Copyright
©The Author(s) 2023.
World J Orthop. Feb 18, 2023; 14(2): 42-54
Published online Feb 18, 2023. doi: 10.5312/wjo.v14.i2.42
Published online Feb 18, 2023. doi: 10.5312/wjo.v14.i2.42
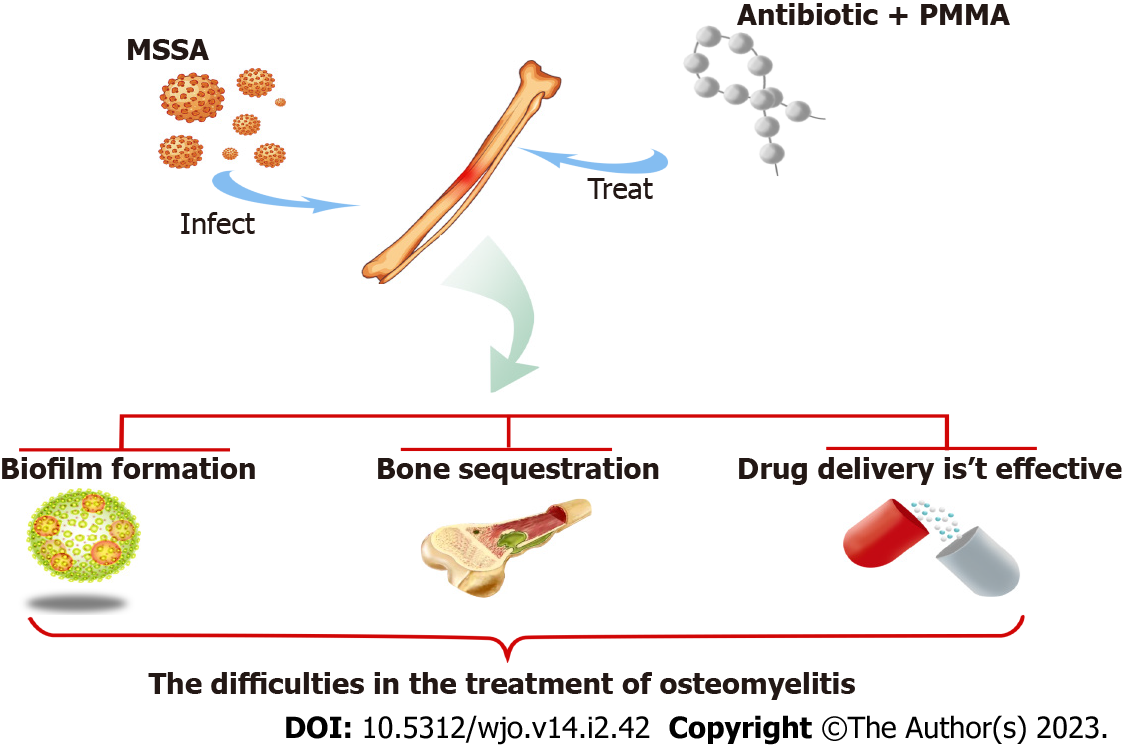
Figure 1 A schematic of major challenges in the treatment of osteomyelitis.
MSSA: Methicillin-susceptible Staphylococcus aureus; PMMA: Polymethyl methacrylate.
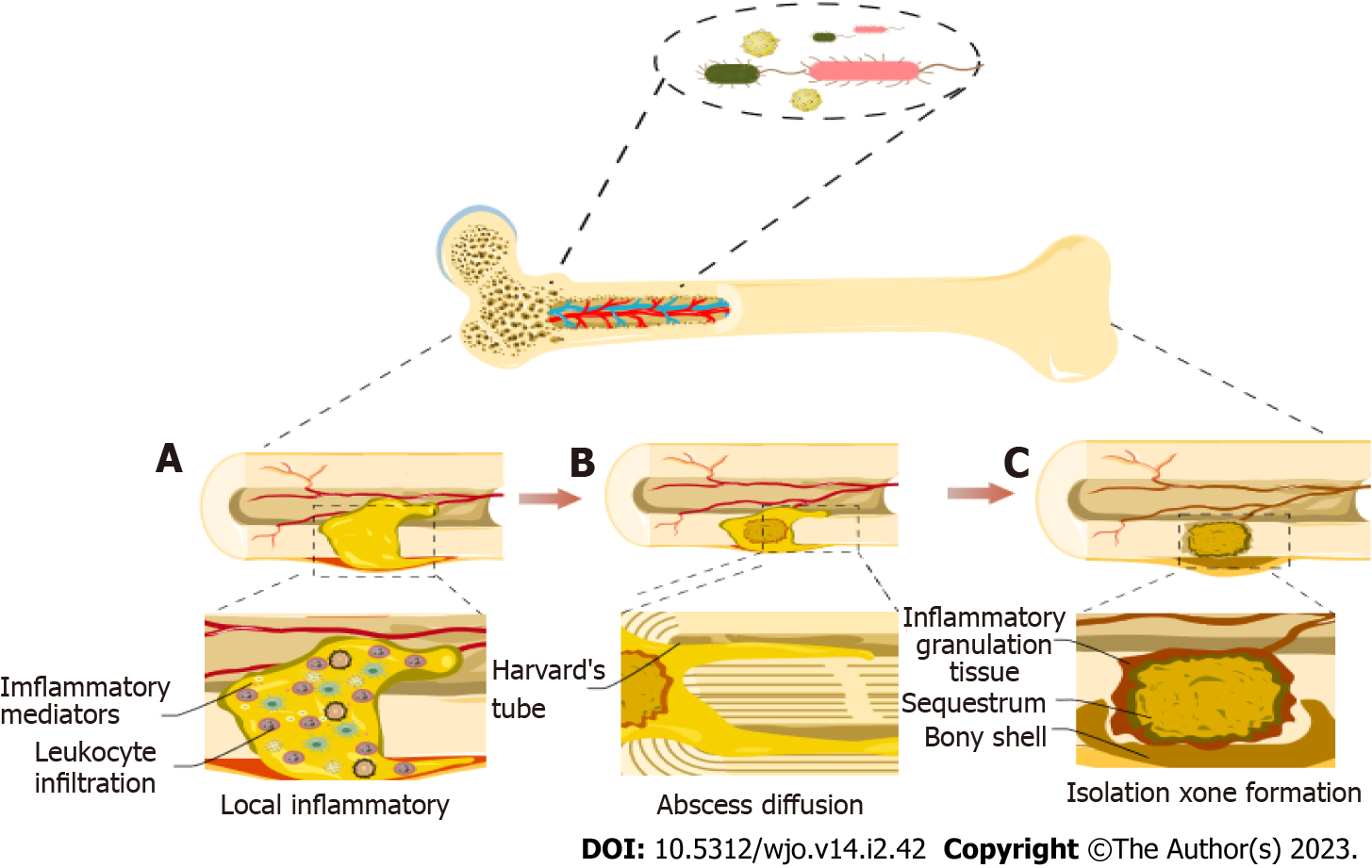
Figure 2 Pathophysiological mechanism of osteomyelitis.
A: Leukocyte necrosis releases inflammatory mediators to destroy bone matrix and bone trabeculae, forming abscesses; B: The infected lesions spread to the adjacent bone structures through Harvard’s tube, and the intraosseous pressure is increased; C: Bone destruction and vascular obstruction resulted in different degrees of osteonecrosis and encapsulation.
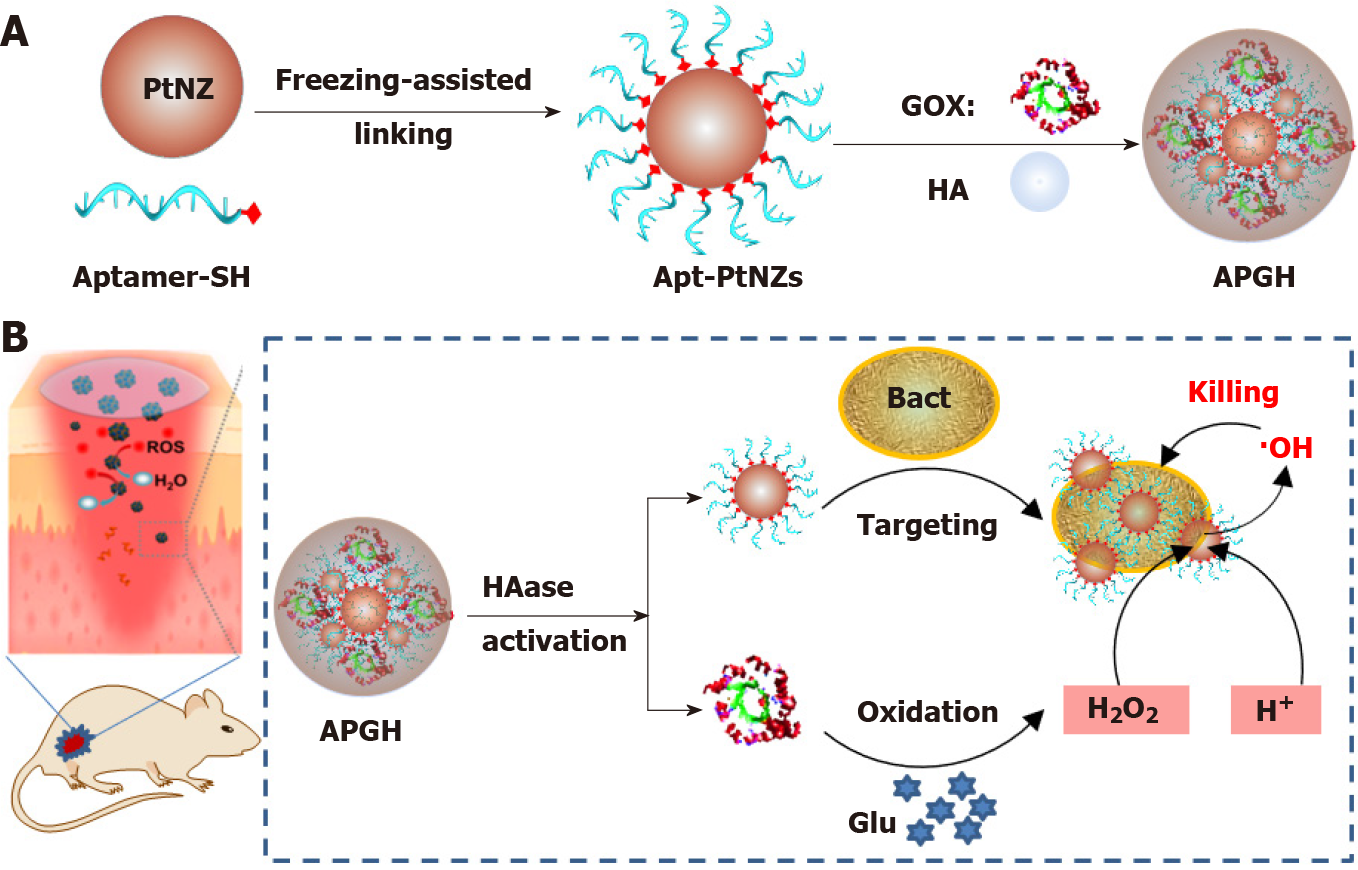
Figure 3 The illustration of APGH released the Aptamer-functionalized platinum nanozymes and glucose oxidase and its application for chemodynamic sterilization.
A: The preparation route for the nanozyme capsule (APGH) with aptamer-functionalized platinum nanozymes, glucose oxidase and hyaluronic acid; B: Schematic illustration of APGH activation, activity switching in the infected wound, and its application for chemodynamic sterilization through in situ generation of COH on bacteria surface. Apt-PtNZ: Aptamer-functionalized platinum nanozymes; HA: Hyaluronic acid; GOX: Glucose oxidase. Citation: Chen L, Xing S, Lei Y, Chen Q, Zou Z, Quan K, Qing Z, Liu J, Yang R. A Glucose-Powered Activatable Nanozyme Breaking pH and H2O2 Limitations for Treating Diabetic Infections. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl 2021; 60: 23534-23539. Copyright ©The Author(s) 2021. Published by John Wiley and Sons. The authors have obtained the permission for figure using from the John Wiley and Sons and Copyright Clearance Center (Supplementary material).
Figure 4 Antibacterial effects of Fe3O4/carbon nanotube/Gent on methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus-infected osteomyelitis in vivo.
A: Macro images of femur and tibia in each group of animal models 14 d after treatment. Scale bars = 1 cm; B: Wet-stained images, scale bars = 20 μm, 14 d after treatment; C: Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus count in bone marrow of each group after 2 d of antibacterial treatment. CNT: Carbon nanotubes. Citation: Qiao Y, Liu X, Li B, Han Y, Zheng Y, Yeung KWK, Li C, Cui Z, Liang Y, Li Z, Zhu S, Wang X, Wu S. Treatment of MRSA-infected osteomyelitis using bacterial capturing, magnetically targeted composites with microwave-assisted bacterial killing. Nat Commun 2020; 11: 4446. MRSA: Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Copyright ©The Author(s) 2021. Published by Springer Nature. The authors have obtained the permission for figure using from the Springer Nature group (Supplementary material).
- Citation: Zeng M, Xu Z, Song ZQ, Li JX, Tang ZW, Xiao S, Wen J. Diagnosis and treatment of chronic osteomyelitis based on nanomaterials. World J Orthop 2023; 14(2): 42-54
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2218-5836/full/v14/i2/42.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5312/wjo.v14.i2.42