Copyright
©2013 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Orthop. Oct 18, 2013; 4(4): 186-197
Published online Oct 18, 2013. doi: 10.5312/wjo.v4.i4.186
Published online Oct 18, 2013. doi: 10.5312/wjo.v4.i4.186
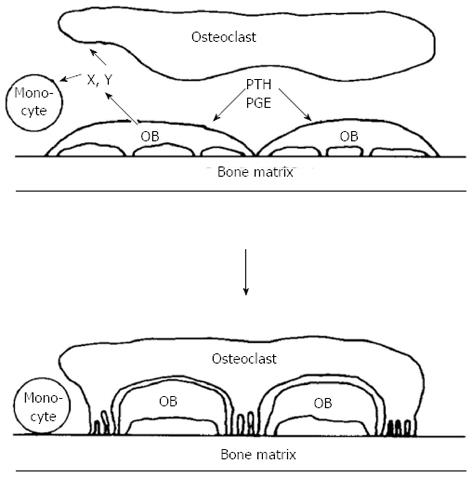
Figure 1 Schematic representation of osteoblast involvement in hormone - stimulated bone resorption (reproduced with permission).
OB: Osteoblast; PTH: Parathyroid hormone; PGE: Prostaglandin E.
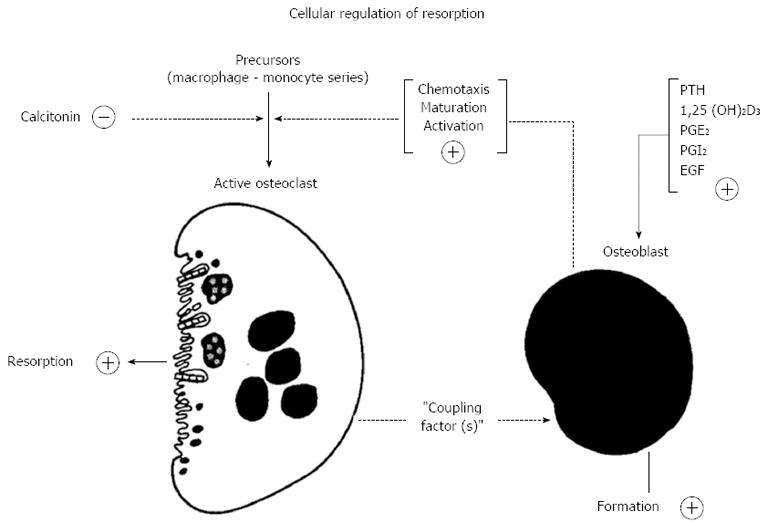
Figure 2 Proposed participation of cells in the osteoblast lineage in the action of the bone - resorbing hormones (reproduced with permission from Ref.
39). PTH: Parathyroid hormone; PGE2: Prostaglandin E2; EGF: Epidermal growth factor.
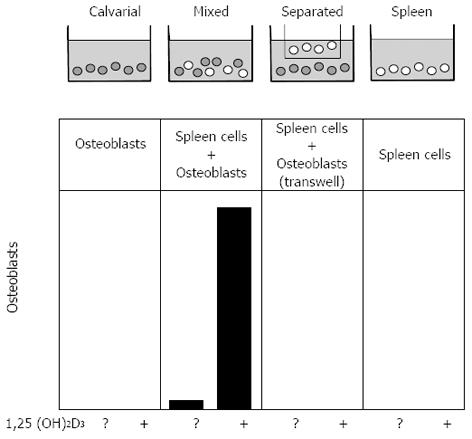
Figure 3 Representation of the co-culture method that showed the contact-dependent promotion of osteoclast formation by stromal osteoblasts.
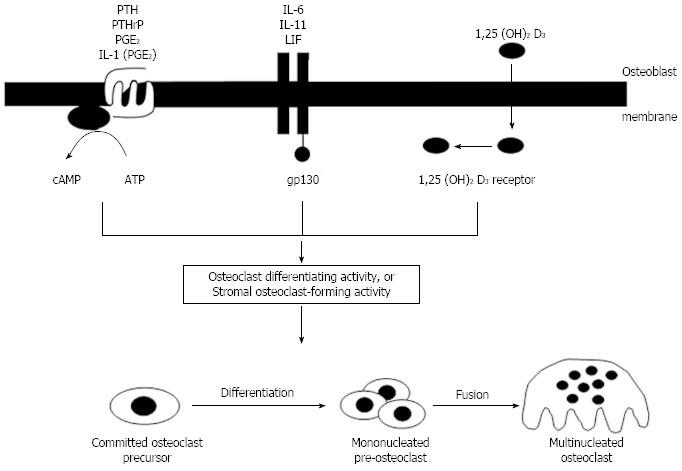
Figure 4 Concepts of regulation of osteoclastogenesis from the mid-1980’s until the discovery of the molecular regulation mechanisms.
Three different signaling pathways converged to promote formation of osteoclasts through undefined mechanisms. IL: Interleukin; PTH: Parathyroid hormone; LIF: Leukemia inhibitory factor.
- Citation: Martin TJ. Historically significant events in the discovery of RANK/RANKL/OPG. World J Orthop 2013; 4(4): 186-197
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2218-5836/full/v4/i4/186.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5312/wjo.v4.i4.186