Copyright
©The Author(s) 2016.
World J Orthop. Nov 18, 2016; 7(11): 766-775
Published online Nov 18, 2016. doi: 10.5312/wjo.v7.i11.766
Published online Nov 18, 2016. doi: 10.5312/wjo.v7.i11.766
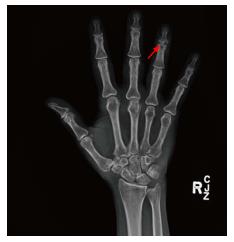
Figure 1 Plain radiograph anteroposterior view right hand showed osseous erosive changes at the 4th finger distal interphalangeal joint (arrow).
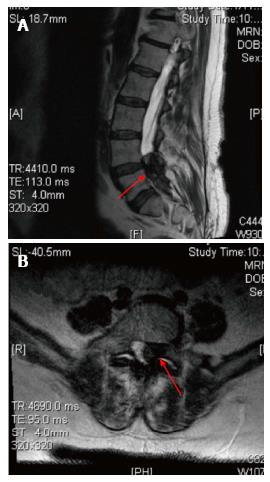
Figure 2 T2 weighted magnetic resonance imaging scan mid sagittal (A) and axial (B) showed intraspinal extradural hypodense lesion causing spinal canal stenosis at L4-S1.
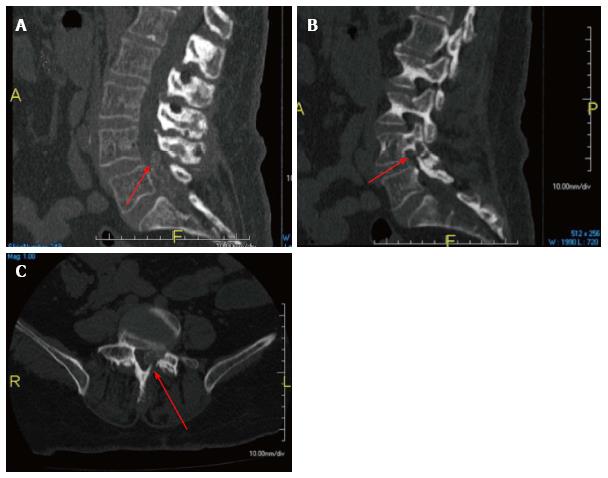
Figure 3 Computed tomography scan mid sagittal (A), left parasagittal (B), and axial (C) views showed the intraspinal lesion was calcified with erosive changes at the left L4-5 facet joint and L4 lamina (arrows).
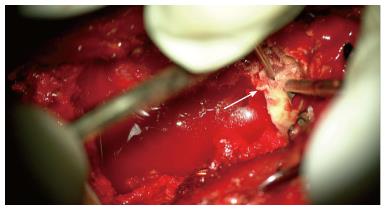
Figure 4 Intraoperative photograph taken by the surgical microscope showed a well-demarked chalky white tophous lesion (arrow).
- Citation: Elgafy H, Liu X, Herron J. Spinal gout: A review with case illustration. World J Orthop 2016; 7(11): 766-775
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2218-5836/full/v7/i11/766.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5312/wjo.v7.i11.766