Copyright
©The Author(s) 2021.
World J Orthop. Mar 18, 2021; 12(3): 119-128
Published online Mar 18, 2021. doi: 10.5312/wjo.v12.i3.119
Published online Mar 18, 2021. doi: 10.5312/wjo.v12.i3.119
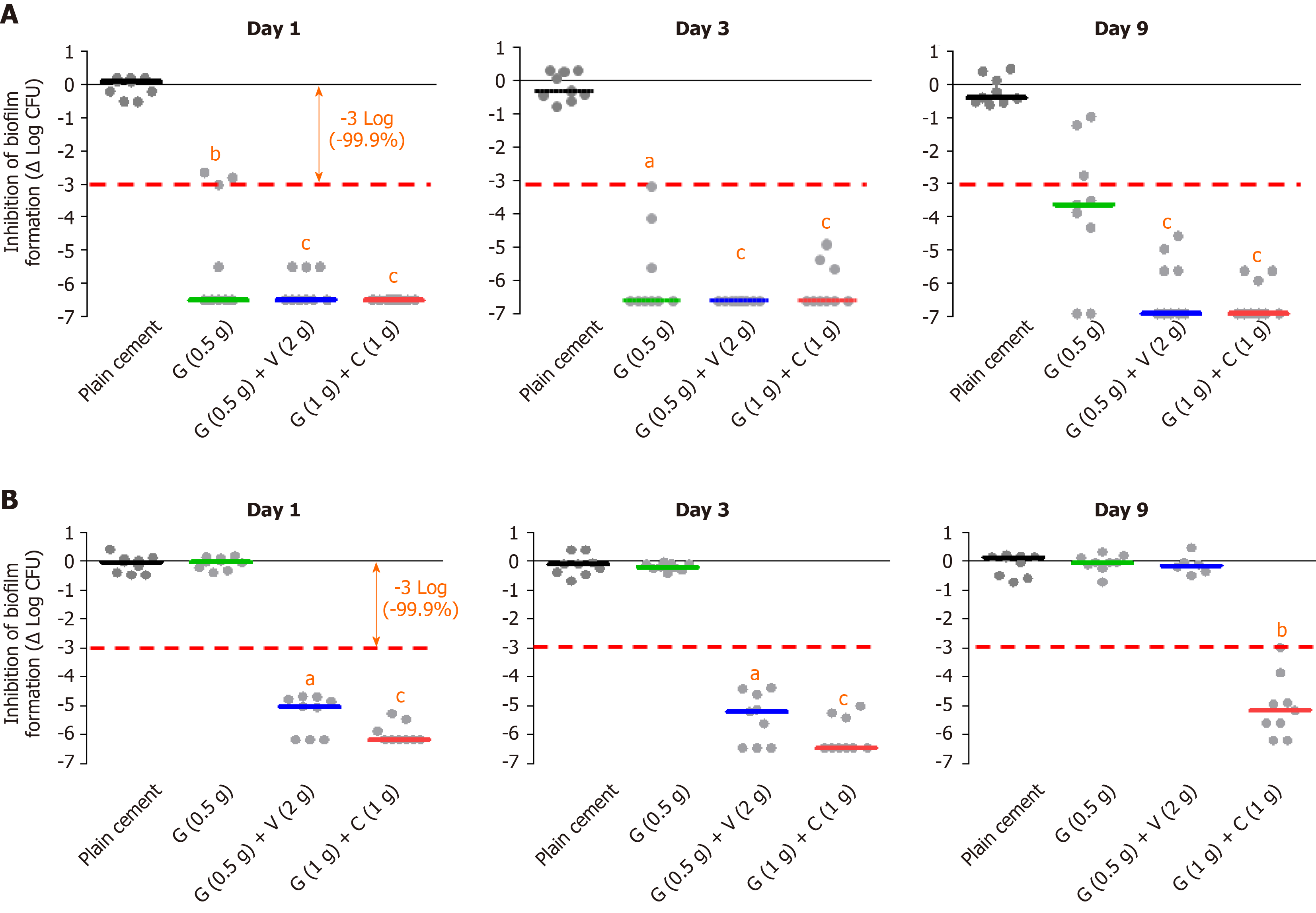
Figure 1 In vitro biofilm inhibition experiments with different bone cement types (plain, single and dual antibiotic-loaded bone cement).
A: Prophylactic anti-biofilm effect of three different antibiotic-loaded bone cements against a gentamicin and methicillin-susceptible Staphyloccus aureus strain at day 1, day 3 and day 9 on basis of three independent experiments; B: Prophylactic anti-biofilm effect of three different antibiotic-loaded bone cements against a gentamicin- and methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus epidermidis strain on basis of three independent experiments. aP < 0.05, bP < 0.01, or cP < 0.001 respectively in comparison with PALACOS R (cement without antibiotic). G: Gentamicin; C: Clindamycin; V: Vancomycin.
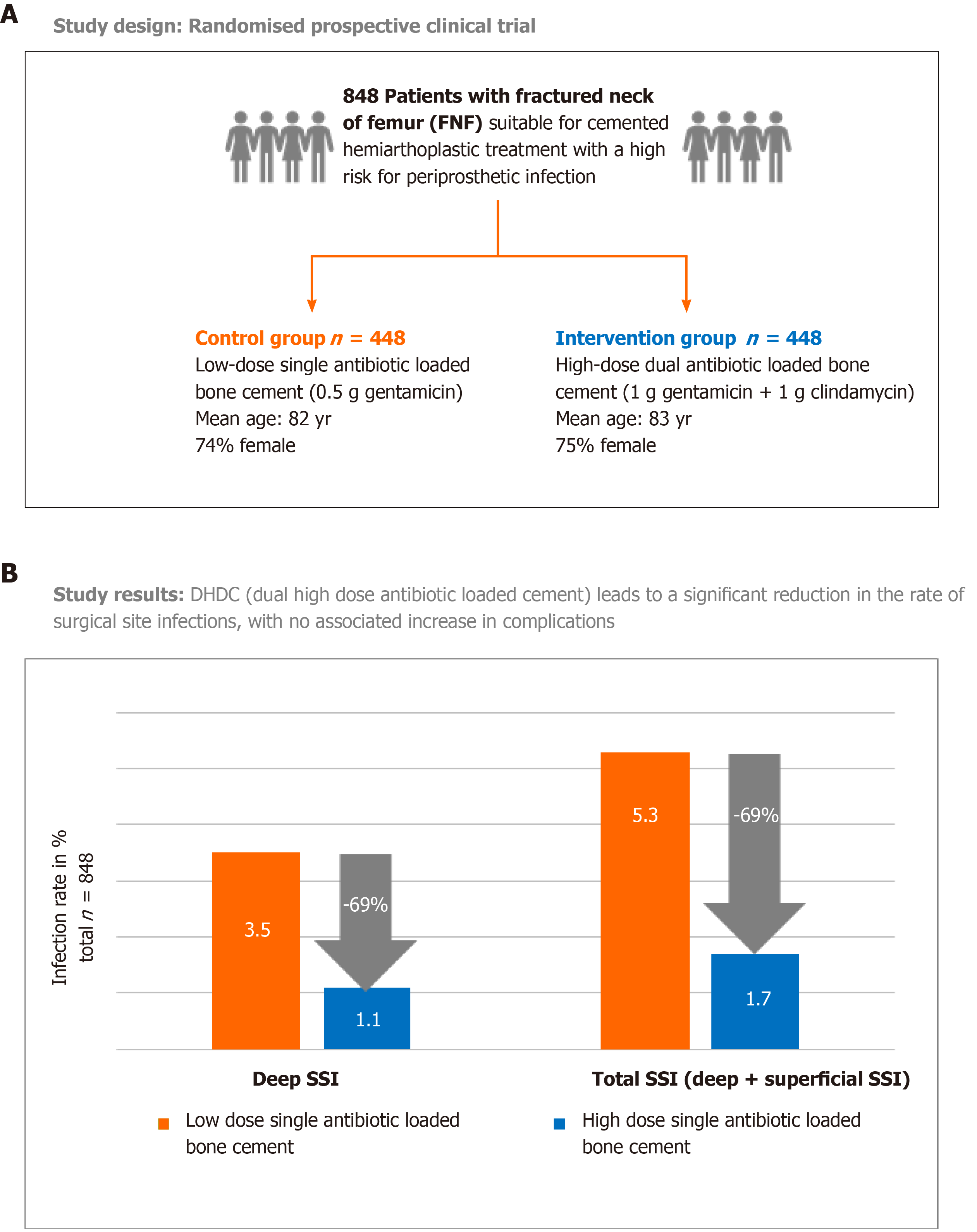
Figure 2 Randomized clinical trial in femoral neck fracture patients comparing prosthetic joint infection rate in low dose single antibiotic loaded bone cement group with high dose dual antibiotic loaded bone cement group.
A: Study design, 848 patients were randomised to receive either hemiprostheses cemented with a low dose single antibiotic-loaded bone cement (PALACOS R + gentamicin = control group) or with a high dose dual antibiotic-loaded bone cement (COPAL gentamicin + clindamycin = intervention group); B: Study results: Primary endpoint was the deep surgical site infection rate (SSI) in the observation period of ≥ 1 yr in each group. Secondary endpoint was the rate of superficial SSI. For the calculation of the total SSI, both deep and superficial SSI cases in each group were combined. SSI: Surgical site infection.
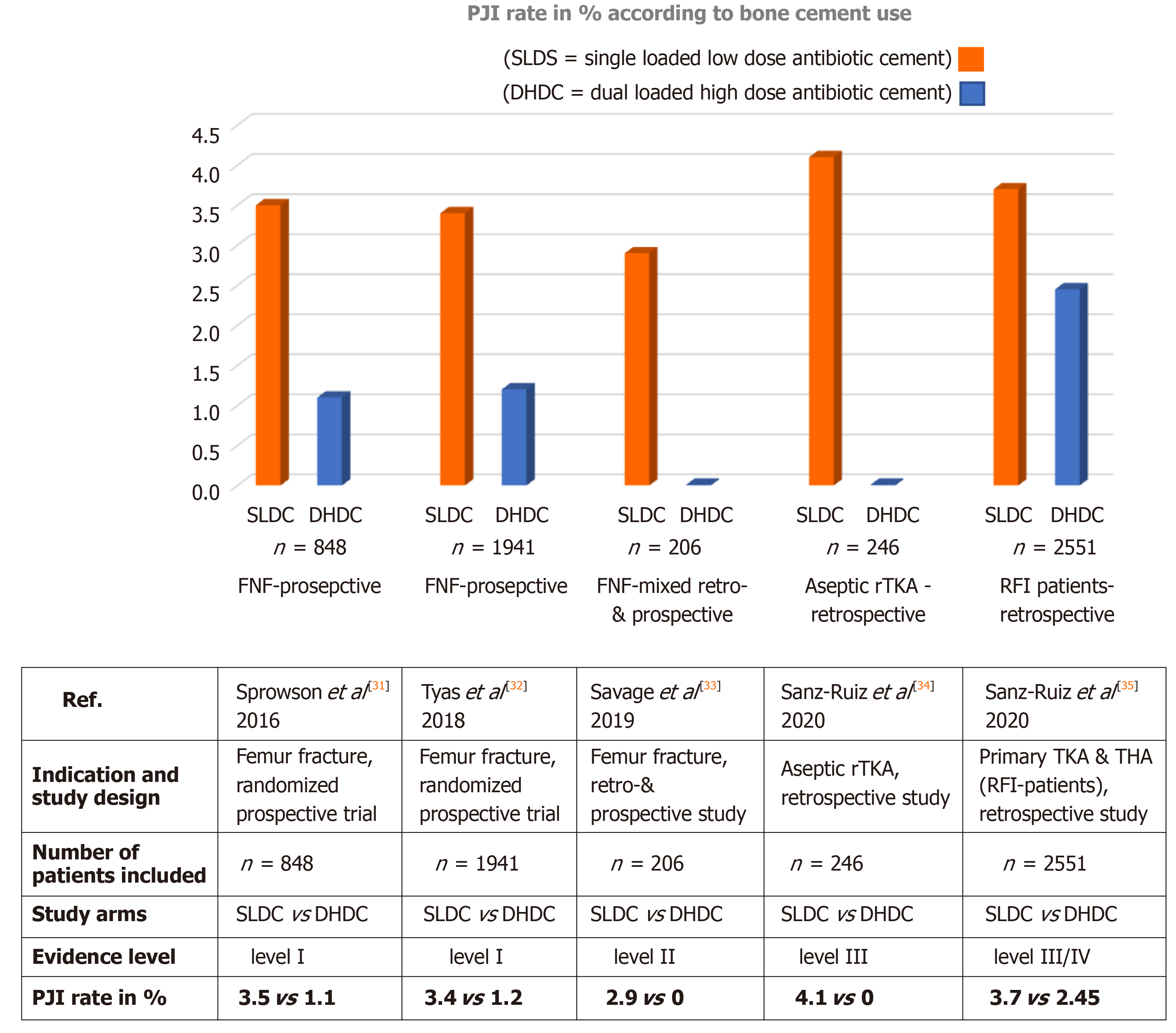
Figure 3 Overview of published clinical study results comparing prosthetic joint infection rate in patients in single low dose cement and dual high dose cement group across different indications.
The table below lists the main study authors, indication and study design, number of patients included, evidence level of clinical study and prosthetic joint infection rate in % in both study groups. PJI: Prosthetic joint infection; SLDC: Single low dose cement = PALACOS R+G (containing 0.5 g of gentamicin); DHDC: Dual high dose cement = COPAL G+C (gentamicin + clindamycin); FNF: Femoral neck fracture; rTKA: Revision total knee arthroplasty; RFI: Risk for infection; THA: Total hip arthroplasty.
- Citation: Berberich CE, Josse J, Laurent F, Ferry T. Dual antibiotic loaded bone cement in patients at high infection risks in arthroplasty: Rationale of use for prophylaxis and scientific evidence. World J Orthop 2021; 12(3): 119-128
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2218-5836/full/v12/i3/119.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5312/wjo.v12.i3.119