Copyright
©The Author(s) 2022.
World J Orthop. Dec 18, 2022; 13(12): 1038-1046
Published online Dec 18, 2022. doi: 10.5312/wjo.v13.i12.1038
Published online Dec 18, 2022. doi: 10.5312/wjo.v13.i12.1038
Figure 1 Anteroposterior tear size was measured as the greatest distance between the anterior tendon edge and the posterior tendon edge in sagittal oblique magnetic resonance imaging slices.
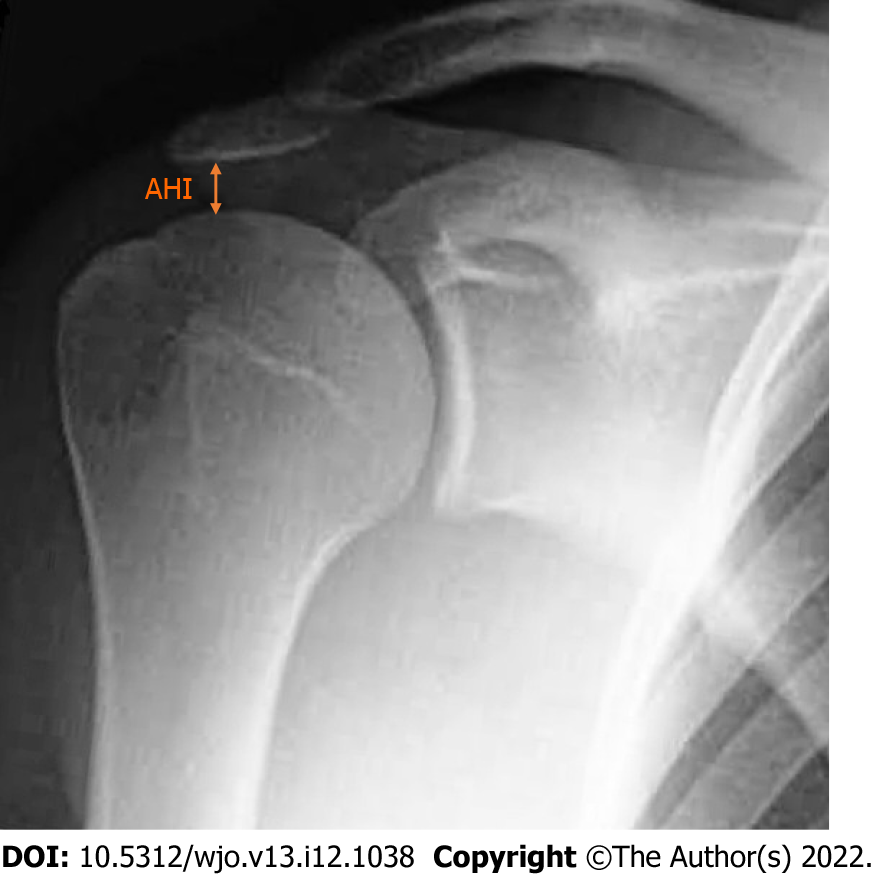
Figure 2 The acromiohumeral interval was measured as the distance between the inferior border of acromion and the superior aspect of the humeral head on true anteroposterior plain radiography.
AHI: Acromiohumeral interval.
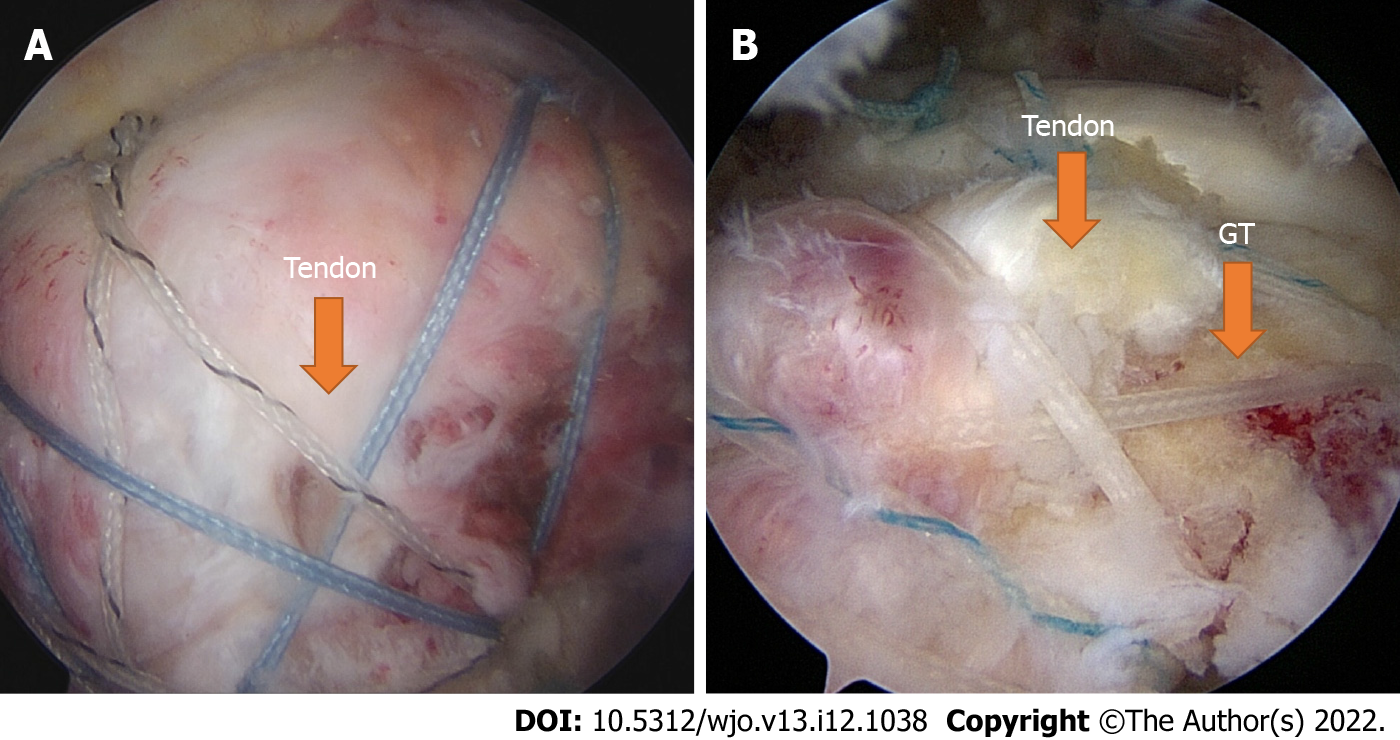
Figure 3 Arthroscopic view of rotator cuff repair.
A: After arthroscopic rotator cuff repair, the tendon is seen to over more than 50% of the anatomical footprint following complete repair. B: In partial repair, the tendon covers less than 50% of the anatomical footprint. GT: Greater tuberosity.
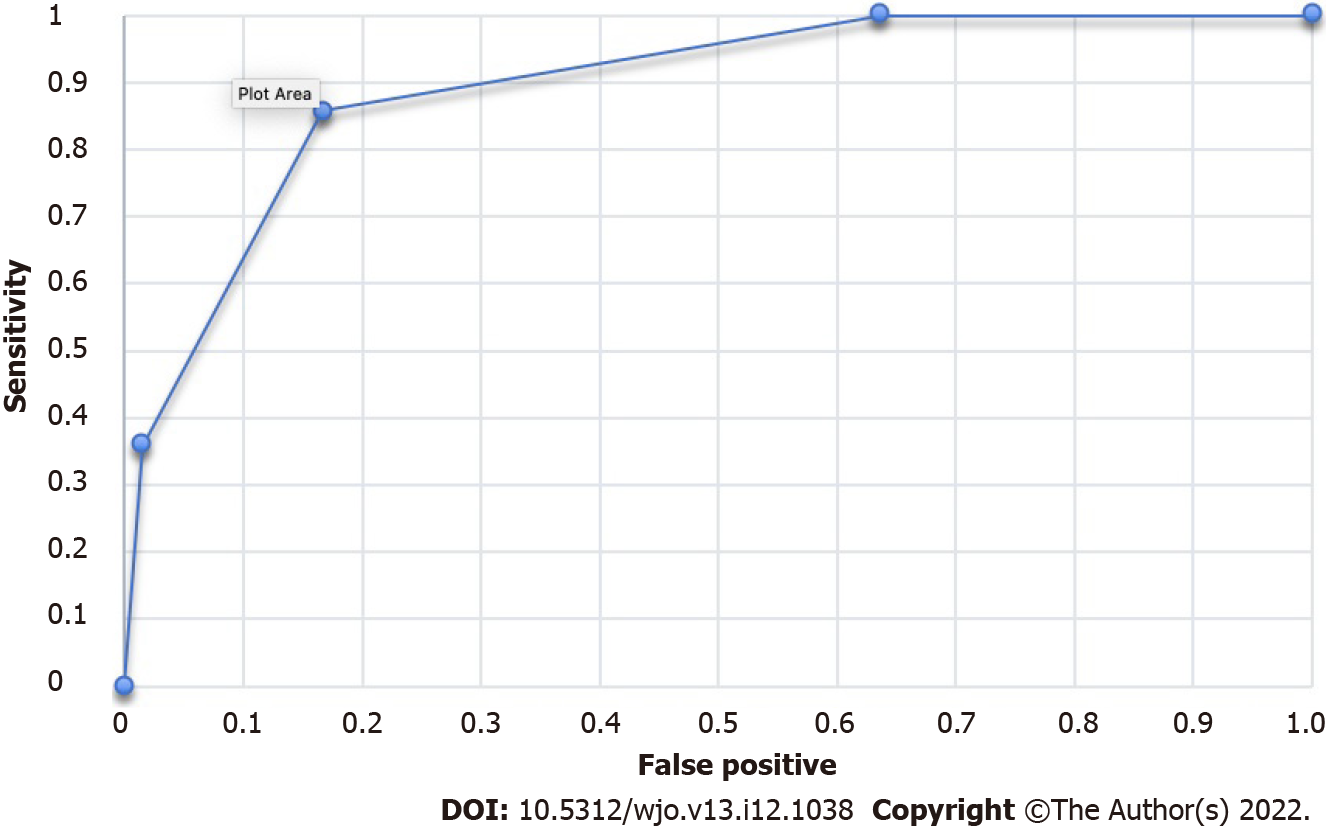
Figure 4 Receiver operating characteristics curve of the rotator cuff reparability score.
- Citation: Prasathaporn N, Kuptniratsaikul V, Thamrongskulsiri N, Itthipanichpong T. Accuracy of the rotator cuff reparability score. World J Orthop 2022; 13(12): 1038-1046
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2218-5836/full/v13/i12/1038.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5312/wjo.v13.i12.1038