Copyright
©The Author(s) 2015.
World J Orthop. Dec 18, 2015; 6(11): 867-876
Published online Dec 18, 2015. doi: 10.5312/wjo.v6.i11.867
Published online Dec 18, 2015. doi: 10.5312/wjo.v6.i11.867
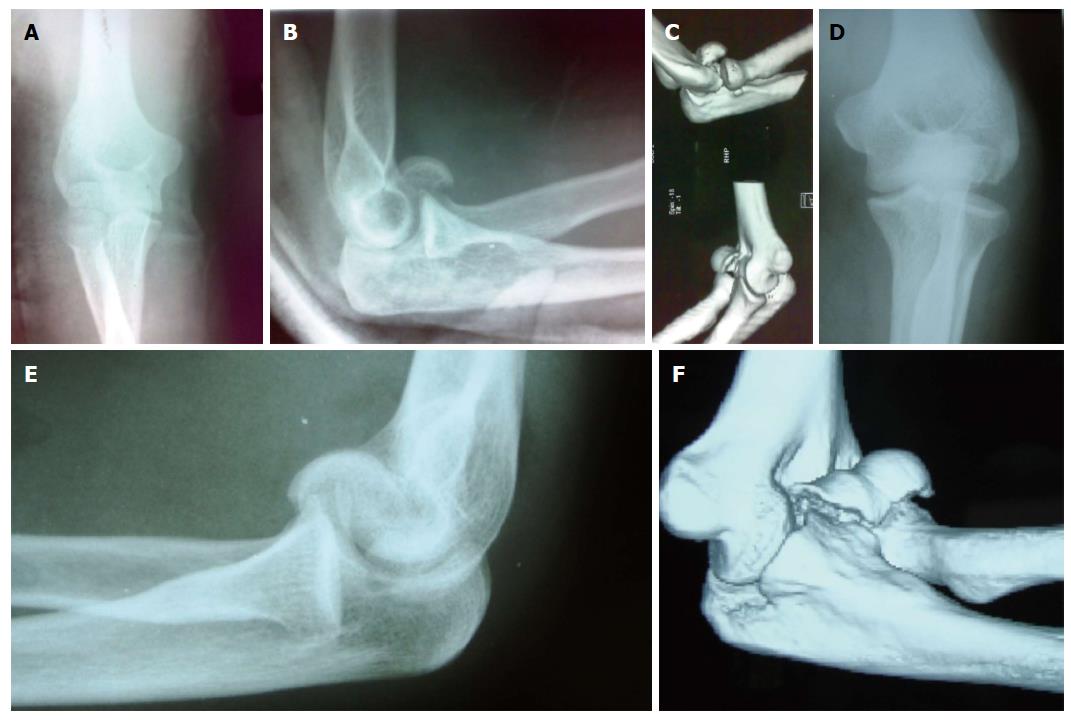
Figure 1 Radiographic and three dimensional tomograhic images of type 1 and type 4 capitellum fractures.
A: Thirty-year-old female with history of fall presented with pain in the elbow region. On anteroposterior view no fracture is seen; B: On lateral view capitellum fracture is seen; C: Her computed tomogram confirms type 1 fracture; D: Thirty-four-year-old male presented with elbow pain after road side accident. Anteroposterior view shows noobvious fracture; E: Lateral view shows a capitellar fracture; F: His computed tomogram shows type 4 capitellotrochlear fragment. The choice of implant and approach is decided preoperatively if detailed imaging is done.
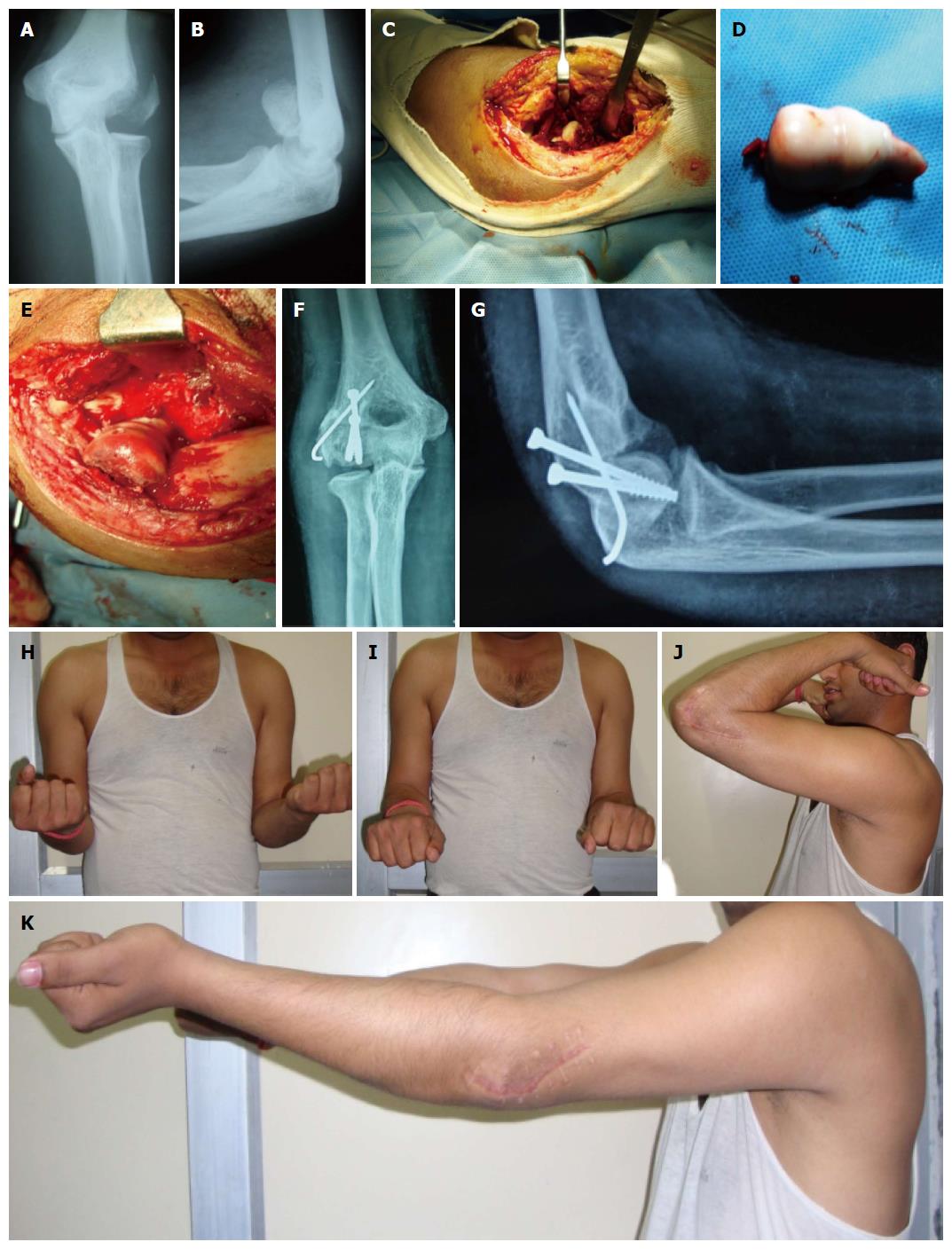
Figure 2 Type 4 capitellum fracture with fracture lateral condyle in adult male-radiological and clinical outcome.
A: Anteroposterior view of left elbow showing type 4 capitello trochlear fragment with lateral condyle fracture in a 34-year-old male after road traffic accident; B: Lateral view showing the fracture fragment. The internally rotated fragment is not giving double arc appearance; C: Lateral extensile approach was done. Intraoperative picture; D: The fragment was free of soft tissue attachments. It was debrided on table and repositioned; E: It was fixed with two cannulatedcancellous screws from posterior to anterior direction and lateral condyle was fixed with K-wire; F: Follow-up anteroposterior view; G: Lateral view. Follow-up shows good consolidation; H: Excellent supination; I: Excellent pronation; J: Flexion; K: Extension. Patient is having excellent MEPS score.
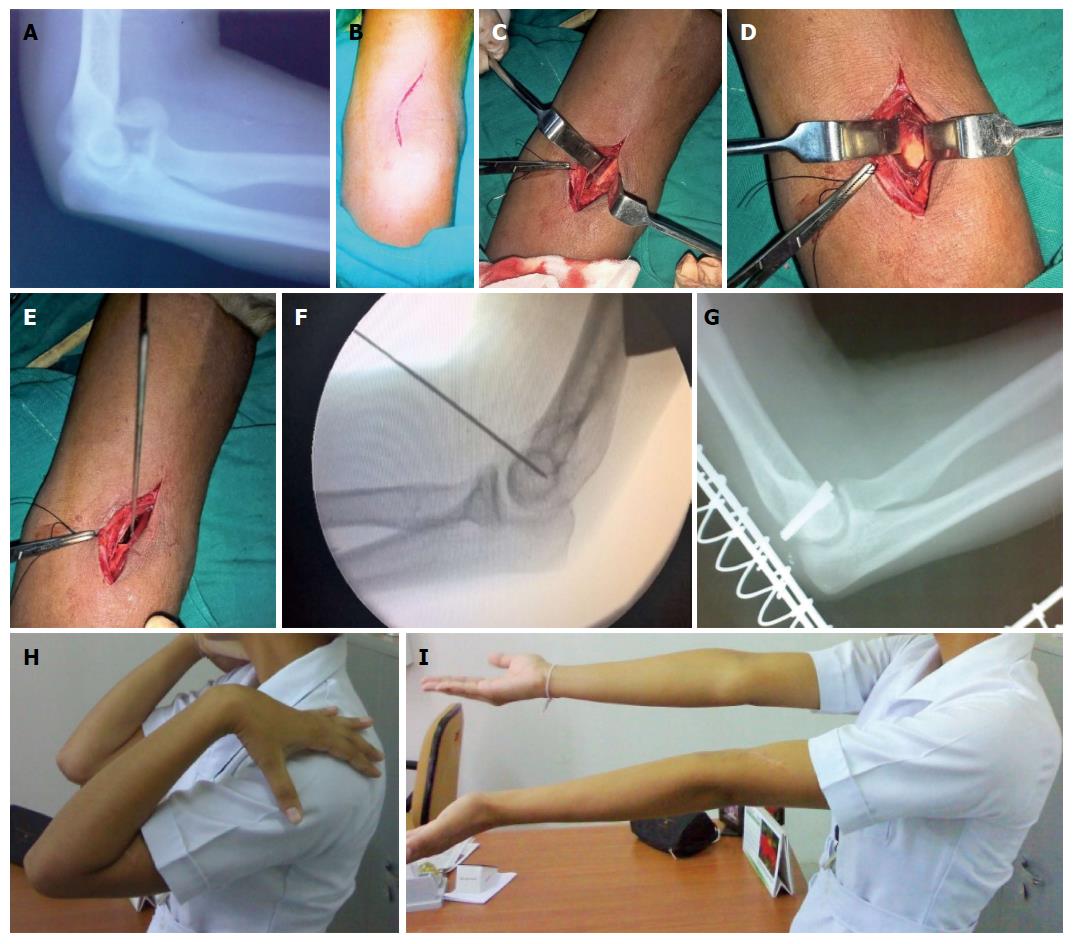
Figure 3 Type 1 capitellum fracture in young female showing anterior approach detail and clinico-radiological follow-up.
A: Twenty-two-year-old nursing student had a fall on left elbow and had type 1 capitellum fracture; B: Anterior approach incision; C: Radial nerve exposed; D: Capitellum fracture surface visible; E: Provisional fixation with K-wire; F: After reduction and fixation with K-wire; G: Lateral radiograph showing fixation with headless screws; H: Excellent extension at follow-up; I: Flexion.
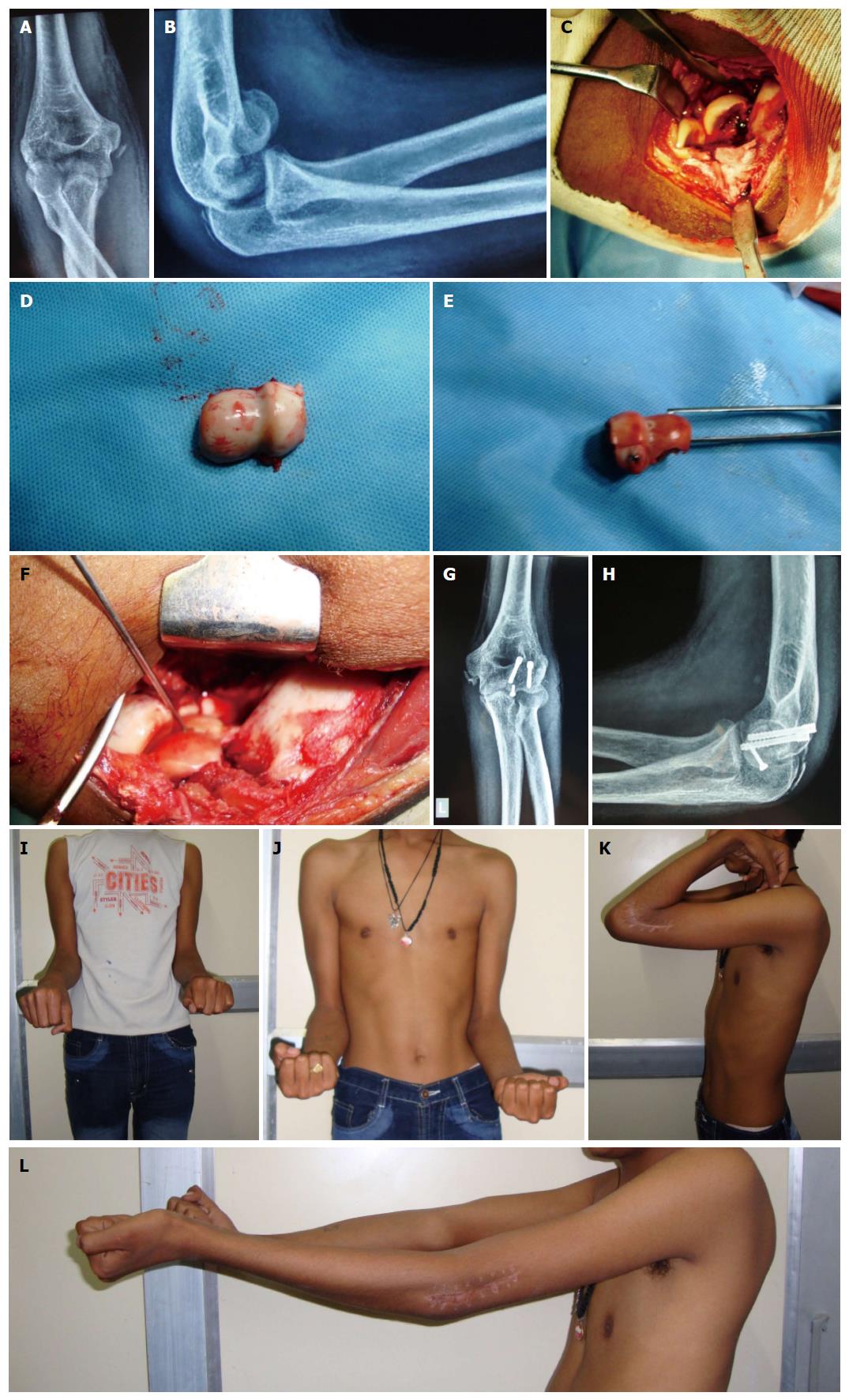
Figure 4 Type 4 capitello-trochlear fracture with medial epicondyle and olecranon chip fracture in adolescnt.
It was managed by articular reconstruction by lateral approach. A: Fourteen-year-old male presented with left elbow type 4 capitellum fracture after road traffic accident. Associated injuries are medial epicondyle and chip fracture olecranon. Anteroposterior view; B: Lateral view showing double arc sign; C: Extensile lateral approach was done. Intraoperative picture showing fractured fragment; D: Major capitellar fragment debrided on table; E: On table reconstruction of the articular fragment was done by 2.7 mm screw; F: Final fixation was done by two headless screws; G: Follow-up AP view; H: Lateral view; I and J: Rotations at follow-up; K: Flexion at follow-up. The patient is having excellent Mayo Elbow Performance Score; L: Extension. The lag is attributed to type of fracture and the approach.
- Citation: Singh AP, Singh AP. Coronal shear fractures of distal humerus: Diagnostic and treatment protocols. World J Orthop 2015; 6(11): 867-876
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2218-5836/full/v6/i11/867.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5312/wjo.v6.i11.867