Copyright
©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Orthop. Jul 18, 2025; 16(7): 107913
Published online Jul 18, 2025. doi: 10.5312/wjo.v16.i7.107913
Published online Jul 18, 2025. doi: 10.5312/wjo.v16.i7.107913
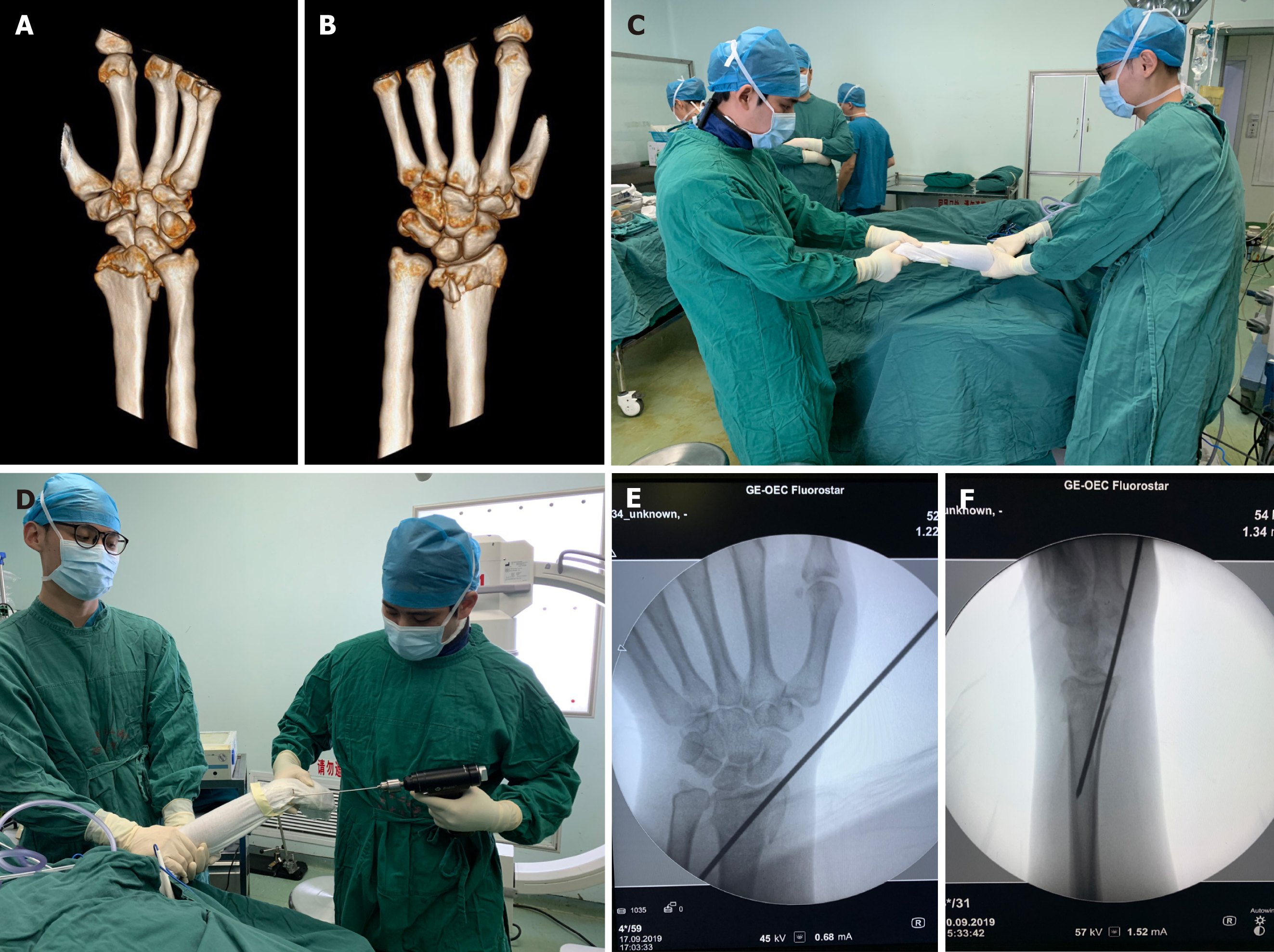
Figure 1 A patient with a C1 distal radius fracture underwent manual reduction and temporary Kirschner wire fixation after being anesthetized.
A and B: 3D reconstruction computed tomography of the fracture; C: Closed manipulation reduction; D: A 15 mm diameter Kirschner wire was inserted from the styloid process of the radius to the ulnar side of the proximal fracture; E and F: Anteroposterior and lateral wrist joint X-rays were taken after manual reduction and temporary Kirschner wire fixation.
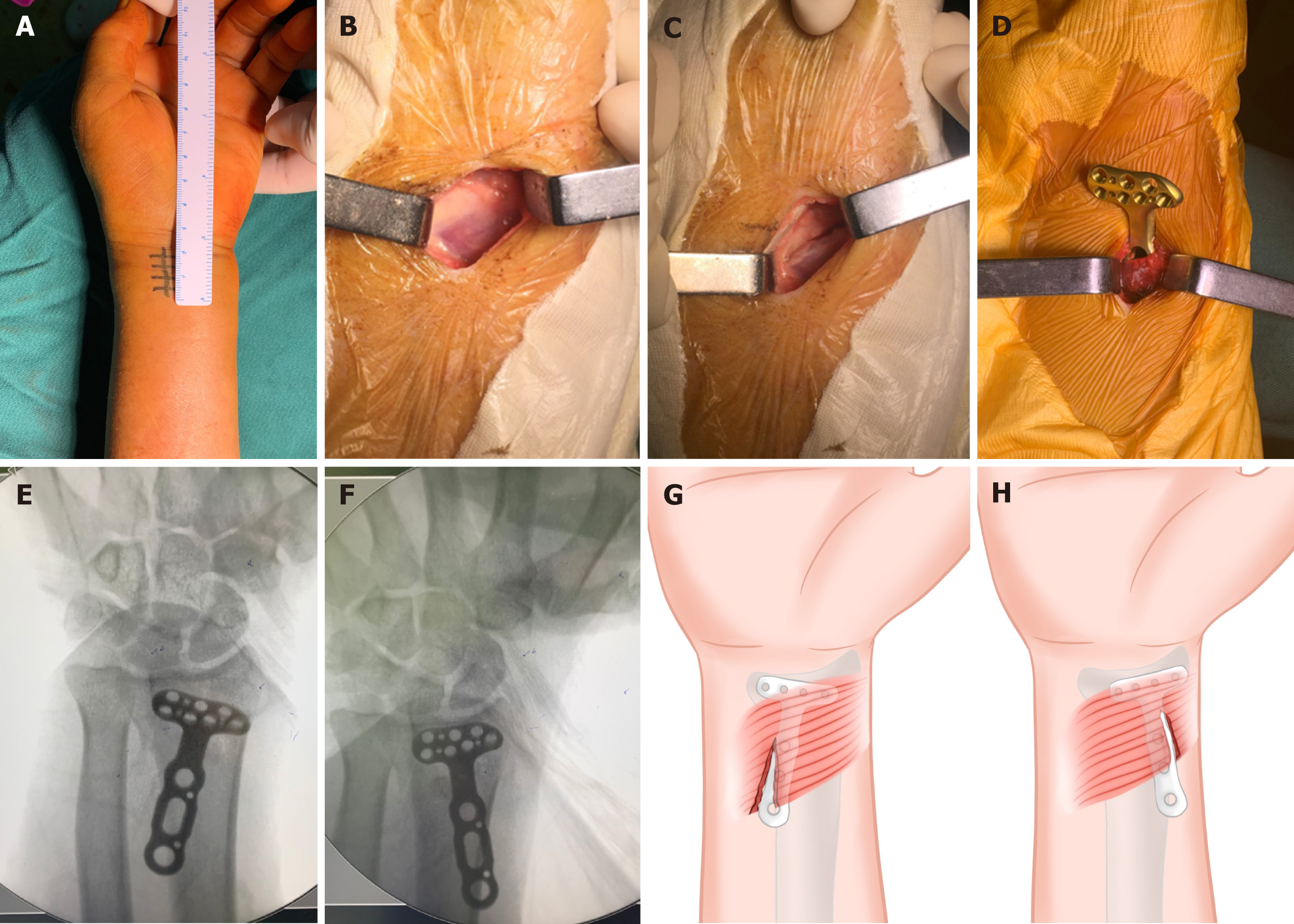
Figure 2 Schematic diagram of injury to the pronator quadratus during minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis with a small incision.
A: The surgical incision; B: The distal margin of the pronator quadratus (PQ) was exposed; C: The PQ was incised; D: The plate was inserted beneath the PQ; E and F: Due to blind penetration, the plate may be placed on the radial or ulnar side during the operation; G and H: The PQ muscle was incised at both its origin and insertion points along the volar surface of the distal third of the radius.
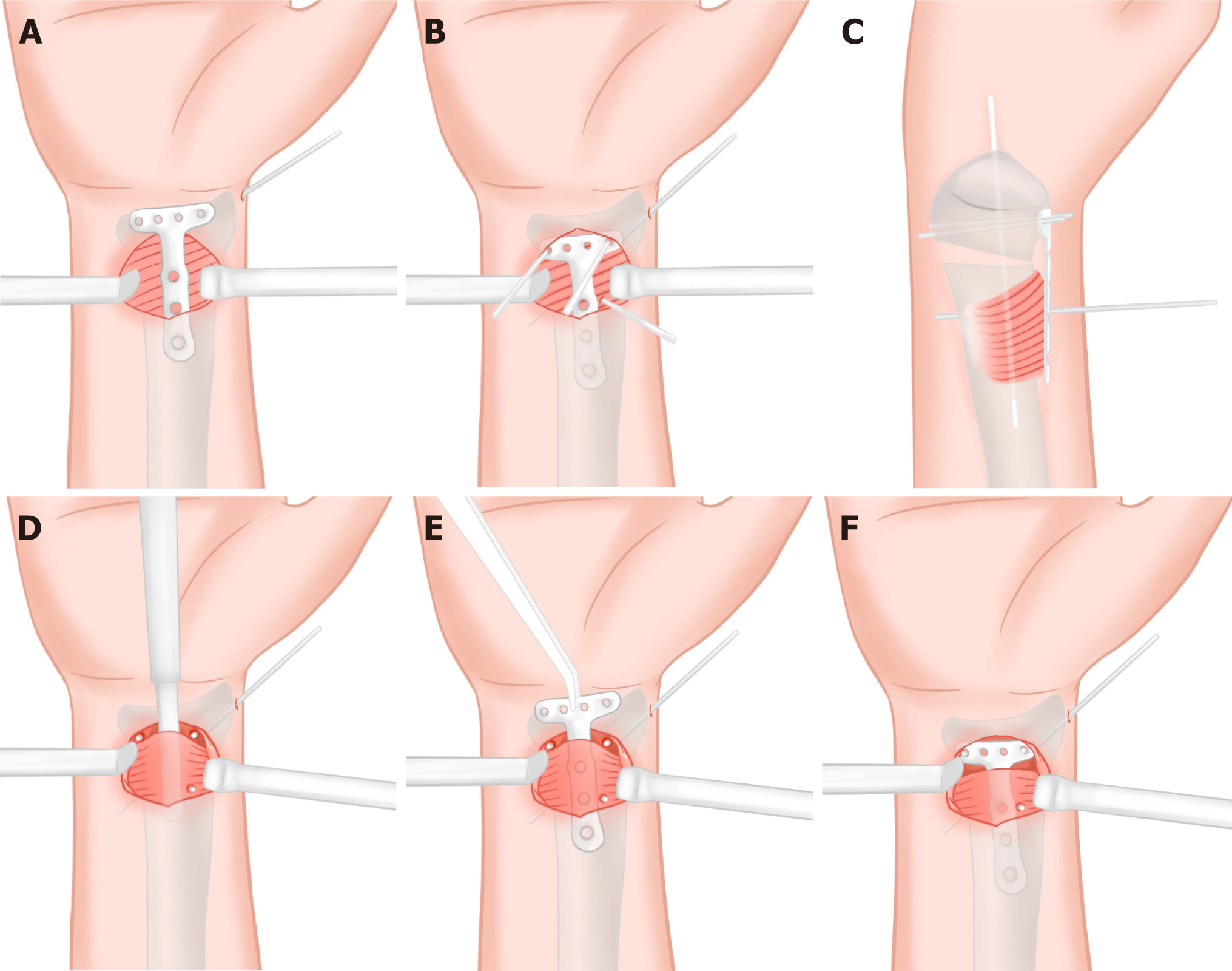
Figure 3 Schematic diagram of the three-point positioning technique.
A: The plate was placed above the unseparated pronator quadratus (PQ) muscle; B and C: Two 1.5 mm Kirschner wires were inserted through the radial and ulnar distal screw holes of the plate, penetrating both cortices. An additional 1.5 mm Kirschner wire was placed adjacent to the ulnar border of the plate's central portion to verify proper radial axis alignment; D: Following trimming of all three Kirschner wires to approximately 0.5 cm in length and leaving them in situ, the plate was removed and subperiosteal dissection of the PQ muscle was performed; E and F: The locking hole of the plate's distal radial and ulnar sides were "guided onto" into the two shorted Kirschner wire posts at the distal end after the plate was inserted into the tunnel from the radial edge of the proximal Kirschner wire.
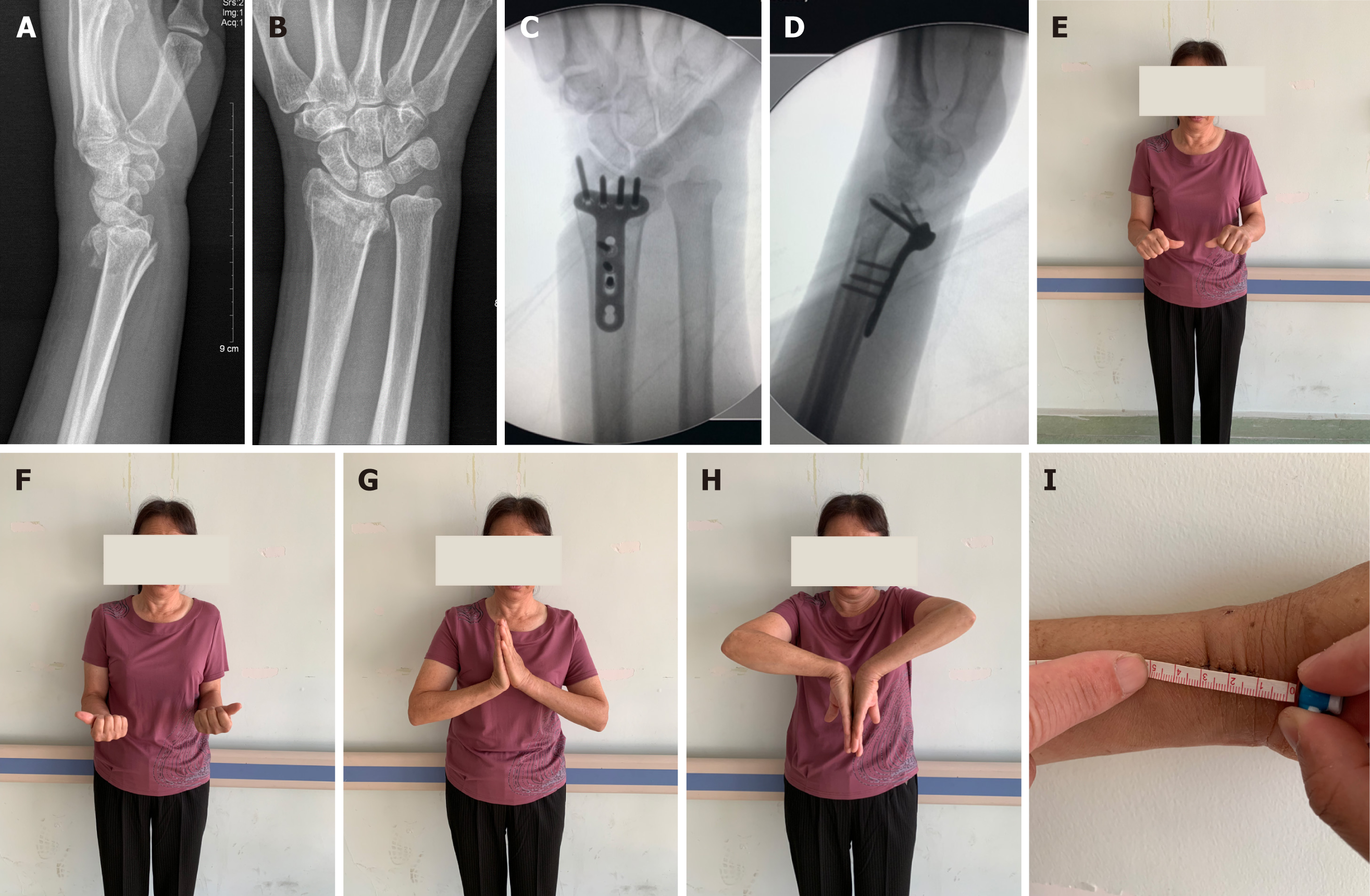
Figure 4 Follow-up data of a 61-year-old woman with C1 fracture.
A and B: Preoperative anteroposterior and lateral X-rays; C and D: Anteroposterior and lateral X-ray immediately after surgery; E-H: Wrist range of motion at final follow-up; I: Incision length and scar appearance.
- Citation: Ye YY, Shen ZQ, Wu CL, Lin YB. Minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis for distal radius fractures using a 3-point positioning technique. World J Orthop 2025; 16(7): 107913
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2218-5836/full/v16/i7/107913.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5312/wjo.v16.i7.107913