Copyright
©2014 Baishideng Publishing Group Inc.
World J Clin Oncol. Oct 10, 2014; 5(4): 646-659
Published online Oct 10, 2014. doi: 10.5306/wjco.v5.i4.646
Published online Oct 10, 2014. doi: 10.5306/wjco.v5.i4.646
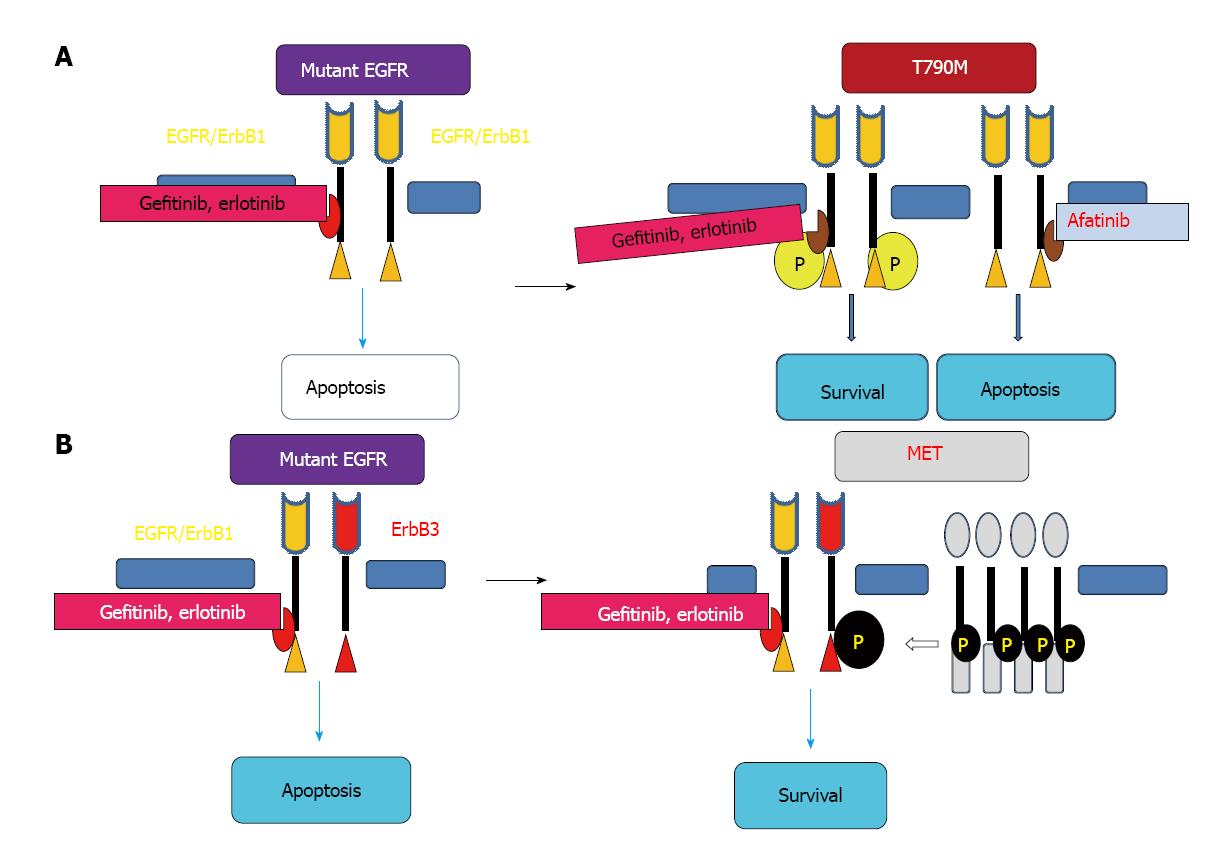
Figure 2 Major mechanisms of epidermal growth factor receptor resistance to epidermal growth factor receptor-tyrosine kinase inhibitors in lung cancer cell.
Secondary epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) T790M mutation prevents binding of first-generation EGFR-tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs), including gefitinib and erlotinib to EGFR, resulting in cancer cell survival (A). Afatinib inhibits the ATP-binding site of the tyrosine kinase associated with EGFR T790M, leading to apoptosis of cancer cell. MET amplification has been shown to confer resistance to EGFR-TKIs by activating phosphorylation of ErbB3 with activating of the PI3K/AKT pathway, resulting in cancer cell survival (B).
- Citation: Asami K, Atagi S. Epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitors for non-small cell lung cancer. World J Clin Oncol 2014; 5(4): 646-659
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2218-4333/full/v5/i4/646.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5306/wjco.v5.i4.646