Copyright
©2014 Baishideng Publishing Group Inc.
World J Orthop. Sep 18, 2014; 5(4): 425-443
Published online Sep 18, 2014. doi: 10.5312/wjo.v5.i4.425
Published online Sep 18, 2014. doi: 10.5312/wjo.v5.i4.425
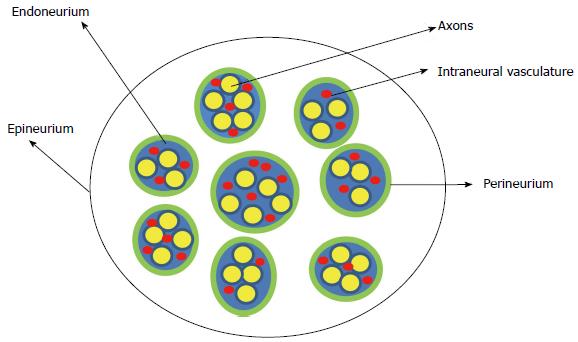
Figure 1 Schematic representation of the cross section of the peripheral nerve.
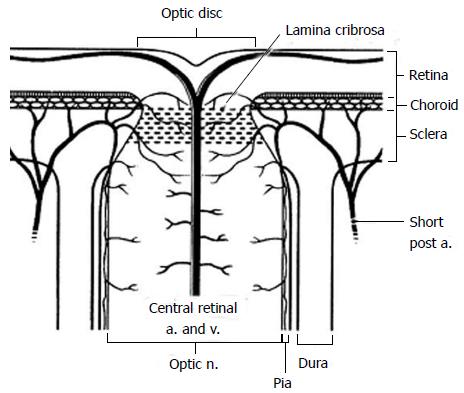
Figure 2 Diagram of the anterior optic nerve showing the arterial and small vessel supply to the choroid and optic nerve as it passes through the lamina cribrosa.
Short post a: Short posterior ciliary artery; a: Artery; v: Vein; n: Nerve (Reprinted from Williams et al[140] with permission).
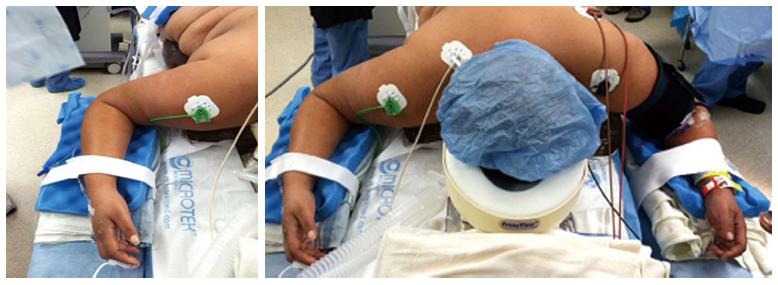
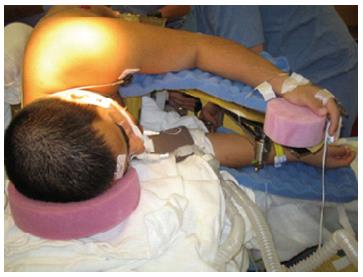
Figure 3 Positioning patient in the prone surrender (superman) position.
The head should be in neutral position on foam supporting head frame (e.g., proneview®) to avoid any direct pressure to the eye. The shoulders should be abducted less than 90°, lateral rotation of the upper arm and extreme elbow flexion should be avoided. The forearm should be positioned in the neutral position to minimize direct pressure on the ulnar nerve in the elbow. Soft foam padding should be placed under the elbows and between the inner upper around the gel rolls (or supporting frame) supporting the body. The level of the forearm should be at or below the mattress surface.
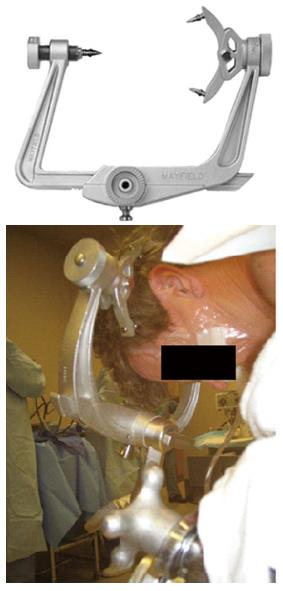
Figure 4 Mayfield (pinned) head holder.
Figure 5 The proneview® allows prone positioning without any pressure on the facial structures.
The mirror provided allows frequent checking of facial structures in the prone position.
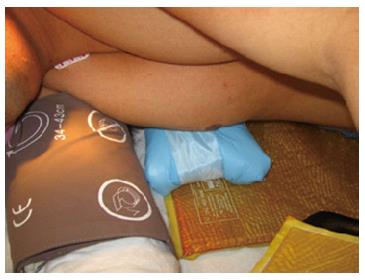
Figure 6 Proper placement of chest roll under the dependent chest in the lateral decubitus position.
The chest roll should not be placed under the dependent axilla.
Figure 7 Positioning the upper extremity in the lateral decubitus position.
The shoulder abduction more than 90°, extreme elbow flexion and forearm pronation should be avoided in the nondependent arm. The nondependent and dependent elbows should be padded with foam. Placing foam or blankets under the dependent hand and foreram to avoid full extension may reduce the likelihood of median nerve injury. Head and neck should be in neutral forward position avoiding neck flexion extension, lateral rotation and lateral flexion.
- Citation: Kamel I, Barnette R. Positioning patients for spine surgery: Avoiding uncommon position-related complications. World J Orthop 2014; 5(4): 425-443
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2218-5836/full/v5/i4/425.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5312/wjo.v5.i4.425