Copyright
©The Author(s) 2023.
World J Orthop. Oct 18, 2023; 14(10): 741-754
Published online Oct 18, 2023. doi: 10.5312/wjo.v14.i10.741
Published online Oct 18, 2023. doi: 10.5312/wjo.v14.i10.741
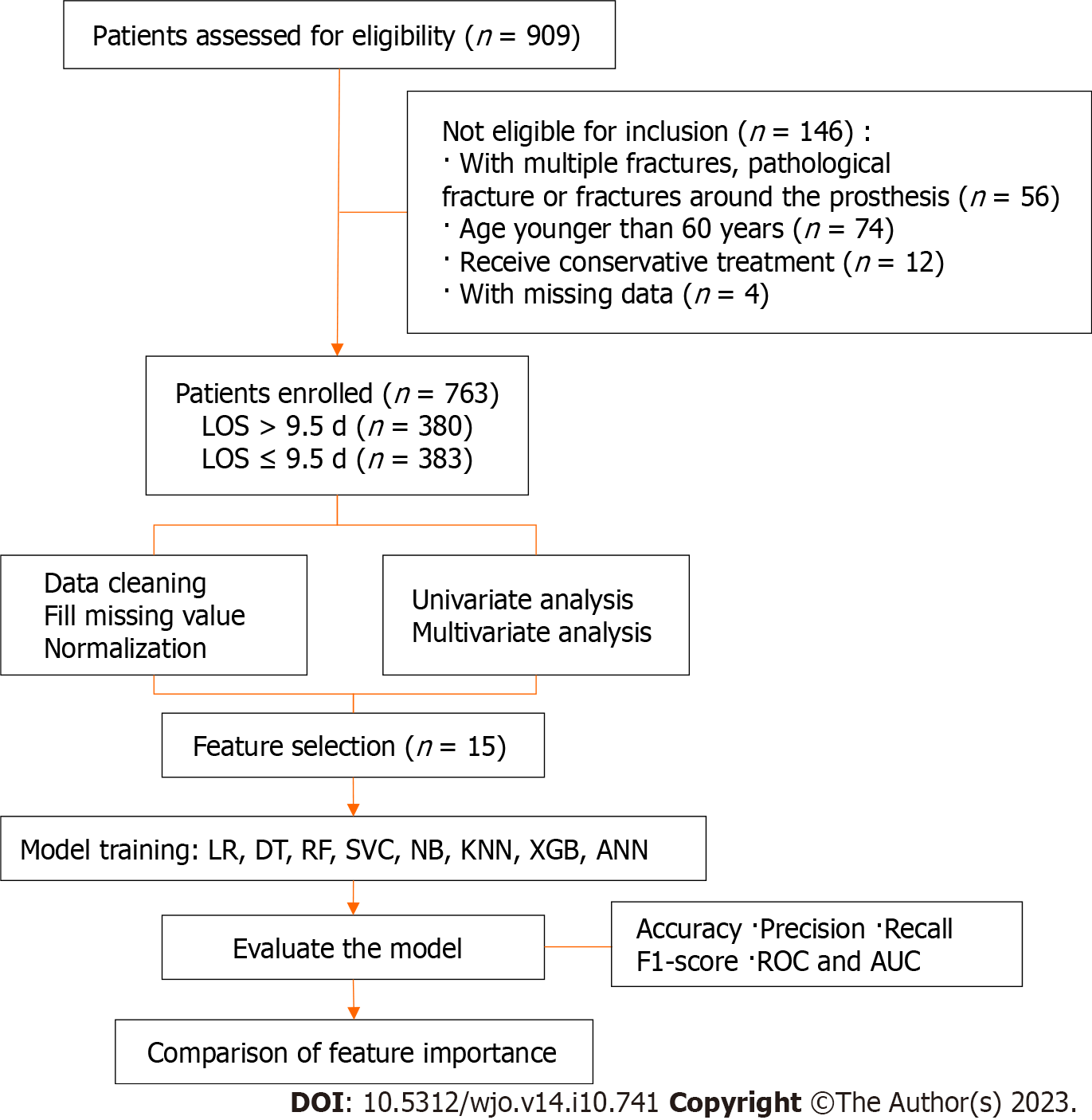
Figure 1 The flow diagram of the research process.
LOS: Length of stay; LR: Logistic regression; DT: Decision tree; RF: Random forest; SVC: Support vector classifier; NB: Naïve bayes; KNN: K-nearest neighbour; XGB: eXtreme Gradient Boosting; ANN: Artificial neural network; ROC: Receiver operating characteristic; AUC: area under the receiver operating characteristic curve.
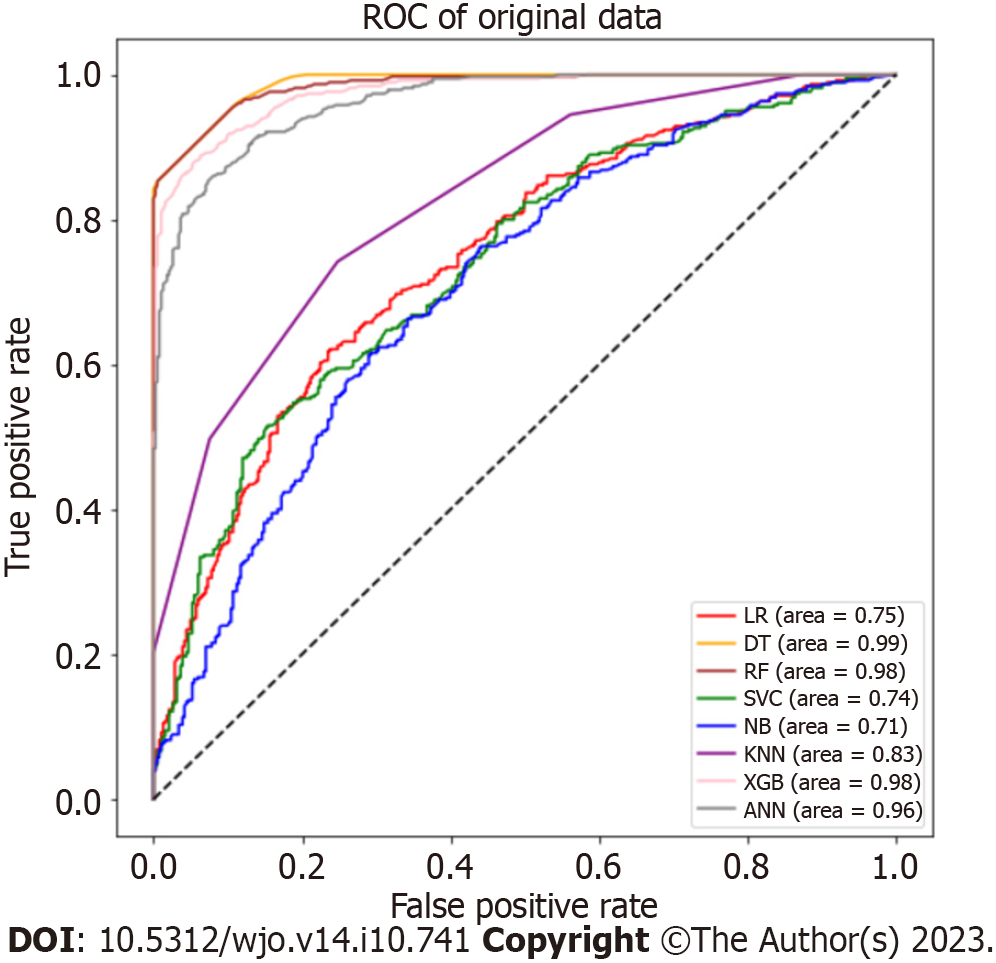
Figure 2 Receiver operating characteristic curve for machine learning models in the original data.
ROC: Receiver operating characteristic; LR: Logistic regression; DT: Decision tree; RF: Random forest; SVC: Support vector classifier; NB: Naïve Bayes; KNN: K-nearest Neighbour; XGB: eXtreme Gradient Boosting; ANN: Artificial neural network.
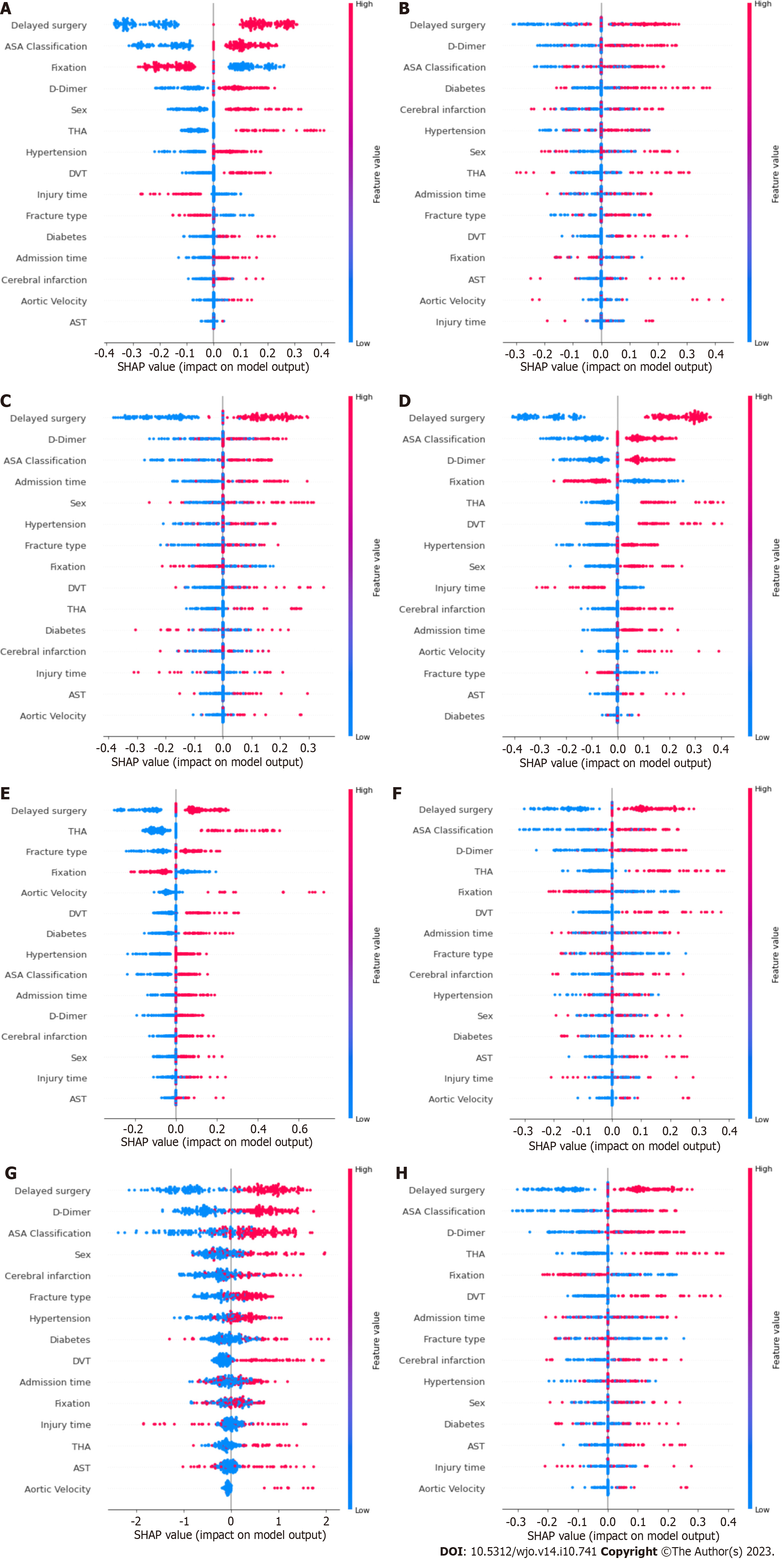
Figure 3 Shapley additive explanations summary plots of each model.
A: Logistic regression; B: Decision tree; C: Random forest; D: Support vector classifier; E: Naïve bayes; F: K-nearest neighbour; G: eXtreme Gradient Boosting; H: Artificial neural network. ASA: American society of anaesthesiologists; THA: Total hip arthroplasty; DVT: Deep venous thrombosis; AST: Aspartate aminotransferase.
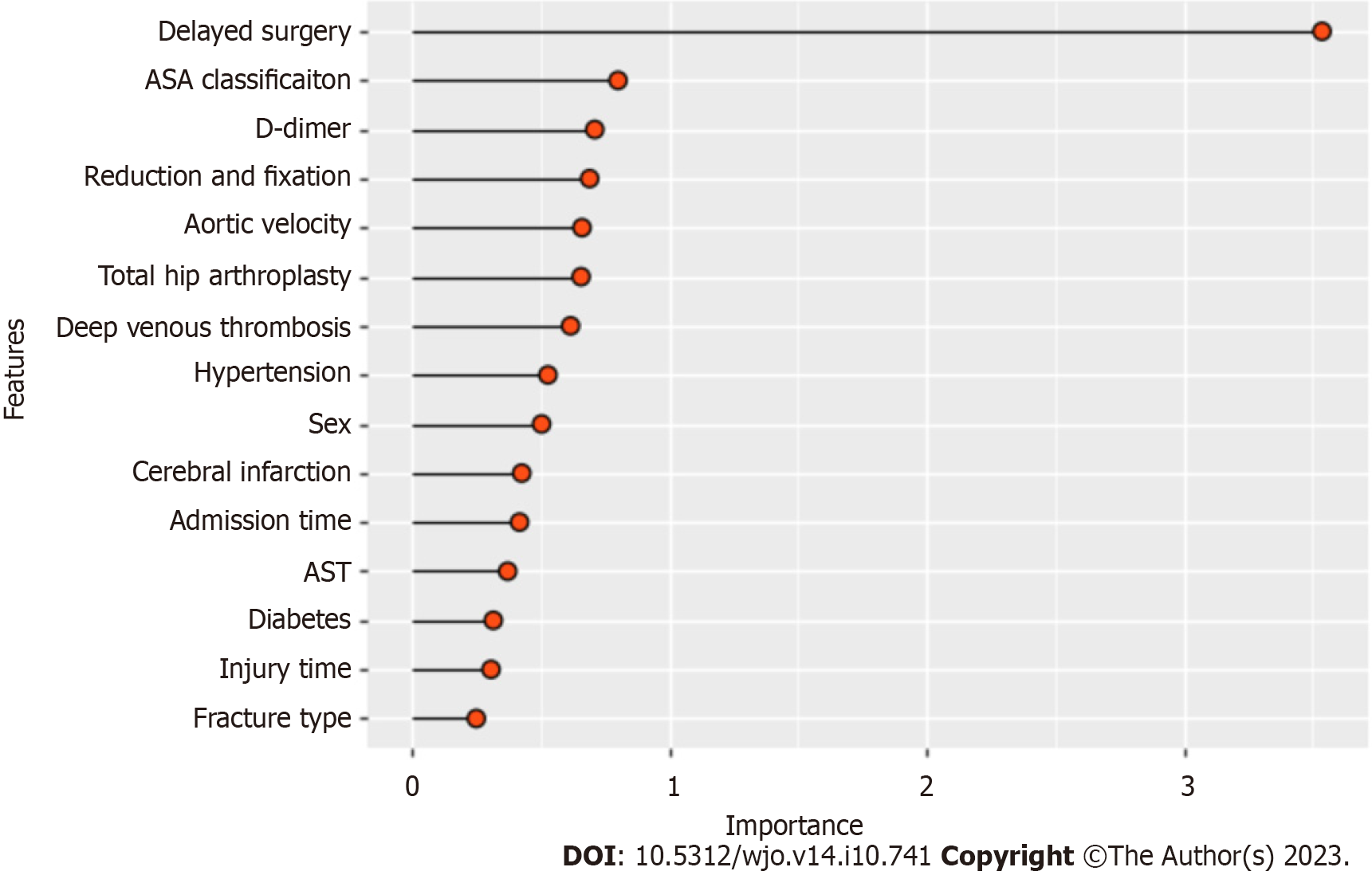
Figure 4 Comprehensive importance of features.
ASA: American society of anaesthesiologists; AST: Aspartate aminotransferase.
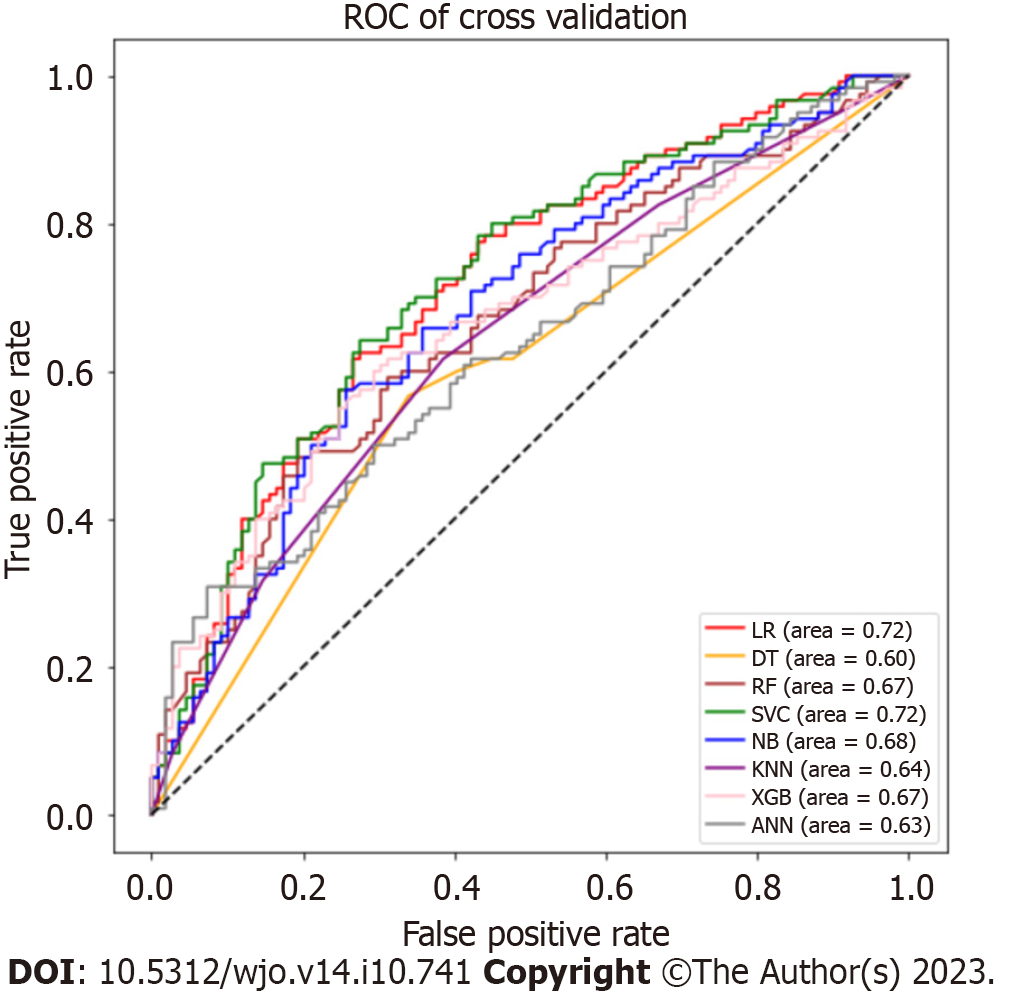
Figure 5 Receiver operating characteristic curve for machine learning models after cross-validation.
ROC: Receiver operating characteristic; LR: Logistic regression; DT: Decision tree; RF: Random forest; SVC: Support vector classifier; NB: Naïve bayes; KNN: K-nearest Neighbour; XGB: eXtreme Gradient Boosting; ANN: Artificial neural network.
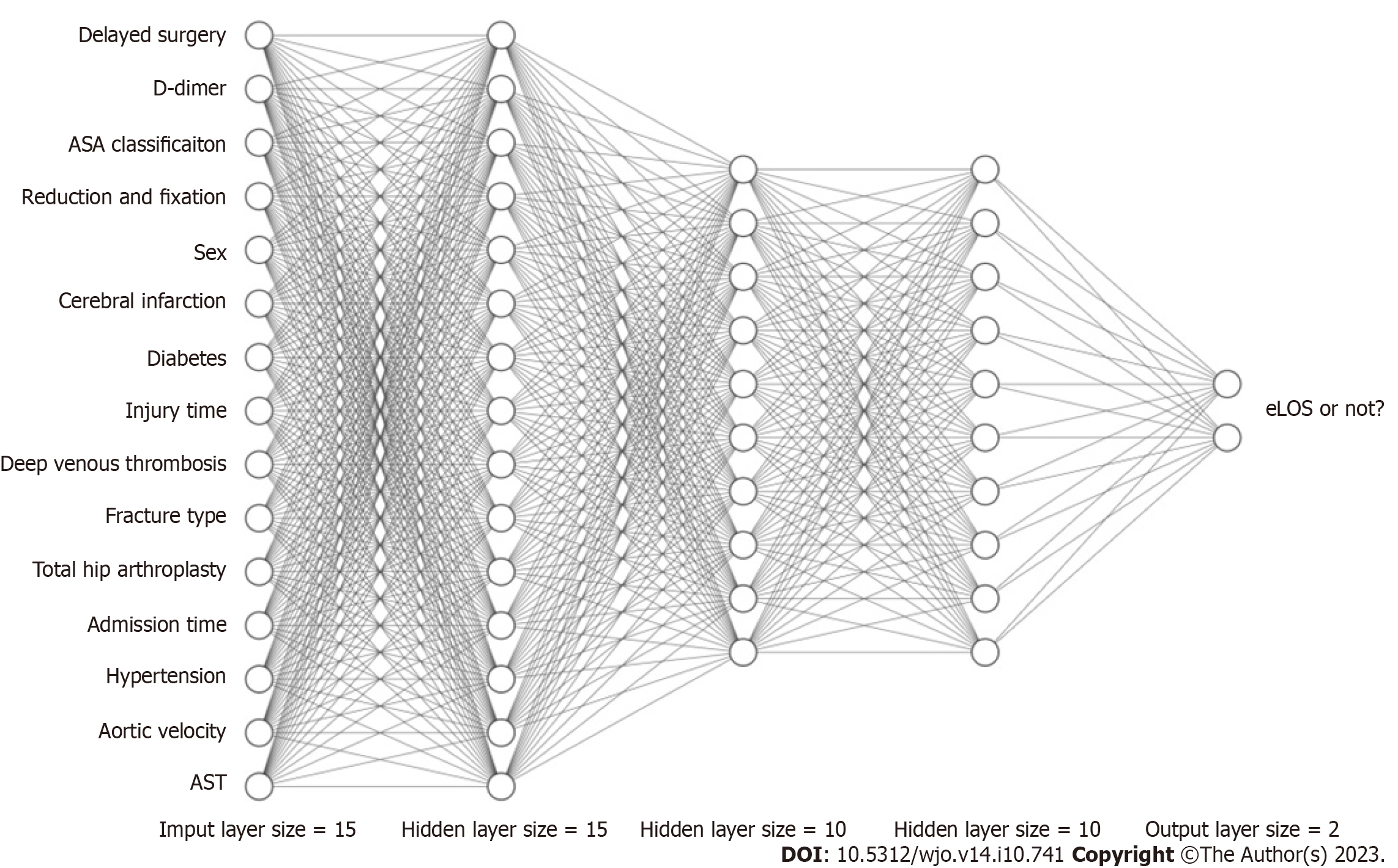
Figure 6 Schematic diagram of an artificial neural network.
ASA: American society of anaesthesiologists; eLOS: Extended length of stay; AST: Aspartate aminotransferase.
- Citation: Tian CW, Chen XX, Shi L, Zhu HY, Dai GC, Chen H, Rui YF. Machine learning applications for the prediction of extended length of stay in geriatric hip fracture patients. World J Orthop 2023; 14(10): 741-754
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2218-5836/full/v14/i10/741.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5312/wjo.v14.i10.741