Copyright
©The Author(s) 2015.
World J Orthop. Aug 18, 2015; 6(7): 505-512
Published online Aug 18, 2015. doi: 10.5312/wjo.v6.i7.505
Published online Aug 18, 2015. doi: 10.5312/wjo.v6.i7.505
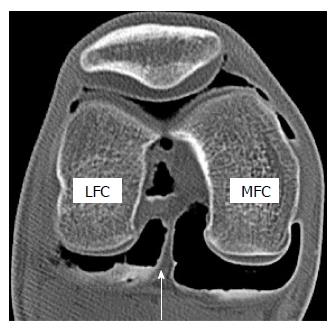
Figure 1 Axial image of double contrast arthrography of the knee.
The white arrow indicates a posterior septum that borders the posterior cruciate ligament anteriorly and posterior capsule posteriorly. Note that posteromedial compartment is larger than posterolateral compartment. LFC: Lateral femoral condyle; MFC: Medial femoral condyle.
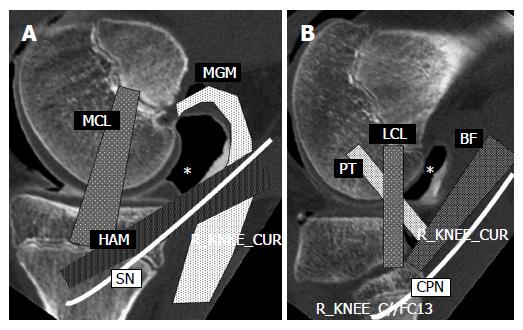
Figure 2 Sagittal images of double contrast arthrography at the levels of the medial (A) and lateral (B) femoral condyle of the knee.
Posteromedial (A) and posterolateral (B) sites are indicated by asterisks (*). The portal site is surrounded by important structures. MCL: Medial collateral ligament; MGM: Medial head of the gastrocnemius muscle; HAM: Hamstrings; SN: Saphenous nerve; LCL: Lateral collateral ligament; PT: Popliteus tendon; BF: Biceps femoris; CPN: Common peroneal nerve.
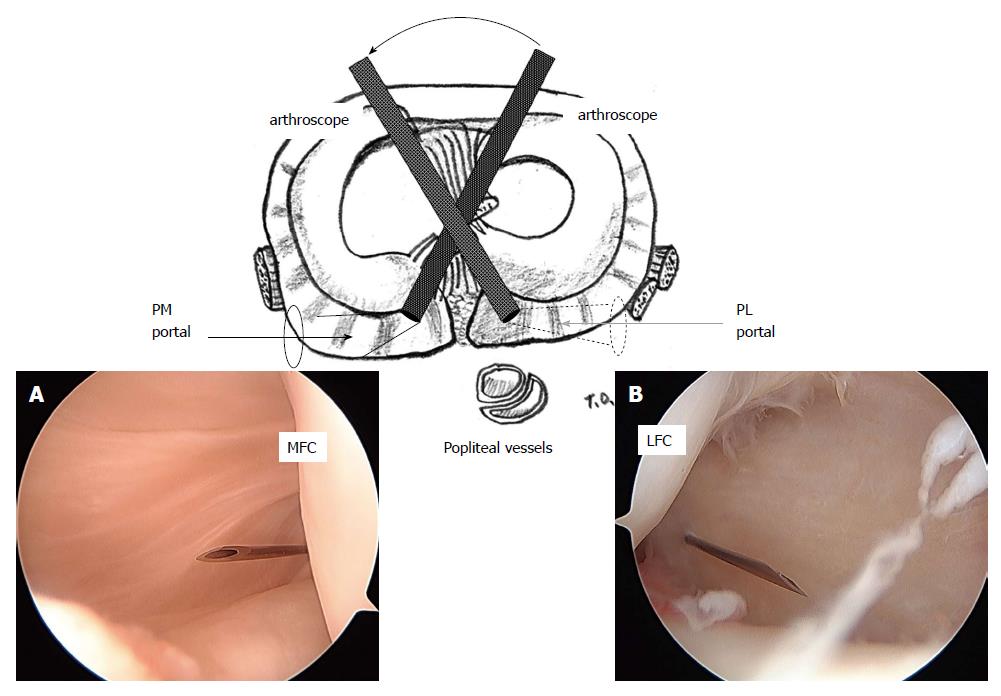
Figure 3 Arthroscopic view of the posteromedial (A) and posterolateral (B) compartment through the intercondylar notch from the anterolateral (A) and anteromedial (B) portals.
A 23-gauge spinal needle is inserted just posterior to the medial (A) and lateral (B) femoral condyle at 5 mm above the tibial articular surface. PM: Posteromedial; PL: Posterolateral; MFC: Medial femoral condyle; LFC: Lateral femoral condyle. (Permission for reproduction was obtained from Nankodo Co., Ltd.).
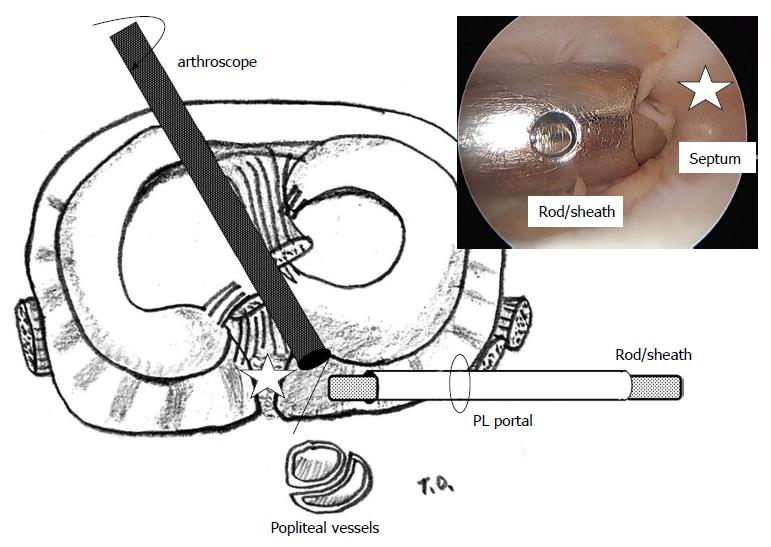
Figure 4 Rod with a sheath is inserted from the posterolateral portal.
The camera head of the 30-degree arthroscope is turned toward the septum so that the operator can confirm attachment of the tip of the rod to the septum (white star). PL: Posterolateral. (Permission for reproduction was obtained from Nankodo Co., Ltd.).
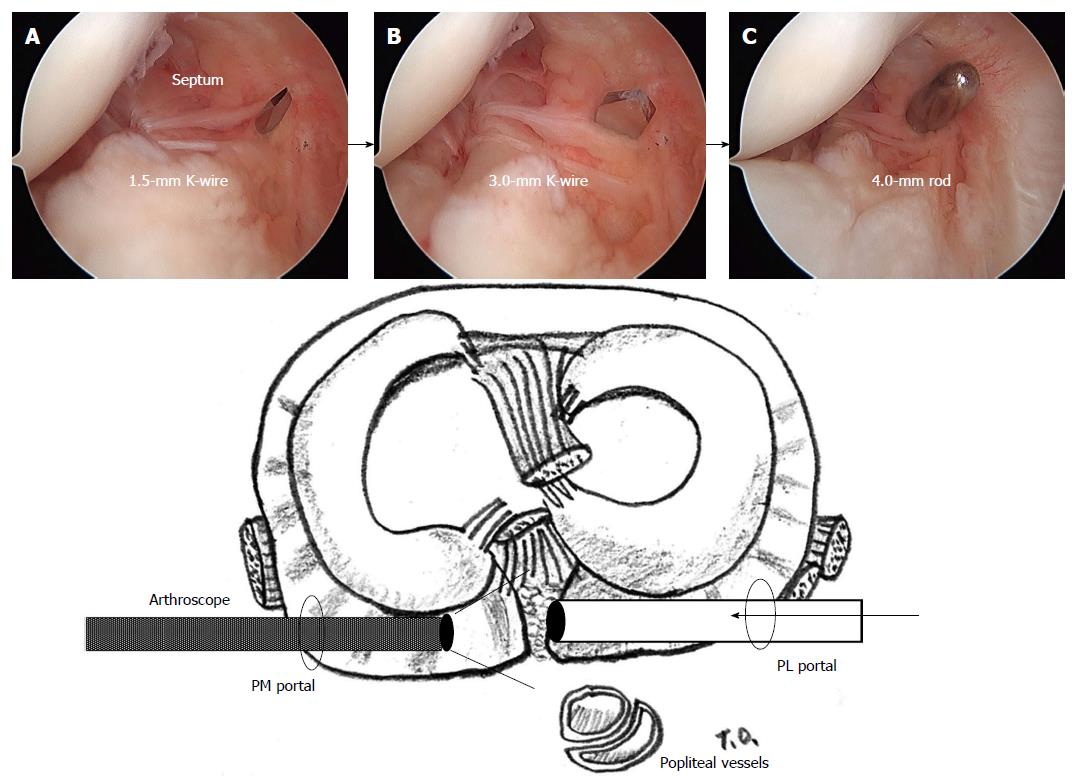
Figure 5 Arthroscopic views from the posteromedial portal.
While maintaining a view of the medial side of the septum using an arthroscope introduced through the posteromedial portal, 1.5-mm (A) and 3.0-mm Kirschner wires (B) are pushed sequentially to the septum through the sheath from the posterolateral portal, finally, a 4.0-mm switching rod is passed through the septum (C). PM: Posteromedial; PL: Posterolateral. (Permission for reproduction was obtained from Nankodo Co., Ltd.).
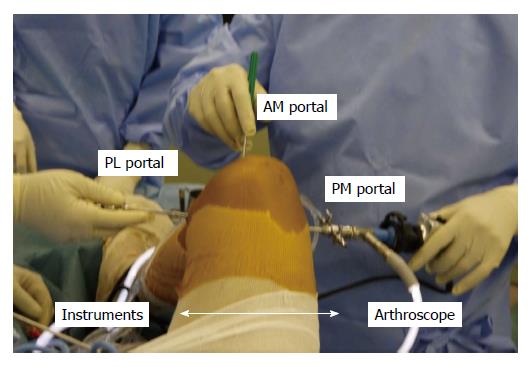
Figure 6 Image taken during an operation involving the posterior transseptal portal.
One of the posterior two portals is used as a viewing portal; the other is used as a working portal. Anterior portals can be also used as working portals. PM: Posteromedial; PL: Posterolateral; AM: Anteromedial.
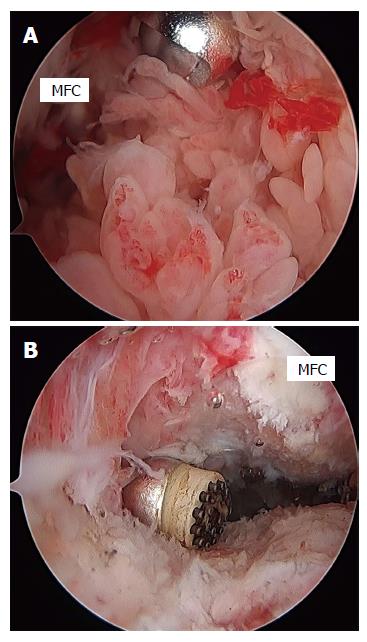
Figure 7 Arthroscopic views of the posterior compartment of the knee in a patient with rheumatoid arthritis.
The posteromedial compartment was filled with synovial villi prior to synovectomy. A shaver is introduced from the posterolateral portal through the transseptal portal (A). An arthroscopic view from the posterolateral portal through the transseptal portal after synovectomy (B). A radiofrequency device is introduced from the posteromedial portal. MFC: Medial femoral condyle.
- Citation: Ohishi T, Takahashi M, Suzuki D, Matsuyama Y. Arthroscopic approach to the posterior compartment of the knee using a posterior transseptal portal. World J Orthop 2015; 6(7): 505-512
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2218-5836/full/v6/i7/505.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5312/wjo.v6.i7.505