Copyright
©The Author(s) 2022.
World J Orthop. Apr 18, 2022; 13(4): 354-364
Published online Apr 18, 2022. doi: 10.5312/wjo.v13.i4.354
Published online Apr 18, 2022. doi: 10.5312/wjo.v13.i4.354
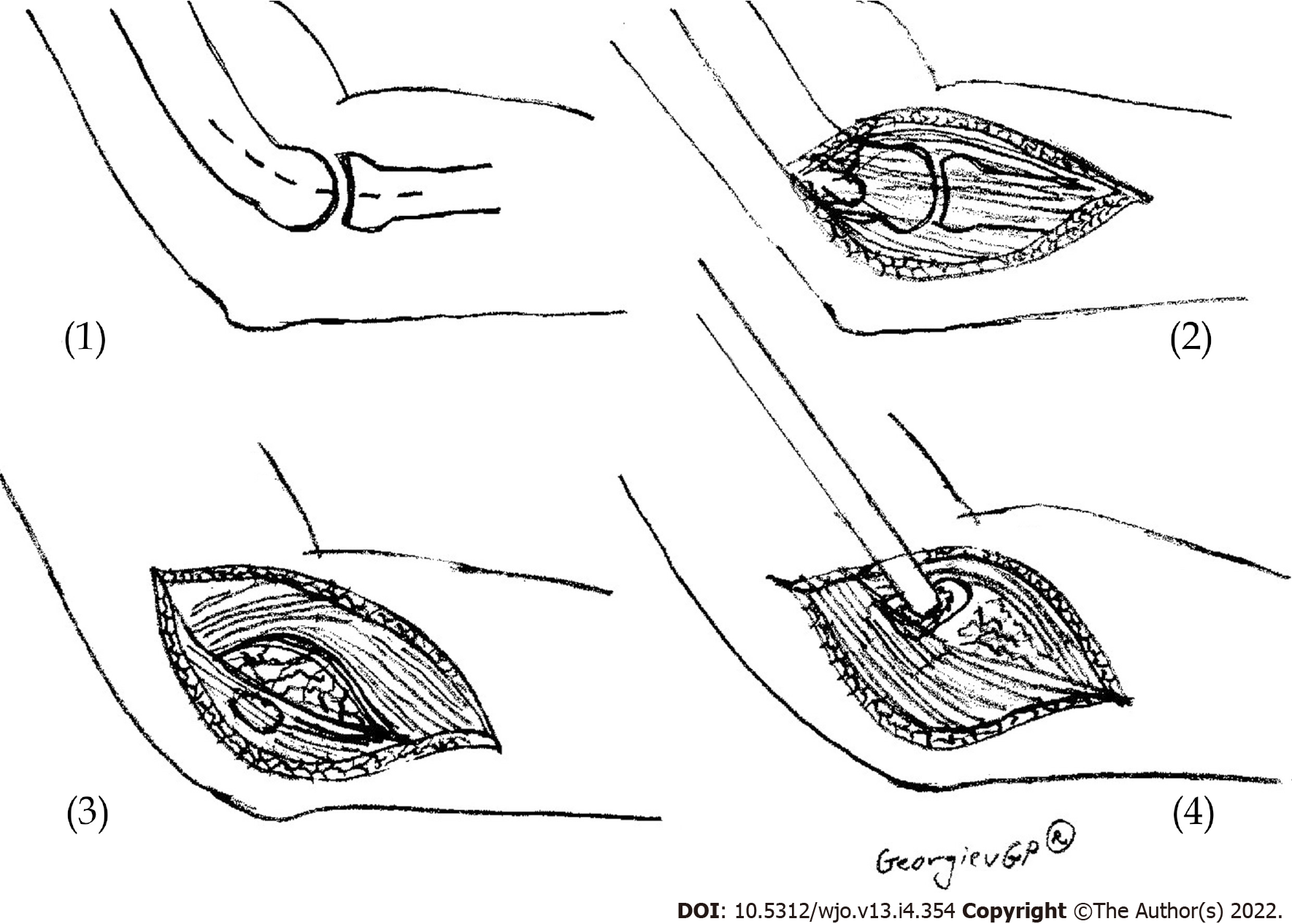
Figure 1 Scheme presenting the open release of lateral epicondylitis.
(1) Skin incision; (2) Extensor carpi radialis longus – extensor digitorum communis interface is identified; (3) Degenerated tissue at extensor carpi radialis brevis muscle is identified and incised; and (4) Osteotome decortication.
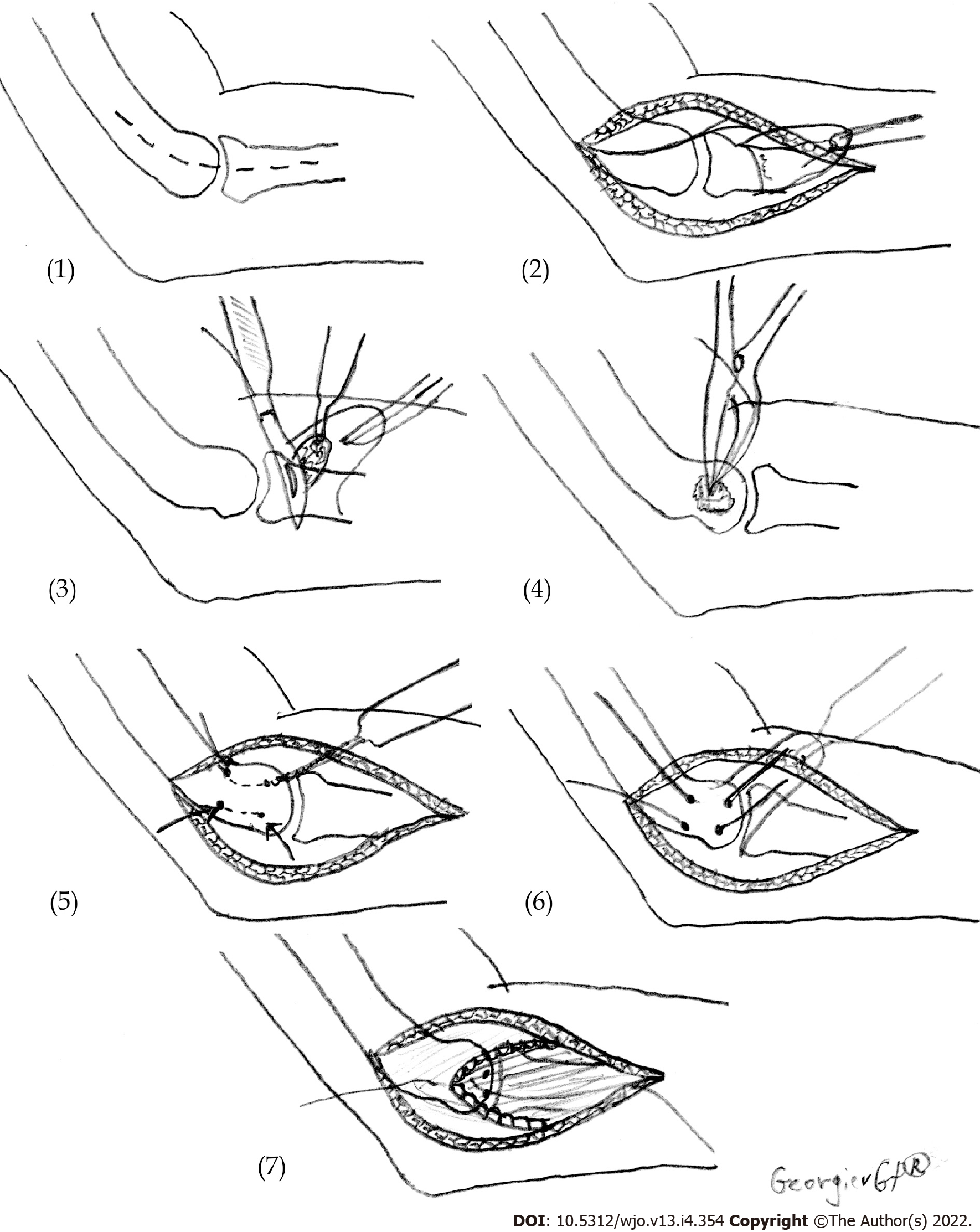
Figure 2 Scheme presenting the technique for the surgical treatment of lateral epicondylitis.
(1) Skin incision; (2) Reflection in the distal direction of the extensor mechanism; (3) Excision of pathologic tissue under the flap of the extensor mechanism; (4) Osteotome decortication; (5) Drilling of two V-shaped tunnels for reattachment of the extensors; (6) Reattachment of the extensor mechanism to the lateral epicondyle; and (7) Restoration of the extensor tendon mechanism.
- Citation: Karabinov V, Georgiev GP. Lateral epicondylitis: New trends and challenges in treatment. World J Orthop 2022; 13(4): 354-364
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2218-5836/full/v13/i4/354.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5312/wjo.v13.i4.354