Copyright
©The Author(s) 2022.
World J Orthop. Jun 18, 2022; 13(6): 603-614
Published online Jun 18, 2022. doi: 10.5312/wjo.v13.i6.603
Published online Jun 18, 2022. doi: 10.5312/wjo.v13.i6.603
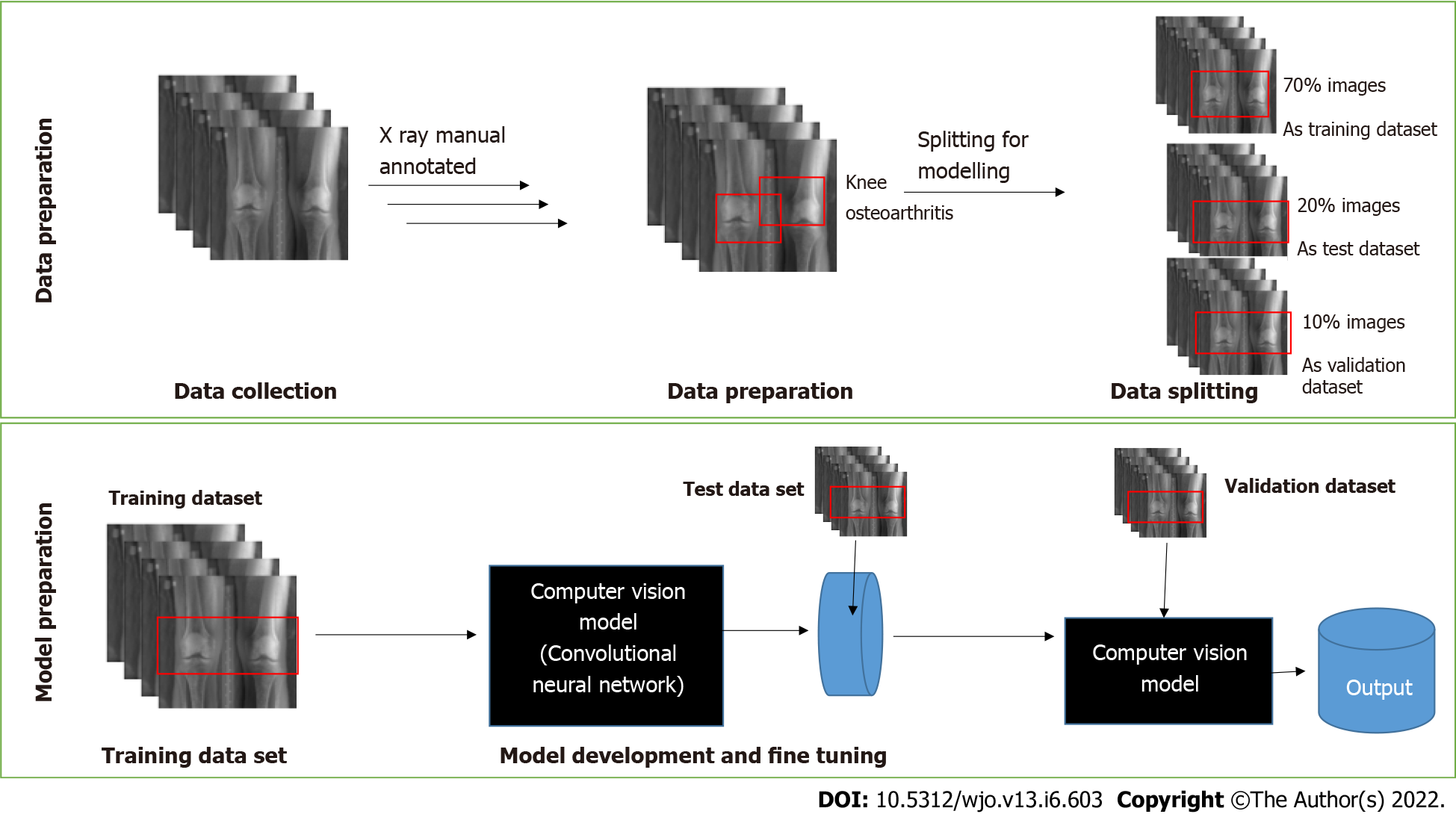
Figure 1 Architecture for deep learning algorithms for orthopedic radiographs.
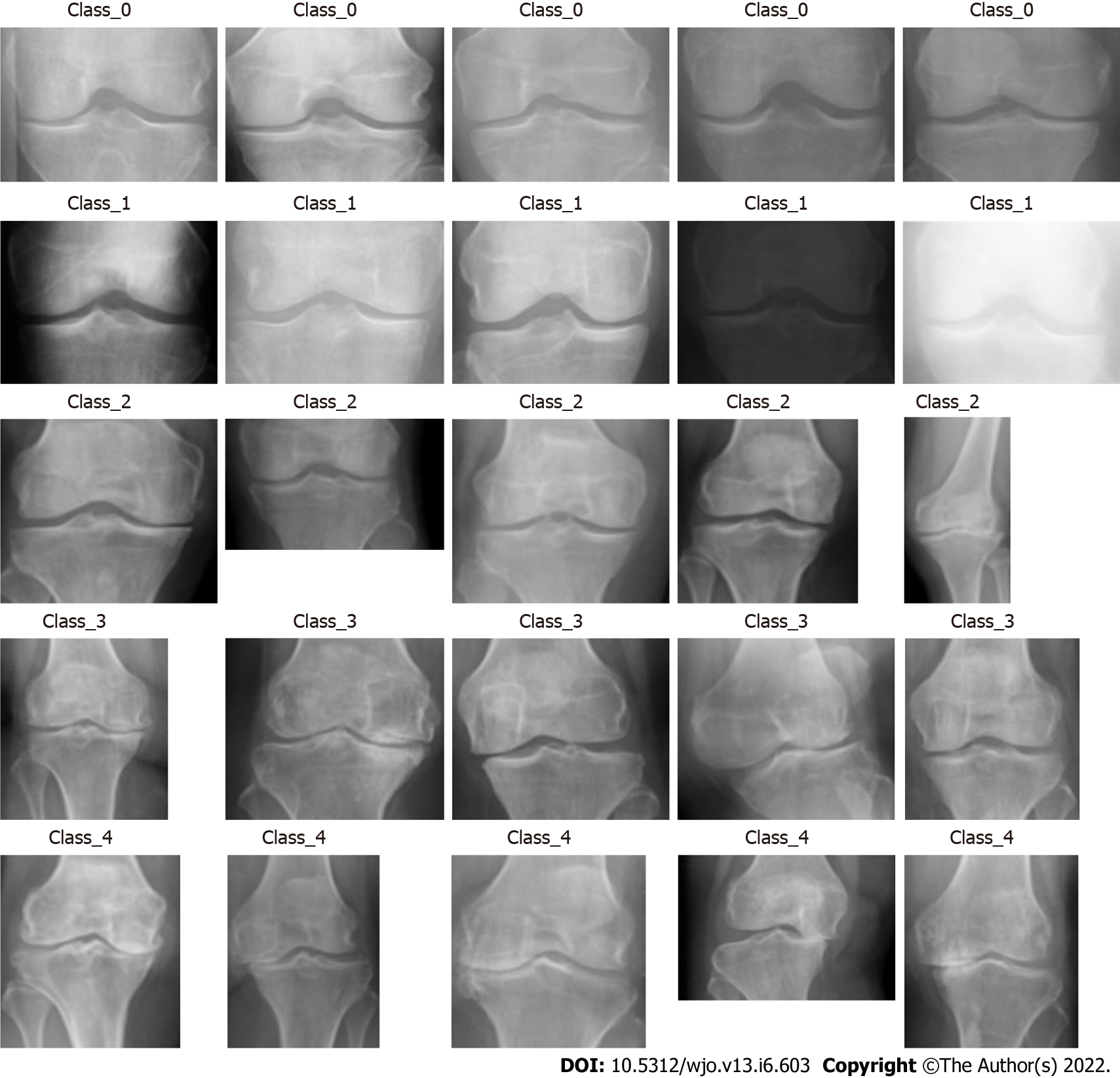
Figure 2 X-ray images of different Kellgren-Lawrence grades for knee osteoarthritis.
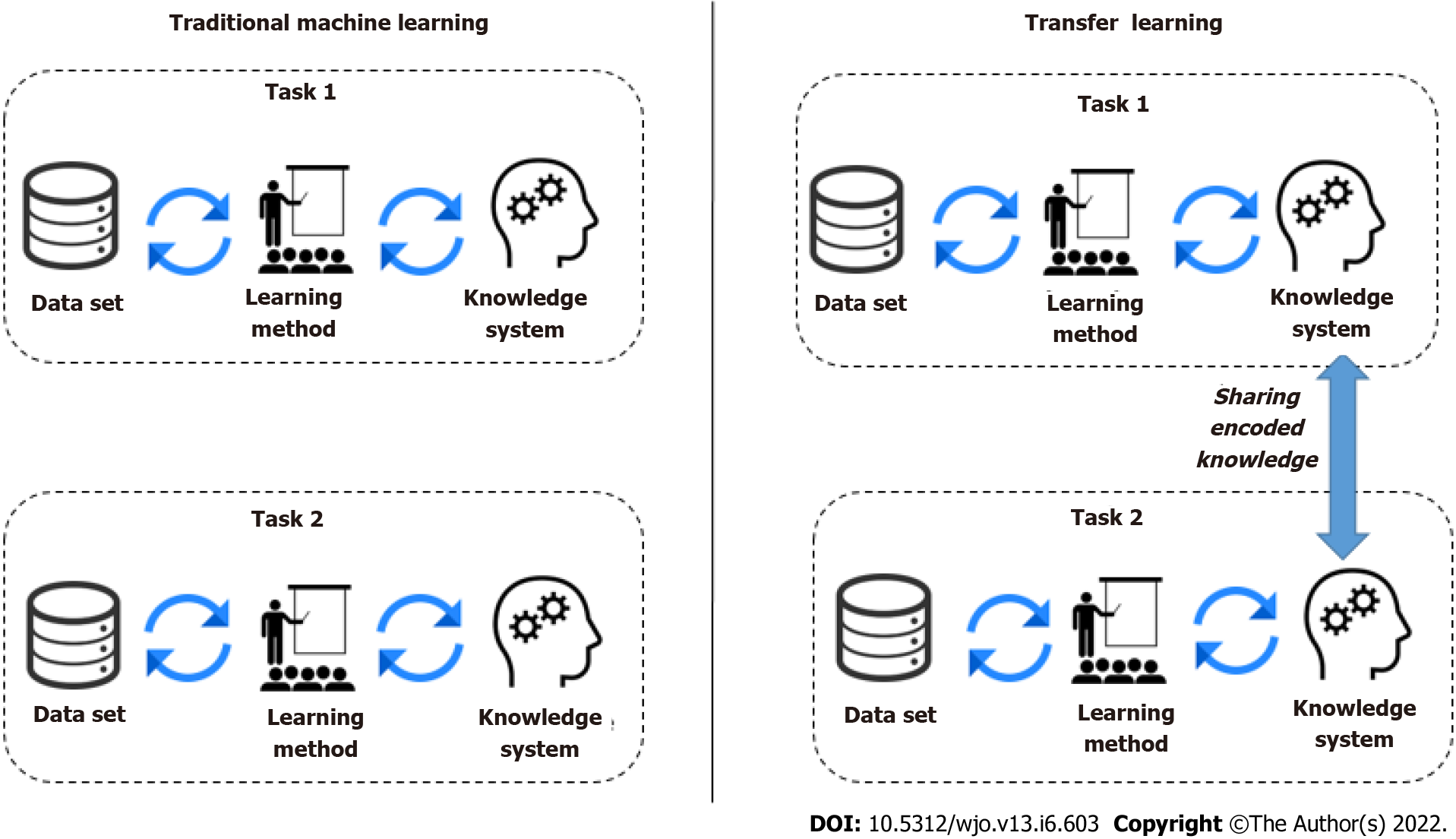
Figure 3 Traditional machine learning vs transfer learning.
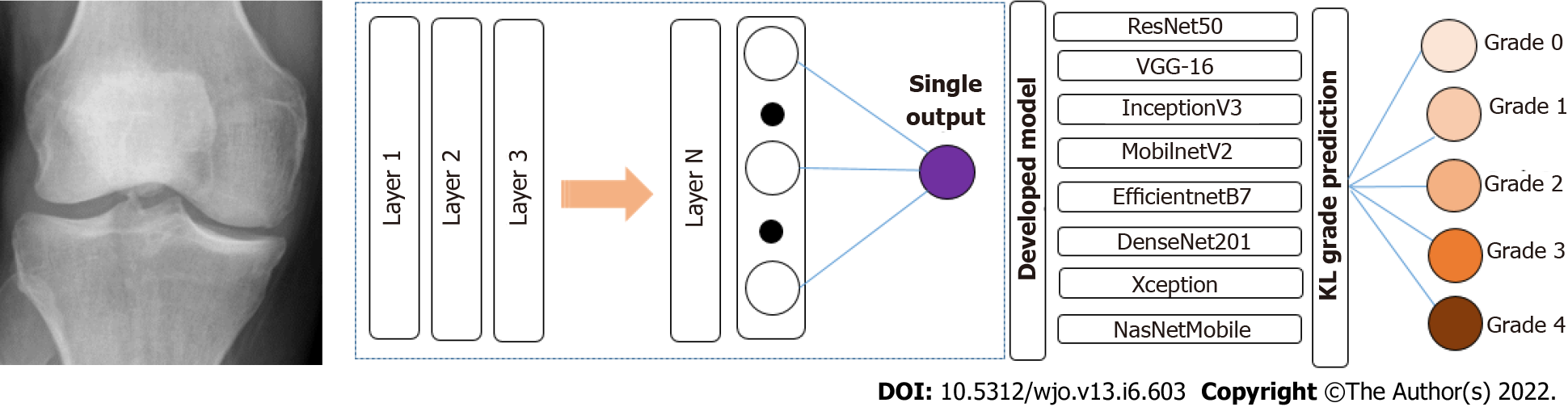
Figure 4 Multimodal pipeline, predicting the risk of osteoarthritis for a particular knee.
We first used a deep convolutional neural network, trained different models in a multitask setting to predict the current stage of osteoarthritis defined according to the Kellgren-Lawrence (KL) grade scale.
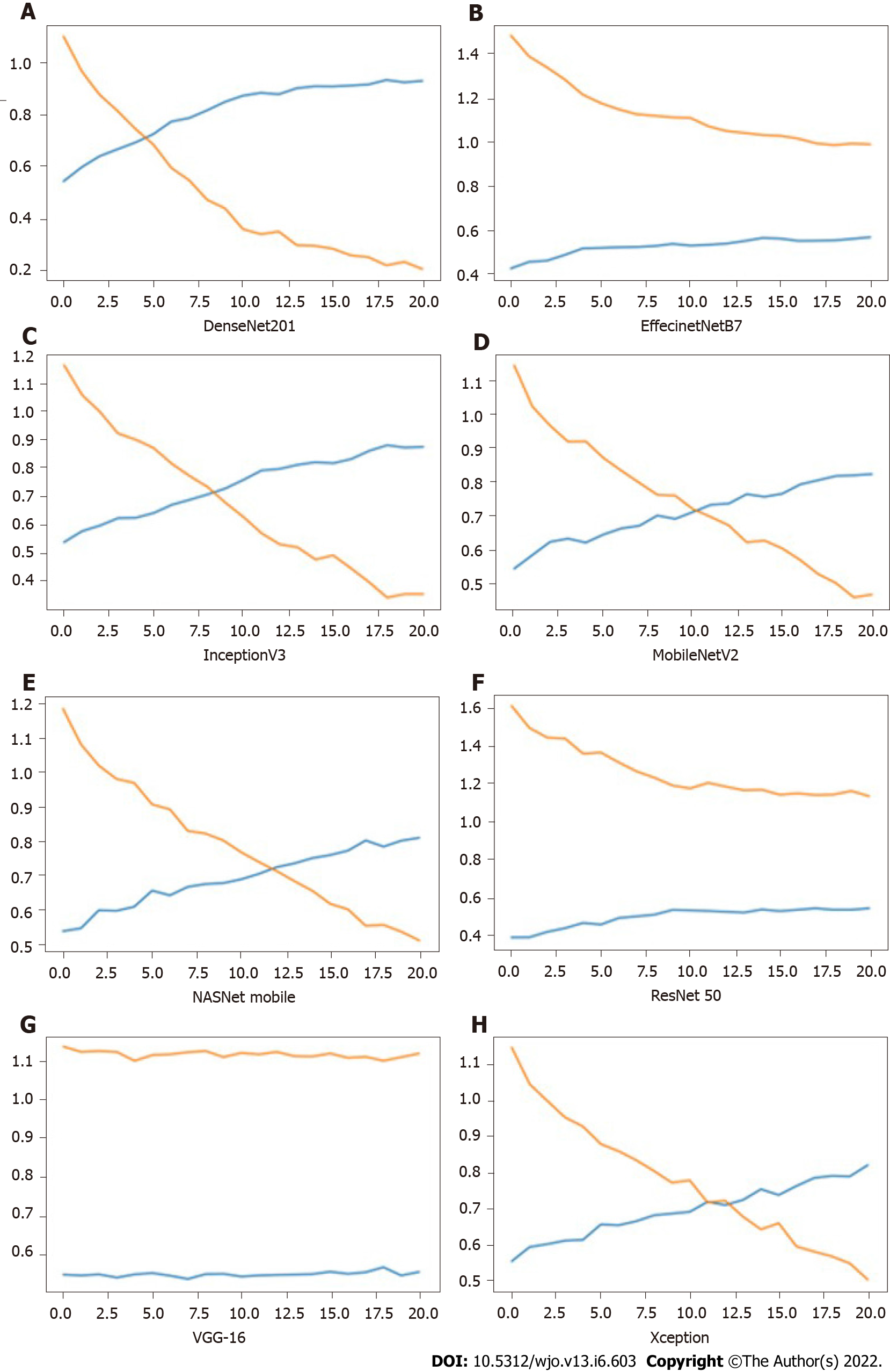
Figure 5 Depicting the loss and accuracy vs number of epochs for different models.
Red line: Loss; Blue line: Accuracy; Y-axis: Depicting the loss and accuracy; X-axis: Number of epochs. A: DenseNet201; B: EffecinetNetB7; C: InceptionV3; D: MobileNetV2; E: NasNetMobile; F: ResNet 50; G: VGG-16; H: Xception.
- Citation: Tiwari A, Poduval M, Bagaria V. Evaluation of artificial intelligence models for osteoarthritis of the knee using deep learning algorithms for orthopedic radiographs. World J Orthop 2022; 13(6): 603-614
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2218-5836/full/v13/i6/603.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5312/wjo.v13.i6.603