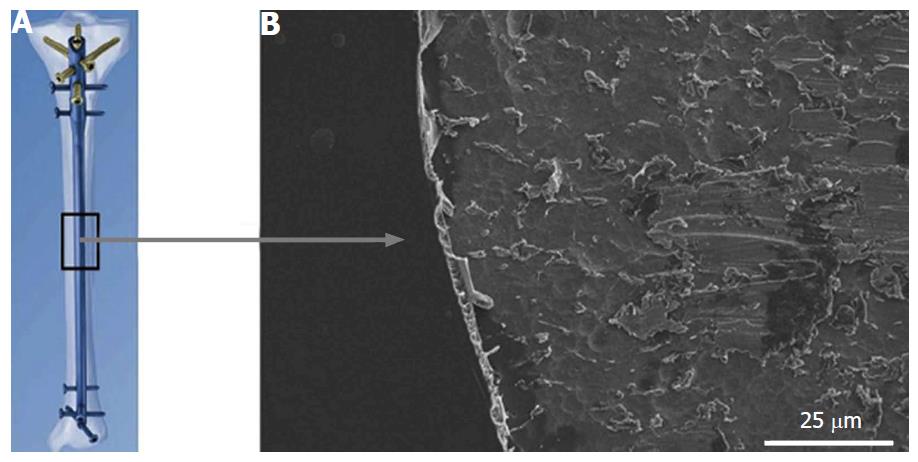
Figure 1 Diagram of tibial nail with gentamicin coating (A), visualized on metal implant using scanning electron microscopy (B)[20].
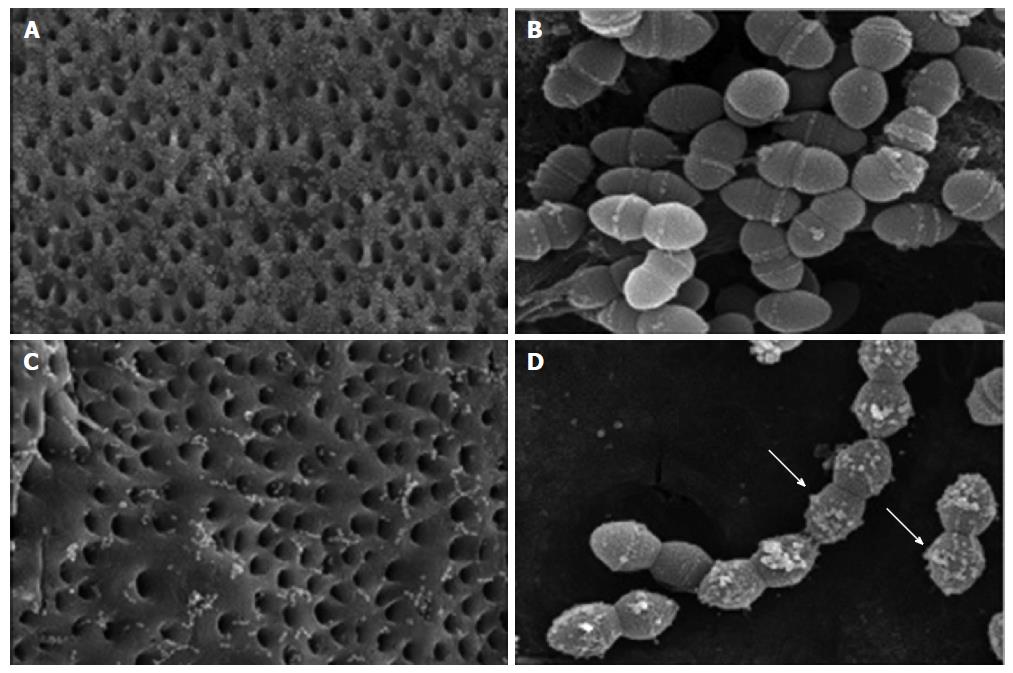
Figure 2 Scanning electron microscopy images of Enterococcus faecalis-infected dentin blocks treated with saline and chlorhexidine.
Blocks treated with saline solution for 10 min show many adhering Enterococcus faecalis (A, × 1500) with normal shape (B, × 20000). The group soaked with 2% chlorhexidine shows fewer adhering bacteria (C, × 1500) and chlorhexidine particles attached to bacterial membranes (D, × 20000, white arrows)[28].
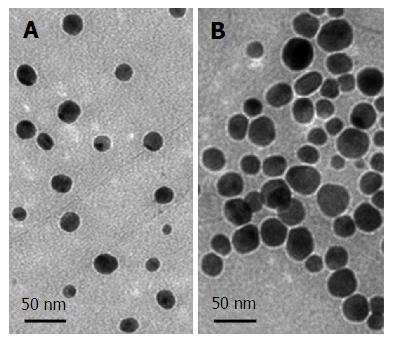
Figure 3 Silver nanoparticles of two sizes: Small (A) and Large (B), visualized via transmission electron microscopy[42].
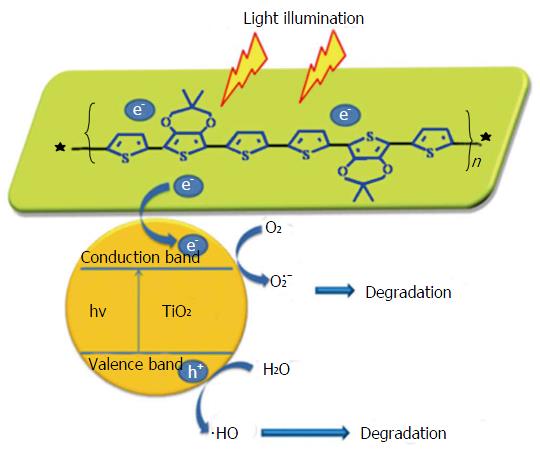
Figure 4 Schematic illustration of proposed photocatalytic and antibacterial mechanisms of a nanocomposite photocatalytic coating[55].
TiO2: Titanium oxide.
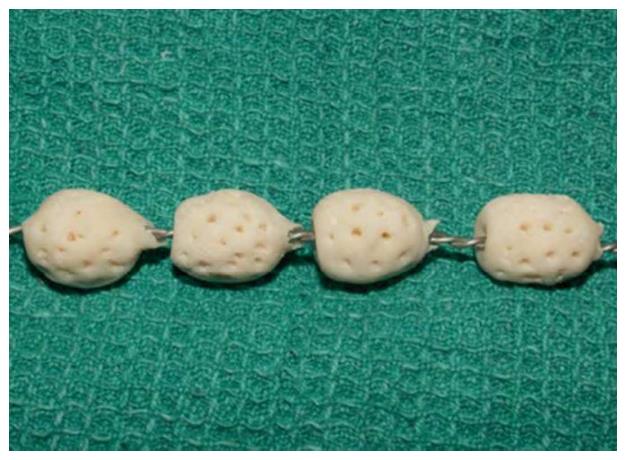
Figure 5 Antibiotic loaded bone cement beads strung on braided stainless steel[58].
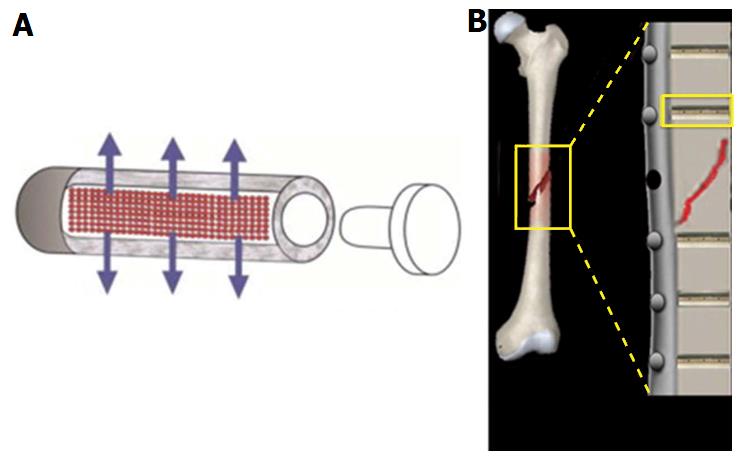
Figure 6 Fixation pins with tubular reservoirs for controlled drug release.
Diagrams highlighting the principle design of fixation pins: A: Scheme of a drug releasing fixation pin. Note the permeation through the porous wall (arrows)[64]; B: Scheme of implanted fixation pins, each capable of eluting local antibiotics around fixation site[65].
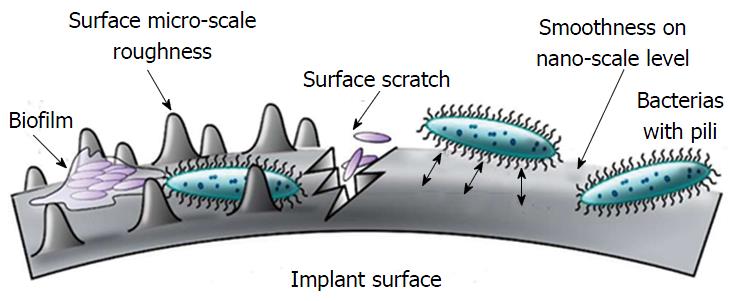
Figure 7 Interaction between surface roughness and bacterial adhesion[69].
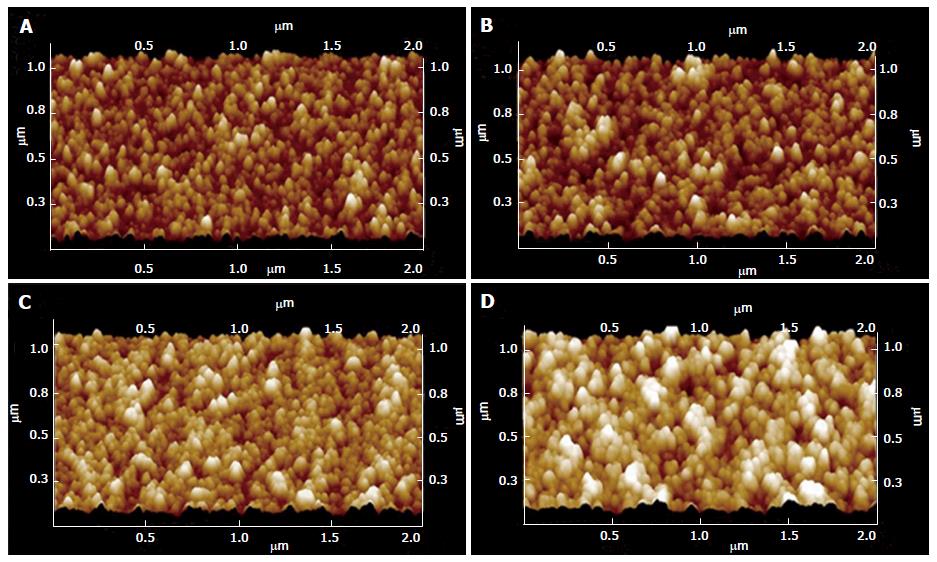
Figure 8 Atomic force microscopy of different surface film topography of increasing thickness (A: 50 nm; B: 100 nm; C: 200 nm; D: 300 nm)[68].
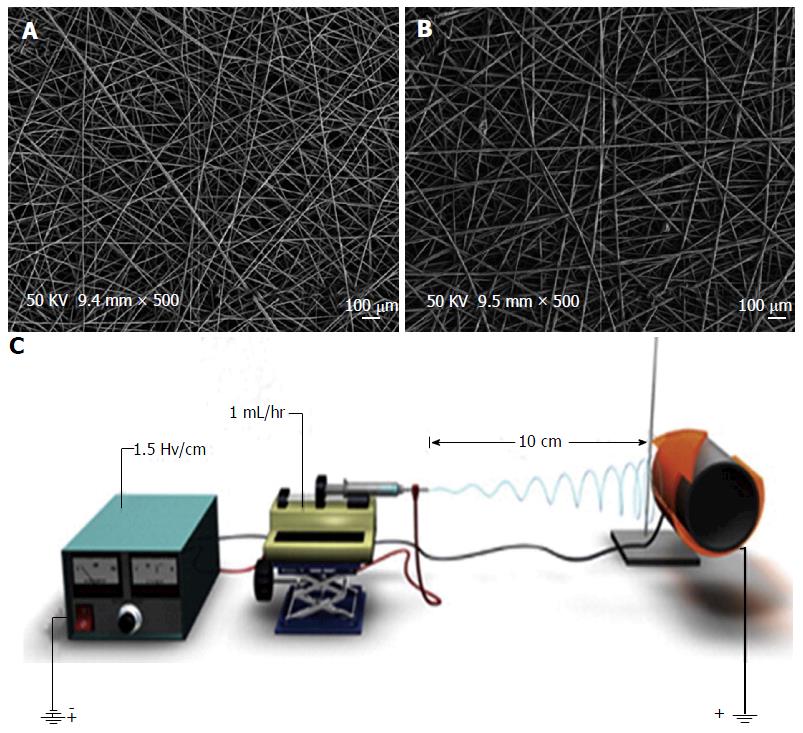
Figure 9 Micrograph and apparatus perspective of electrospinning technology.
Scanning electron microscopy micrographs of PLGA electrospun coatings containing (A) vancomycin and (B) no drug[74]; C: Schematic of a charged electrospinning apparatus spinning a PLGA coating onto an implant device[71]. PLGA: Poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid).
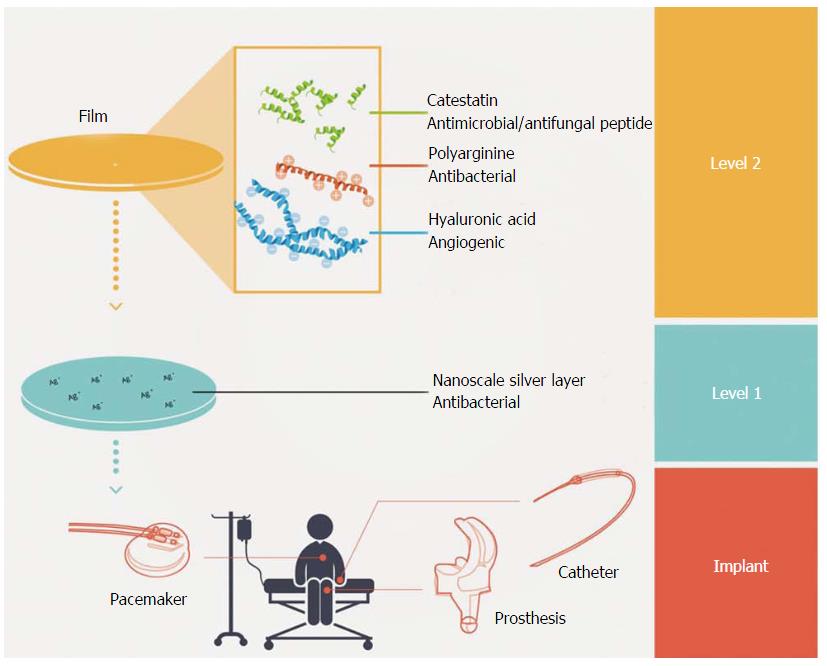
Figure 10 Integration of antimicrobial biofilms into the implant process[75].
- Citation: Eltorai AE, Haglin J, Perera S, Brea BA, Ruttiman R, Garcia DR, Born CT, Daniels AH. Antimicrobial technology in orthopedic and spinal implants. World J Orthop 2016; 7(6): 361-369
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2218-5836/full/v7/i6/361.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5312/wjo.v7.i6.361