Copyright
©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Orthop. Feb 18, 2025; 16(2): 103416
Published online Feb 18, 2025. doi: 10.5312/wjo.v16.i2.103416
Published online Feb 18, 2025. doi: 10.5312/wjo.v16.i2.103416
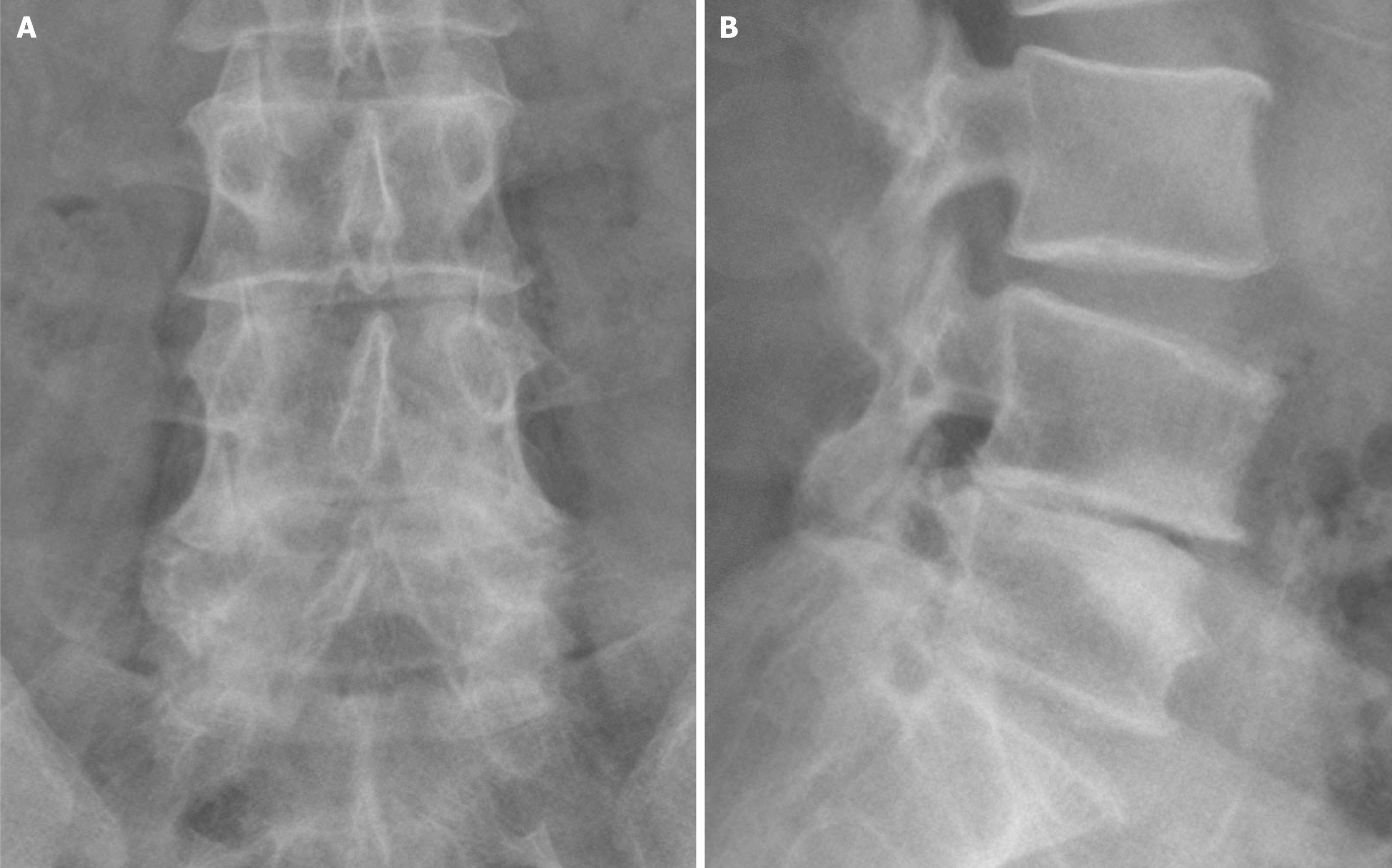
Figure 1 Preoperative lumbar spine X-ray image shows a narrow intervertebral space at L4/5.
A: Anteroposterior view; B: Lateral view.
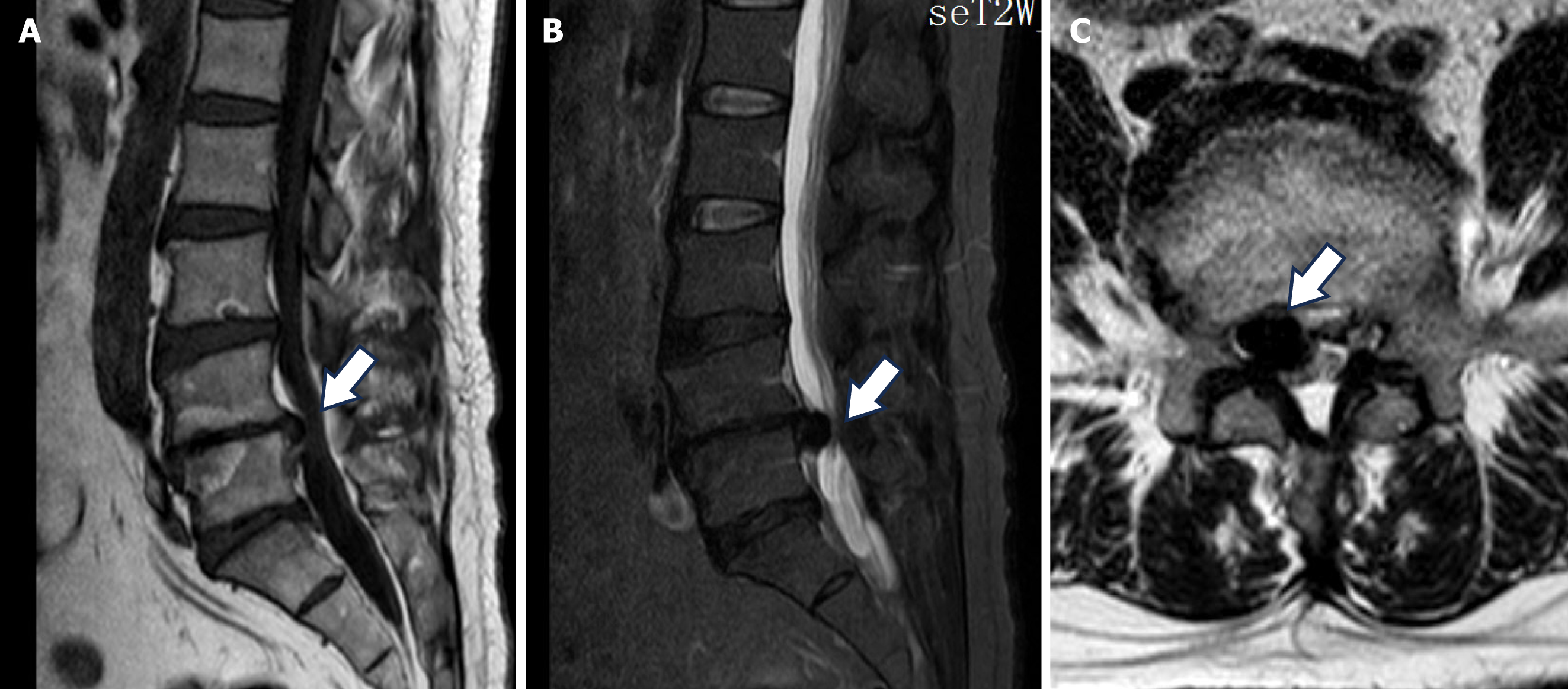
Figure 2 Magnetic resonance imaging reveals a circular mass around the L4/5 intervertebral foramina at the lateral recess, which displayed low signal intensity on both T1 and T2-weighted images, endplate inflammation signs was also found.
A and B: The T1 (A) and T2-weighted images (B); C: Axial T2-weighted magnetic resonance imaging. The white arrow indicates a pseudocyst within the intervertebral foramen.
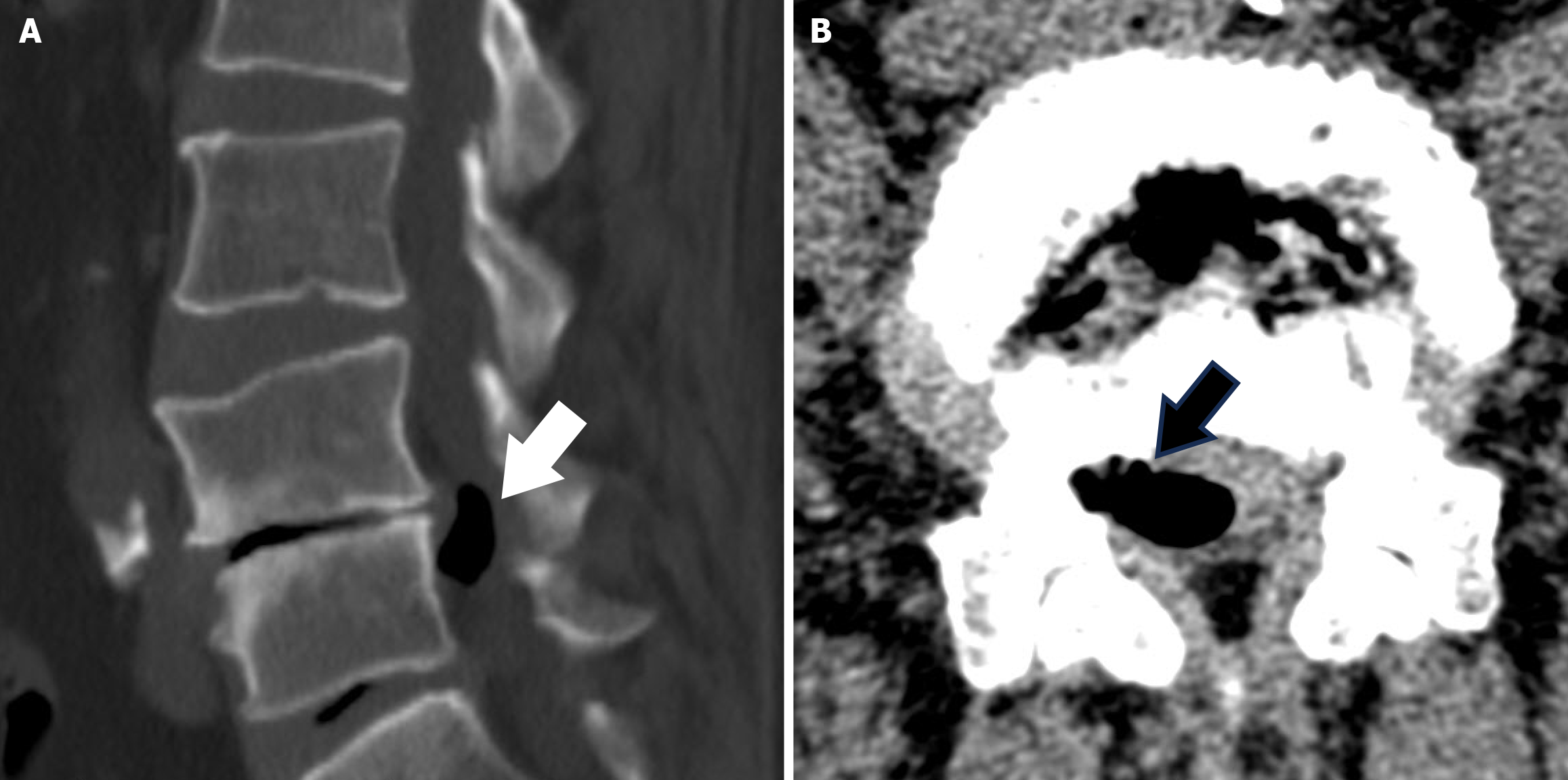
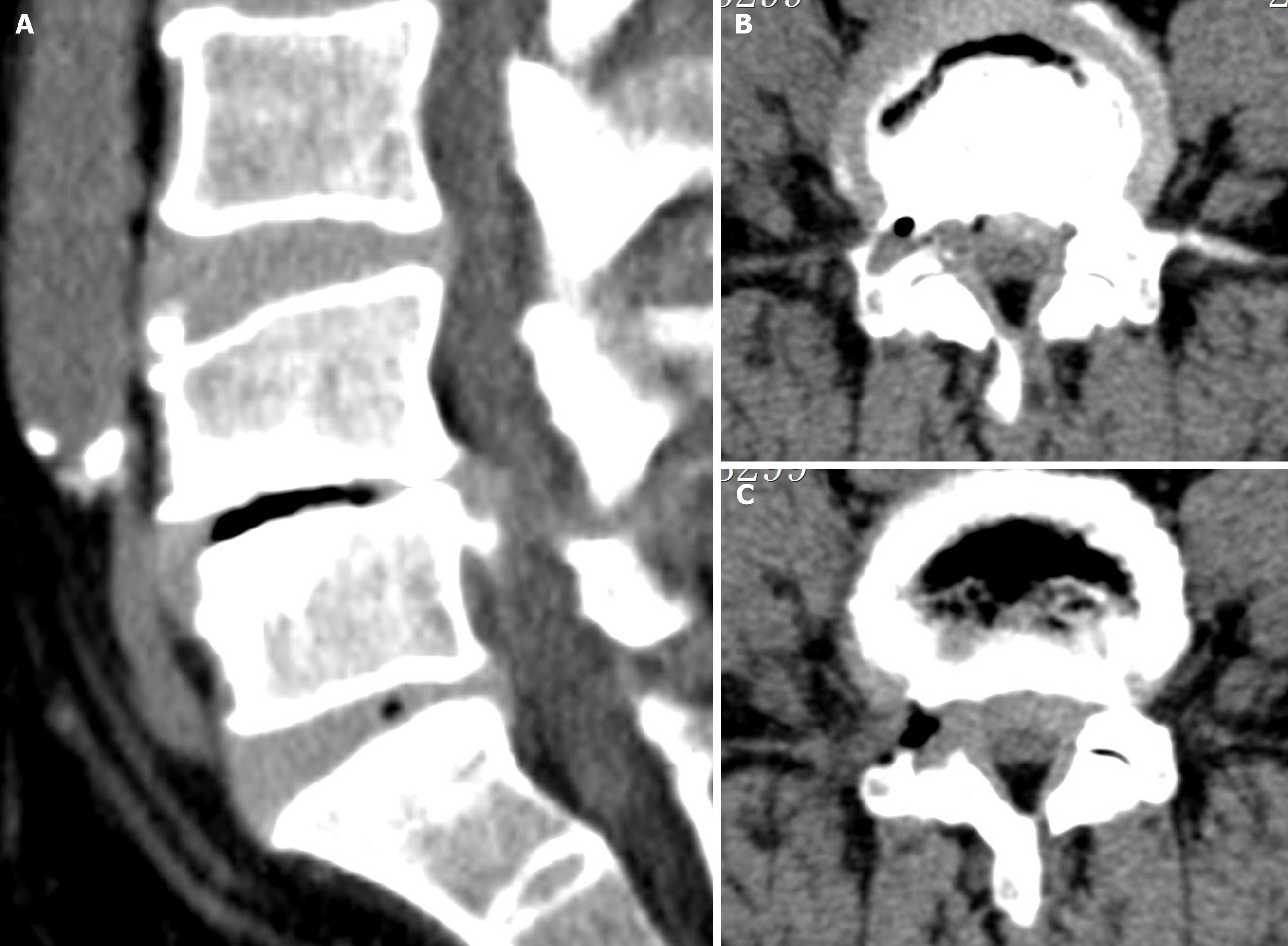
Figure 3 Preoperative computed tomography demonstrating an irregular circular mass of low density surrounding the L4/5 intervertebral foramina.
A: Sagittal image; B: Axial image. The arrow indicates a pseudocyst with gas content outside the intervertebral foramen.
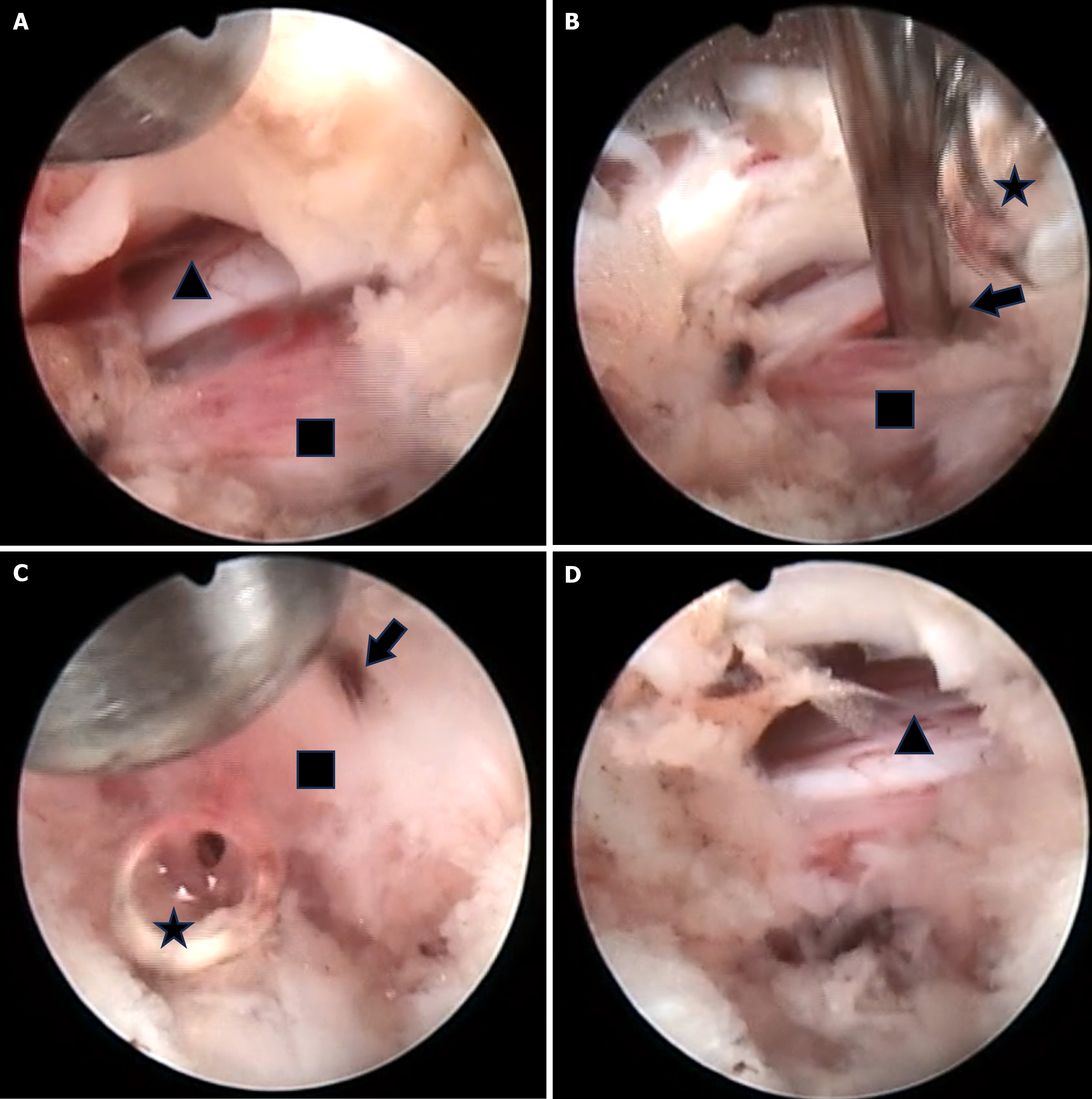
Figure 4 Intraoperative endoscopic images.
A: The L5 nerve root was compressed by a pseudocyst; B: Air bubbles observed when the pseudocyst was punctured; C: Removing the pseudocyst wall using straight and flexible graspers; D: The pseudocyst was completely removed and the nerve root was decompressed. Square: Gas-containing pseudocyst; Triangle: L5 nerve root; Star: Air bubbles; Arrow: Fluid flowing out from the pseudocyst.
Figure 5 Postoperative computed tomography images show that the gas-containing pseudocyst has been removed.
A: Sagittal view; B and C: Axial views.
- Citation: Jiang ZX, Ren JB, Li YC, Chen L. Percutaneous transforaminal endoscopic treatment of gas-containing pseudocyst compressing the L5 nerve root: A case report. World J Orthop 2025; 16(2): 103416
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2218-5836/full/v16/i2/103416.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5312/wjo.v16.i2.103416