Copyright
©The Author(s) 2016.
World J Orthop. Feb 18, 2016; 7(2): 102-108
Published online Feb 18, 2016. doi: 10.5312/wjo.v7.i2.102
Published online Feb 18, 2016. doi: 10.5312/wjo.v7.i2.102
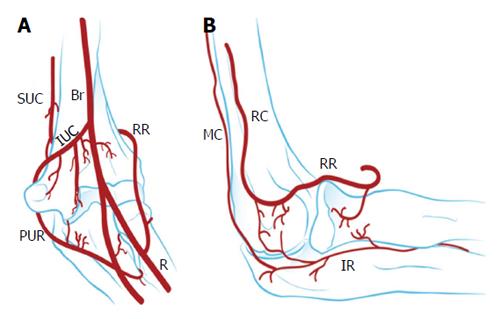
Figure 1 Vascularisation of the capitellum.
A: Anterior view; B: Lateral view. Br: Brachial; IR: Interosseous recurrent; IUC: Inferior ulnar collateral; MC: Middle collateral; PUR: Posterior ulnar recurrent; R: Radial; RC: Radial collateral; RR: Radial recurrent; SUC: Superior ulnar collateral artery.
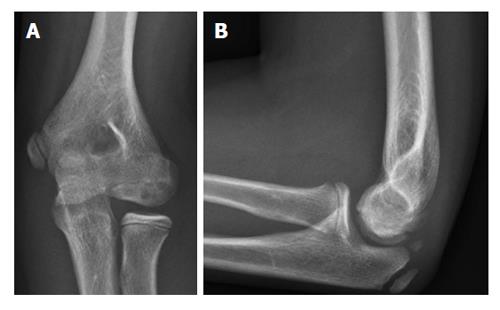
Figure 2 Plain radiography of the elbow showing an osteochondritis dissecans lesion of the capitellum.
A: Anteroposterior; B: Lateral.
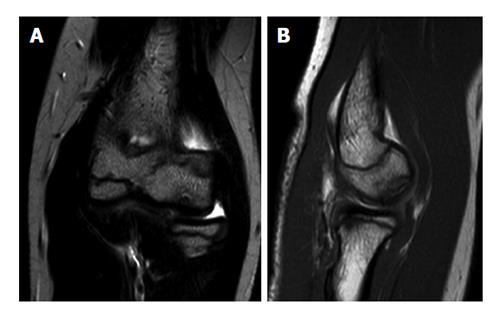
Figure 3 Magnetic resonance images of an elbow affected with osteochondritis dissecans of the capitellum.
A: Coronal view; B: Sagittal view.
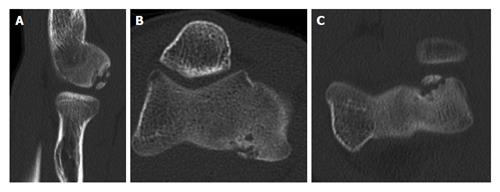
Figure 4 Computed tomography scans showing capitellar osteochondritis dissecans (A-C).
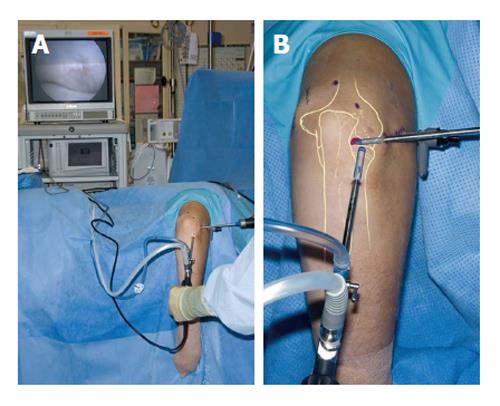
Figure 5 Patient positioning for arthroscopy of a right elbow (A and B).
The patient is in the lateral decubitus position and the arm rests on a support.
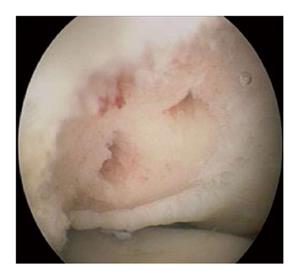
Figure 6 Arthroscopic picture showing an osteochondritis dissecans lesion after debridement and microfracturing.
- Citation: van Bergen CJA, van den Ende KIM, ten Brinke B, Eygendaal D. Osteochondritis dissecans of the capitellum in adolescents. World J Orthop 2016; 7(2): 102-108
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2218-5836/full/v7/i2/102.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5312/wjo.v7.i2.102